2025 CDP Landscape: Our comparison guide
6min • Last updated on Oct 27, 2025

Alexandra Augusti
Chief of Staff
Customer Data Platforms (CDPs) have become essential for companies seeking to maximize the use of their customer data. They allow for the collection, storage, unification, and activation of data across various channels. By unifying data from multiple sources, CDPs offer a 360° view of customers, crucial for personalizing interactions and improving the customer experience.
However, choosing the right CDP for your business can be complex, given the numerous options and criteria to consider. To be convinced, just look at the G2 category of Customer Data Platforms, where about 250 players are positioned.
This article explores the different categories of CDPs, the important criteria to consider when selecting a solution, and provides an overview of some CDPs available on the market.
Definition of a CDP
A brief reminder of what a CDP is and is not, to ensure we are on the same page for the rest of the article.
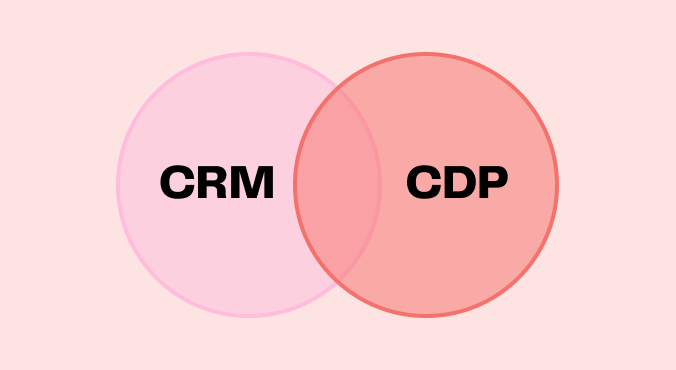
Historically, companies used CRM (Customer Relationship Management) to store and use their customer data. CRM has never gone