All you need to know about Reverse ETL
12min • Last updated on Jun 30, 2025

Alexandra Augusti
Chief of Staff
Reverse ETLs, which first appeared in 2018 and became popular in 2021, are part of a new family of software. They are redefining the way businesses can make the most of their data.
Our customers report a 25% increase in their conversion rate thanks to this solution.
Key takeaways:
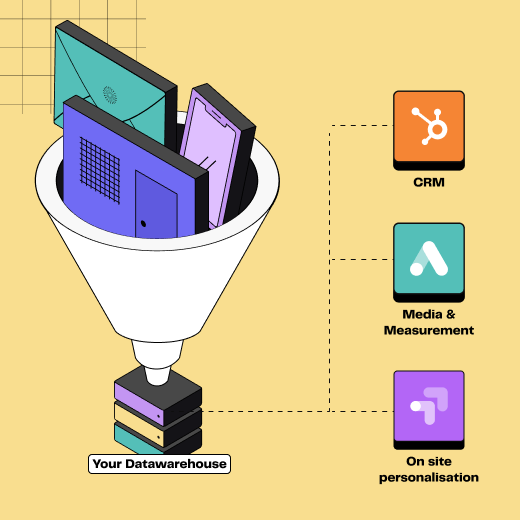
Reverse ETL enables data transfer from a data warehouse to business tools (CRMs, advertising platforms, customer service, etc.).
It is the inverted process of ETL (Extract, Transform, Load), which involves extracting, transforming, and centralising data within a warehouse.
Reverse ETL improves marketing campaigns and provides real-time insights for sales and support teams.
It allows businesses to synchronise customer data, segment audiences, and automate workflows as part of a data-driven approach.
🤔 In this article, you'll learn what Reverse ETLs are and how they can save you time and money. Find out how they work and the criteria for choosing the solution best suited to your needs.
What is ETL?
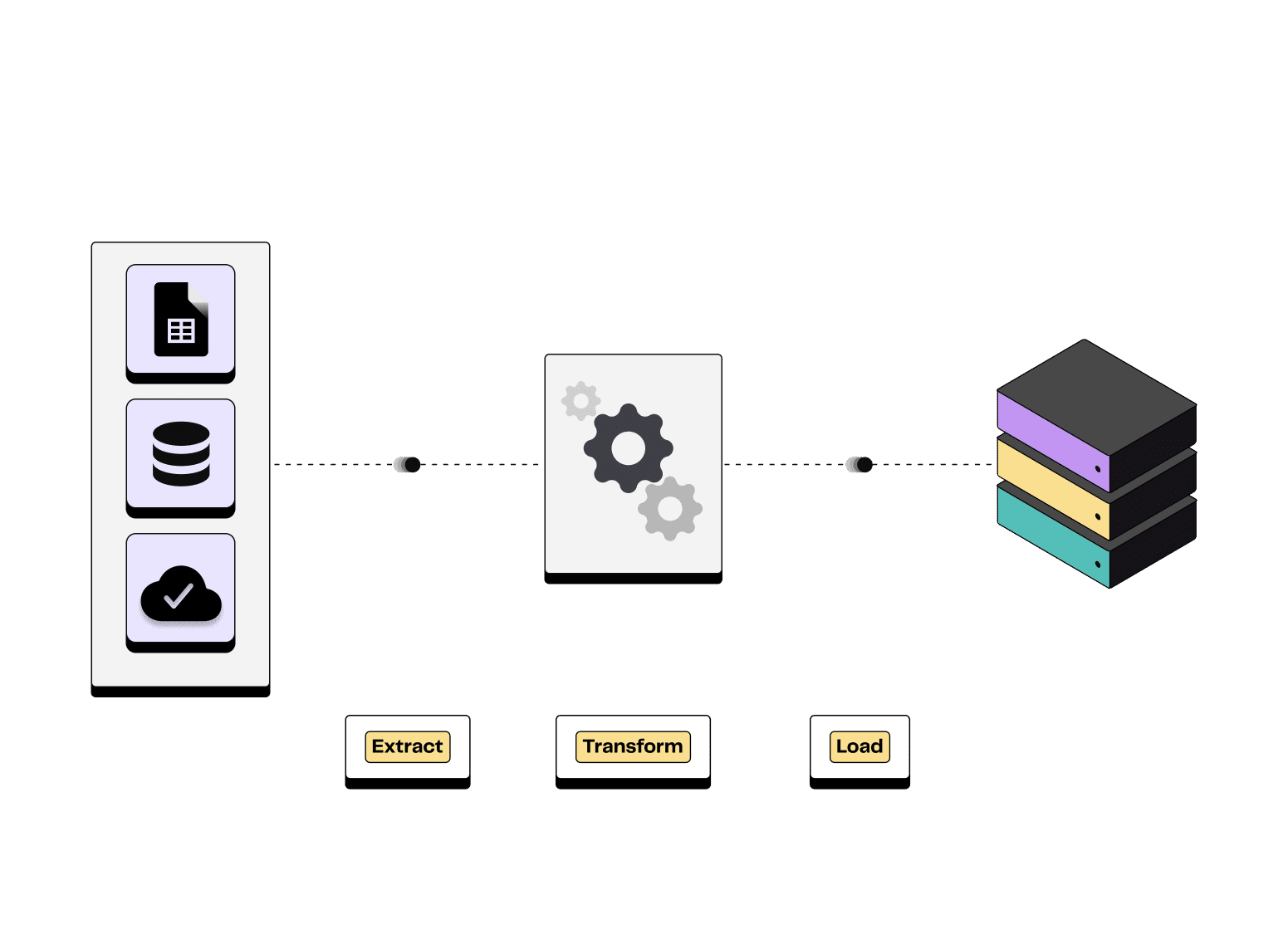
To understand what Reverse ETL is, you need to understand what ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) is. The Extract, Transform and Load process involves extracting data from different sources, transforming it into usable models and then loading it into a data warehouse (DWH).
There are many different ETL tools to choose from, such as Fivetran, AWS Glue or Hevo.
Extract Transform Load process illustration
💡 While ETL and ELT might seem similar, the primary difference is in the timing and location of the data transformation.
In the ETL process, raw data is transformed before it's loaded into the data warehouse. In that case, the raw data is not available in the data warehouse.
In contrast, the ELT process involves loading raw data into the data warehouse first, and then performing transformations on the stored data.
Since the 2010s, huge investments have been made in cloud data storage. And businesses are continuing to invest. A recent IDC study* forecasts a 20% annual growth rate in spending on cloud infrastructure.
Several reasons can be put forward:
Scalability: Substantial upfront investments in hardware are useless as cloud data warehouses allow to handle varying workloads.
Cost Efficiency: Pay-as-you-go model reduces upfront expenses.
Flexibility and Agility: Cloud data warehouses offer a quick deployment and an easy integration.
Security: All solutions go with robust measures, encryption, and compliance certifications.
With stricter and stricter regulations on first-party data, cloud solutions can be the perfect way to regain control over it to address customer requirements.
Yet, most of this data centralised in data warehouses is underused: in 2021, only 9% of companies could optimise dynamic execution across channels throughout the customer journey to achieve operational outcomes.
Indeed, once data resides in the warehouse, retrieving and utilising it in business tools becomes a challenge. This is where Reverse ETL comes into play...
What is Reverse ETL?