away, but new solutions have emerged to make the most of customer data: the Data Management Platform (DMP) and then the Customer Data Platform (CDP).
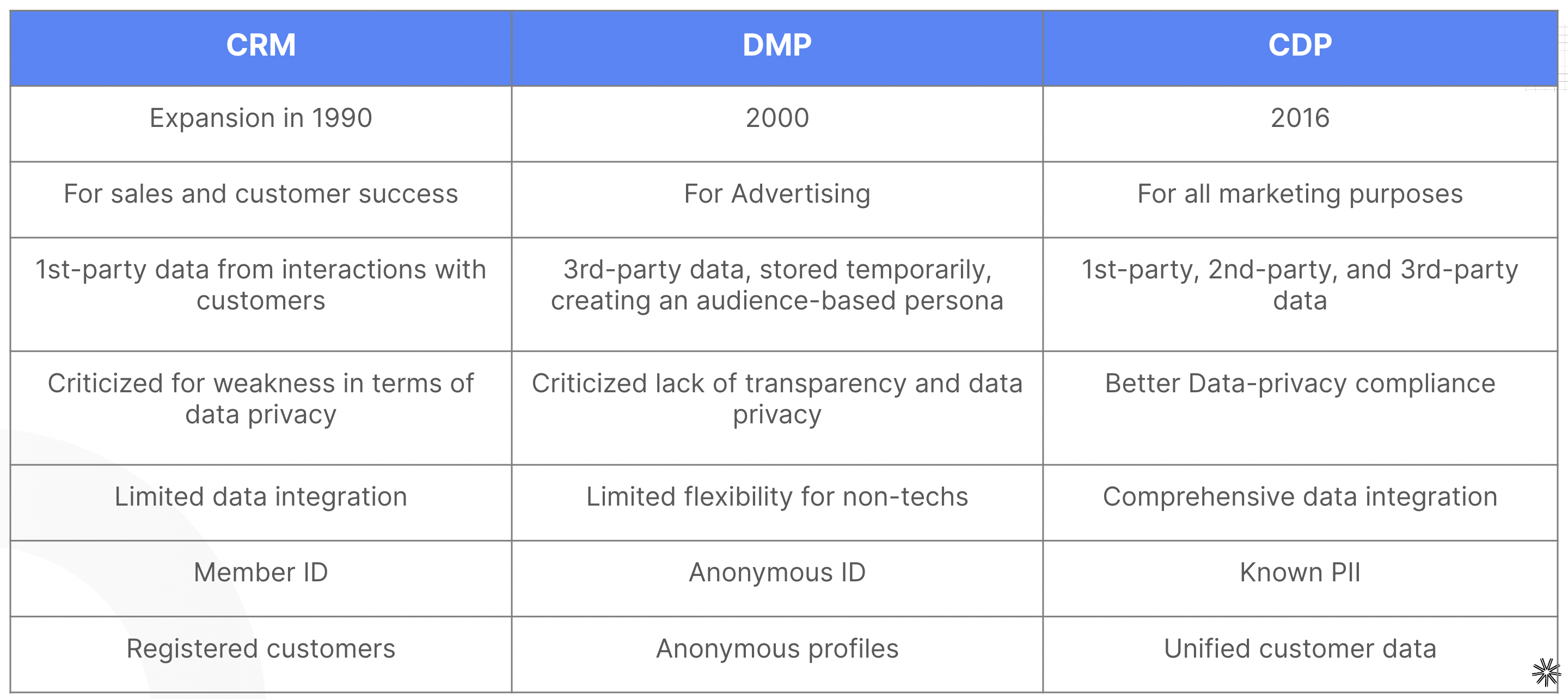
CRM vs CDP vs DMP
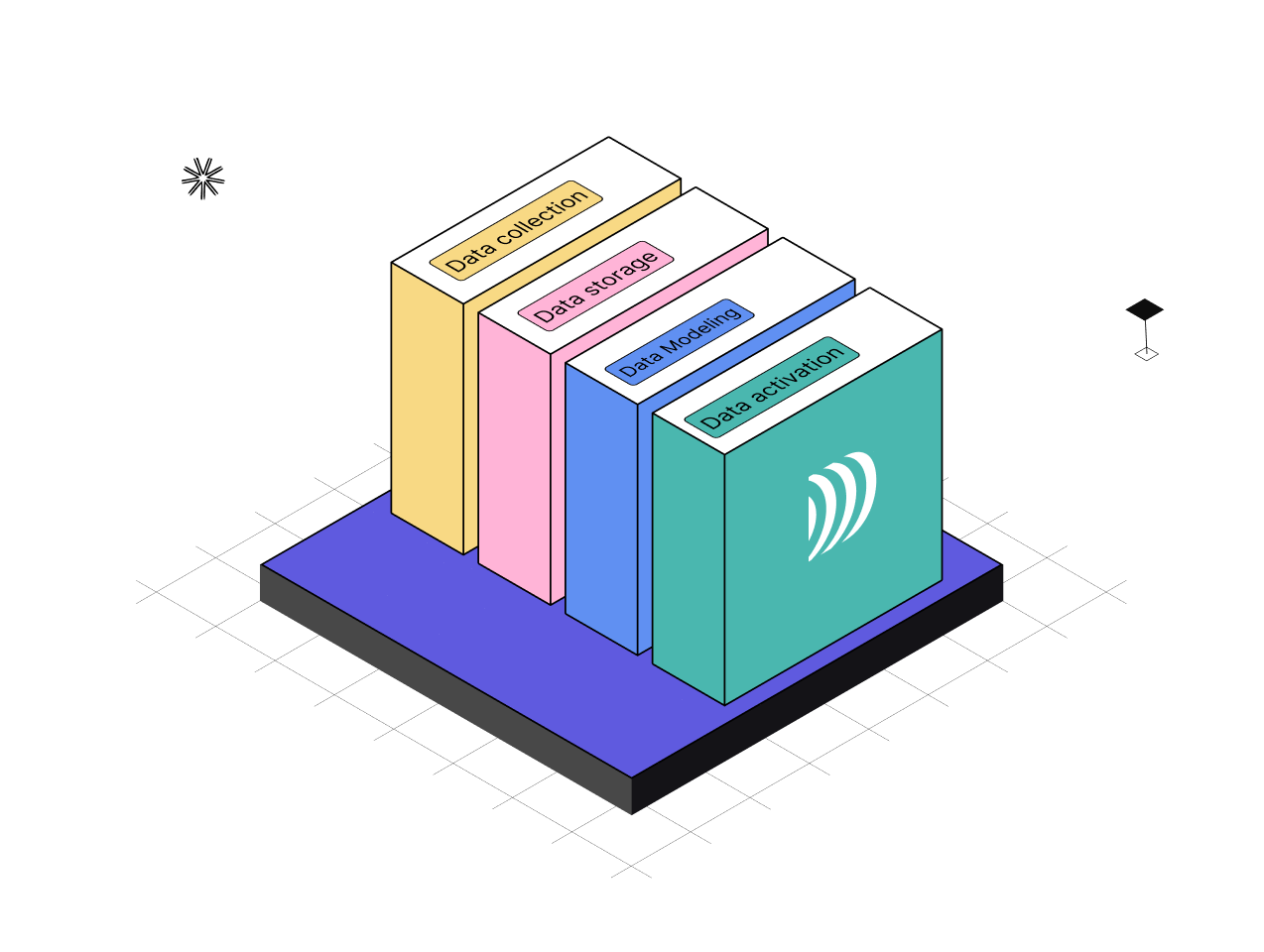
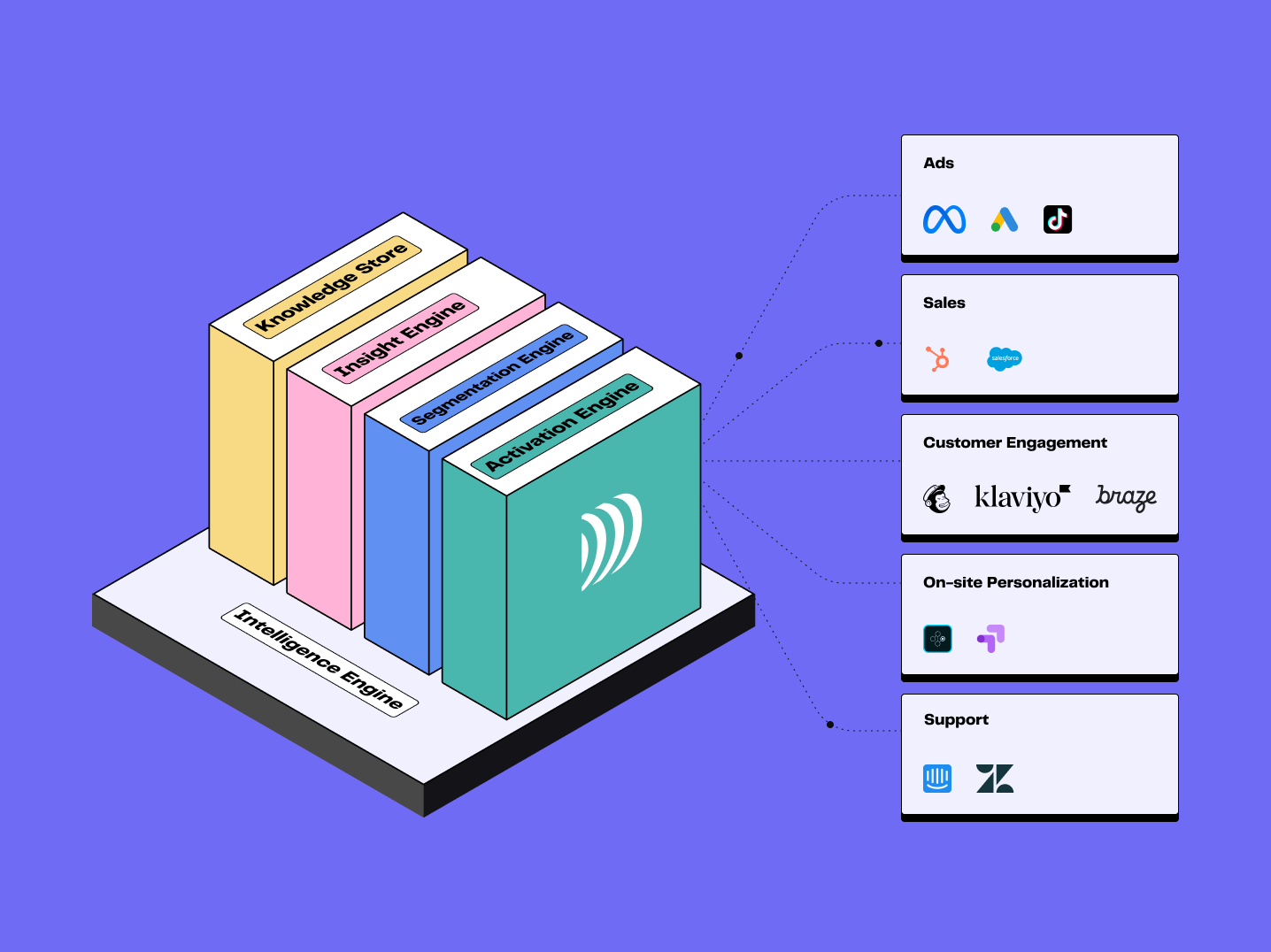
A Customer Data Platform (CDP) is software that collects and organizes customer data from various sources to consolidate, unify, segment, and activate it on marketing platforms. The main goal of a CDP is to build customer profiles to optimize targeting of marketing campaigns and improve the customer experience.
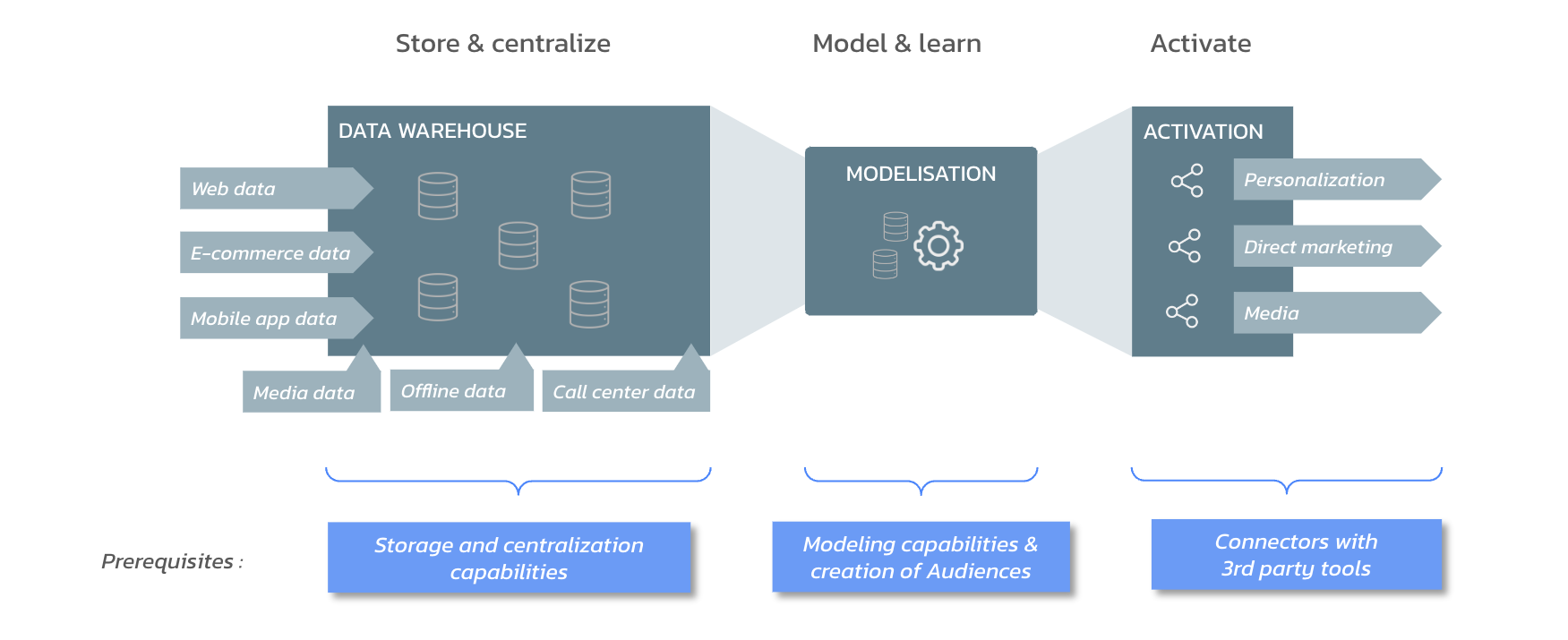
Schematic diagram of a CDP
CDP is widely used by business teams (marketing, CRM, support), in particular to :
Gain a 360° view of customer interactions
Enrich their customer view with predictive attributes
Facilitate data analysis and define new data-driven marketing strategies
Segment their customer base
Improve the customer experience at every stage of the customer journey through better acquisition strategies, marketing automation and personalization across all channels
Categories of CDPs
There are different categories of Customer Data Platforms, and not all of them will meet your needs. Understanding the different categories can save you valuable time when choosing your solution.
On the CDP market, we distinguish:
Traditional CDPs: These are packaged CDPs (standalone entity) that help collect, store, unify, and activate data to operational tools. They are the historical solutions on the market and are designed to facilitate data exploitation by marketing teams.
Composable CDPs: This category corresponds to a modular association of tools within your infrastructure aimed at collecting, storing, unifying, and activating data from a data warehouse to final tools. Although based on technical tools, Composable CDPs are designed for end marketing users, with no-code features and intuitive interfaces.
💡 Feel free to consult our dedicated article to understand the differences between Traditional and Composable CDPs.
👇
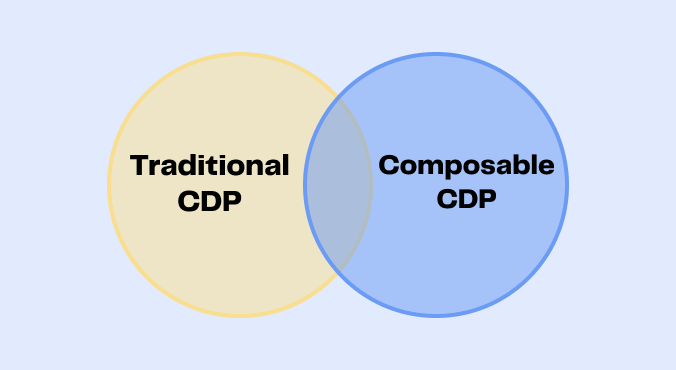
Traditional vs Composable CDP
Hybrid CDPs: A hybrid CDP is generally a packaged CDP that now offers features to integrate into your existing data infrastructure (as Composable CDPs do).
Martech Suites: This category corresponds to suites offered by software vendors (Salesforce, Adobe, etc.) containing various marketing and data management products. Their goal is to collect, store, unify, and activate data — most often within their own embedded suite of tools.
Infrastructure Solutions: Solutions that act as data pipelines, both upstream and downstream of a storage base. The solution is not intended for a marketing audience, who do not necessarily have the technical skills to use it.
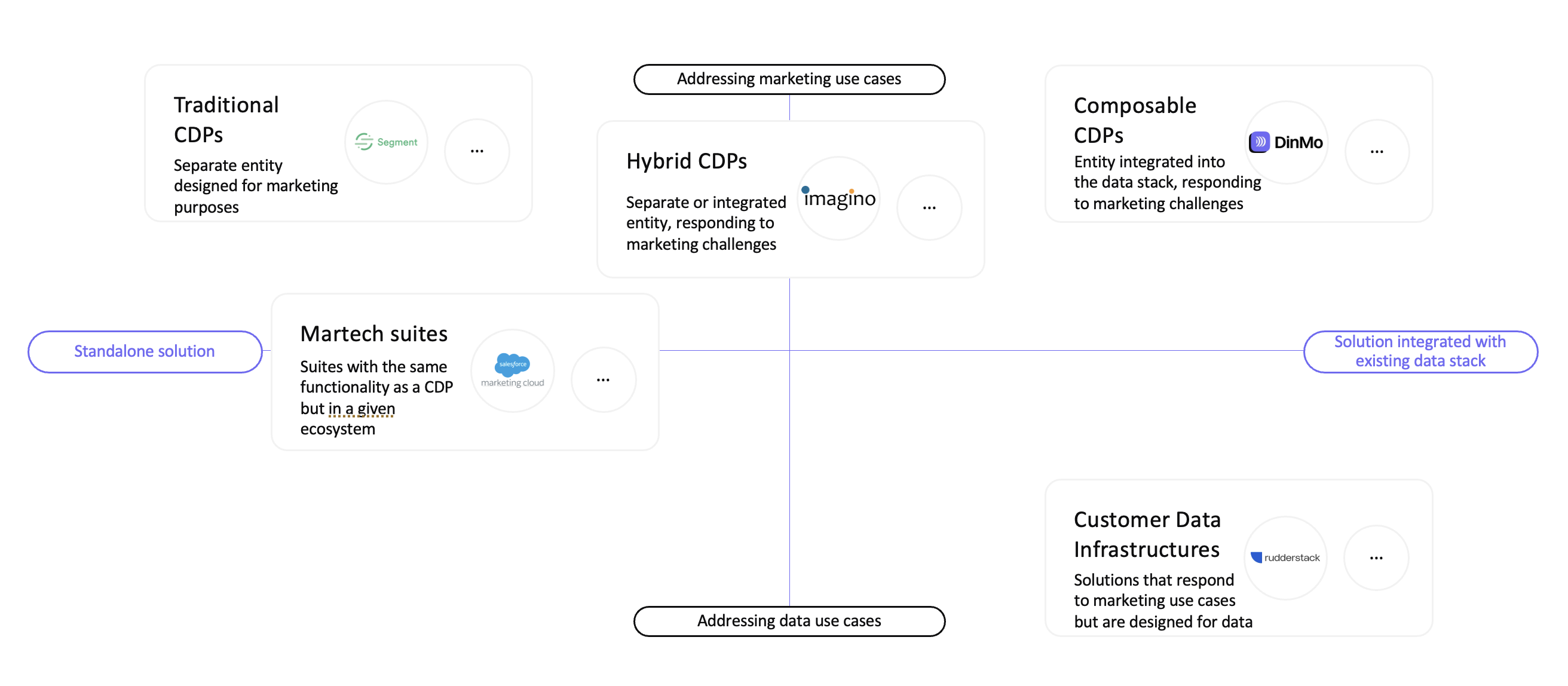
Categories of CDP
Criteria for Choosing a CDP
Even if some categories may have already been excluded after reading their definitions, there are still a multitude of players on the market!
👇 To choose your CDP, we recommend at least analyzing these different criteria and choosing the solution that best suits you.
Functional Differentiation Criteria
Available Connectors: The ideal CDP should be able to collect and unify data from different customer touch points to send to various destinations. If the data sources/destinations considered are not common in the market, traditional CDPs may lack connectors to these tools. Conversely, the most common sources and destinations are obviously supported by packaged CDPs.
Data Structuring: The way data is structured affects segmentation, activation, or reporting capabilities. Your CDP's data model should be flexible enough to model your activity (custom tables, metadata, etc.) and properly use your customer data.
Data Quality: A CDP may offer data processing modules, particularly for identity resolution. Some vendors may offer off-the-shelf features or custom ones. Ensure you choose the option that best suits you!
Data Segmentation: A CDP can be used to define audience and/or personalized data segments. Some packaged CDPs do not allow for the simple calculation of new fields or custom scores, showing some segmentation shortcomings. Composable CDPs, on the other hand, allow for the creation of any data segment from SQL queries or visual segment builders directly from your data warehouse.
Data Hosting: With a packaged SaaS solution, customer data stored with a third party may raise security questions. In the case of cloud hosting with a Composable CDP, data control is instead total.
Adaptation to Technical Stack: For the tool to be adopted by all involved teams, it seems simpler to limit changes to the tools used within a company as much as possible. Besides reducing training needs, this precaution prevents potential employee resistance. Simplified connection to the existing technical stack also reduces timeframes and costs.
Organizational Criteria
Implementation: Depending on the chosen solution, implementation time and difficulty can vary greatly. Setting up a traditional CDP generally takes several months, while a composable solution may require only a few hours. Hybrid solutions offer an in-between. You might also consider whether you need an integrator and the training your teams may require.
Tool Maintenance: A traditional CDP has the advantage of not requiring maintenance from a company. This is done by a third party, so the company does not have to worry about potential connection problems or developing new connectors, for example. Conversely, Analytics Engineering skills are required to maintain data quality in a data warehouse (which may limit the adoption of a Composable CDP).
Budget and Time-to-Value: Packaged CDP license fees generally vary depending on the volume of hosted data. It can also be difficult to correctly estimate the cost of setting up a modular CDP if the company has not made the necessary efforts to structure its data in a data warehouse.
However, if the company has already invested in a cloud data infrastructure, using a Composable CDP means that you can start with simple use cases and go from there, ensuring an almost immediate ROI at every stage.
Composable CDP: A Modular Approach
A Comparison of Some Players
⚠️ Disclaimer: As a publisher, we obviously have an interest in discussing CDPs. However, our goal here is not to compare our competitors versus DinMo, but to evaluate each player by providing as unbiased information as possible.
While it is important not to base your choice exclusively on this article, we hope this overview of the main market players will serve as a starting point to help you identify the solution that best meets your company's needs.
We give you an overview of the main CDP vendors and highlight their main differences:
Traditional CDPs
Segment: Initially specialized in event collection (from a website, mobile apps, SaaS, or servers), Segment has expanded to offer the full functionality of a CDP. The “Twilio Engage” suite allows for creating audiences and orchestrating customer journeys directly on the platform. Data is stored with Segment for up to 3 years.
Treasure Data: Initially recognized as a Big Data platform, Treasure Data repositioned itself on the CDP market, covering almost exclusively marketing use cases. More oriented towards Data Management, this traditional CDP focuses on data unification and preparation (aggregation, scoring, segmentation, etc.). It stands out for its unification and profile enrichment features, notably thanks to its proprietary artificial intelligence algorithms.
mParticle: A traditional CDP that focuses primarily on mobile event collection, mParticle allows for understanding user behaviors and activating them to hundreds of destinations. mParticle integrates with its “Cortex” solution, a Machine Learning platform that predicts certain indicators (Next best offer, Next best action, etc.) for customers.
Composable CDPs
DinMo (🇪🇺): DinMo is the leading European Composable CDP. DinMo makes the power of a CDP accessible to all, quick to implement (a few hours), easy to use, and generating a return on investment from the first month of use. Its key features, such as the Visual Audience Builder, one-click activation, and AI predictions (Next Best Offer, Next best action, etc.), allow marketing teams to launch any marketing strategy independently.
Hightouch: The leading Composable CDP in the United States, Hightouch's platform has evolved beyond its initial Reverse ETL offering by including native data warehouse features such as event collection, identity resolution, and orchestration.
Census : As Hightouch did, Census has evolved beyond its initial Reverse ETL offer, by including new functionalities covering identity resolution, orchestration, etc. Census positions itself as a "Universal Data Platform", which means that its end-users tend to be more technical people.
Martech CDPs
Salesforce: Salesforce Marketing Cloud is a CDP solution that allows for collecting, reconciling, managing, segmenting, and activating data within the Salesforce ecosystem. For a company primarily using Salesforce tools, this solution is recommended. However, activations to destinations outside Salesforce are rather limited.
Adobe: Adobe CDP is an integrated solution within the Adobe Experience Cloud suite, launched in 2019. The platform uses an identity graph to build unified customer profiles in real time. These profiles can then be activated across other Adobe products, particularly within the marketing suite, to deliver personalized experiences. Adobe CDP mainly focuses on Data Management. Note that connectors outside the Adobe suite are rather limited and activation features are not really part of its functional scope. This CDP is especially suitable for large groups with data management expertise.
Hybrid CDPs
Imagino (🇫🇷): Initially focused on data management (unification, data enrichment, segmentation, etc.), Imagino is gradually expanding its functional scope by integrating activation components (campaign management, marketing automation, etc.). Imagino offers great freedom in data storage, proposing a hybrid or full SaaS mode. Unlike traditional CDPs, the data model is not imposed, and ingesting and unifying data from multiple sources is thus simplified.
ActionIQ: Able to integrate directly into its clients' data warehouse or offering an internal deployment, ActionIQ is a hybrid CDP. Note that the “data warehouse” integration is more recent and thus less mature. Its main goal is to centralize and unify customer data in a single place to activate it across all marketing channels afterward. The platform offers several features: data collection, audience segmentation, and even real-time triggers.
Infrastructure CDPs
Rudderstack: A data-oriented solution, Rudderstack is more of a Customer Data Infrastructure (CDI). Rudderstack offers a data infrastructure that focuses on collecting, processing, and storing customer data through its various products: event streaming, ETL, identity stitching, Reverse ETL, and Audience Builder. Rudderstack's primary mission is to help data teams build and maintain their infrastructure rather than a solution designed for marketing. Rudderstack can be implemented to meet CDP use cases, but marketing teams will find it difficult to use autonomously.
Conclusion
In conclusion, choosing a CDP should be based on the specific needs of your company, your technical capabilities, and your data management strategy. The different categories of CDPs - traditional, composable, hybrid, martech, and infrastructure - each offer distinct advantages and features suited to various use cases.
By carefully evaluating the functional and organizational criteria, as well as the offerings of the main market players, you will be able to select the most suitable solution to maximize the value of your customer data and optimize your marketing operations.
🌟 If you would like to discuss your CDP project with us, please do not hesitate to contact us!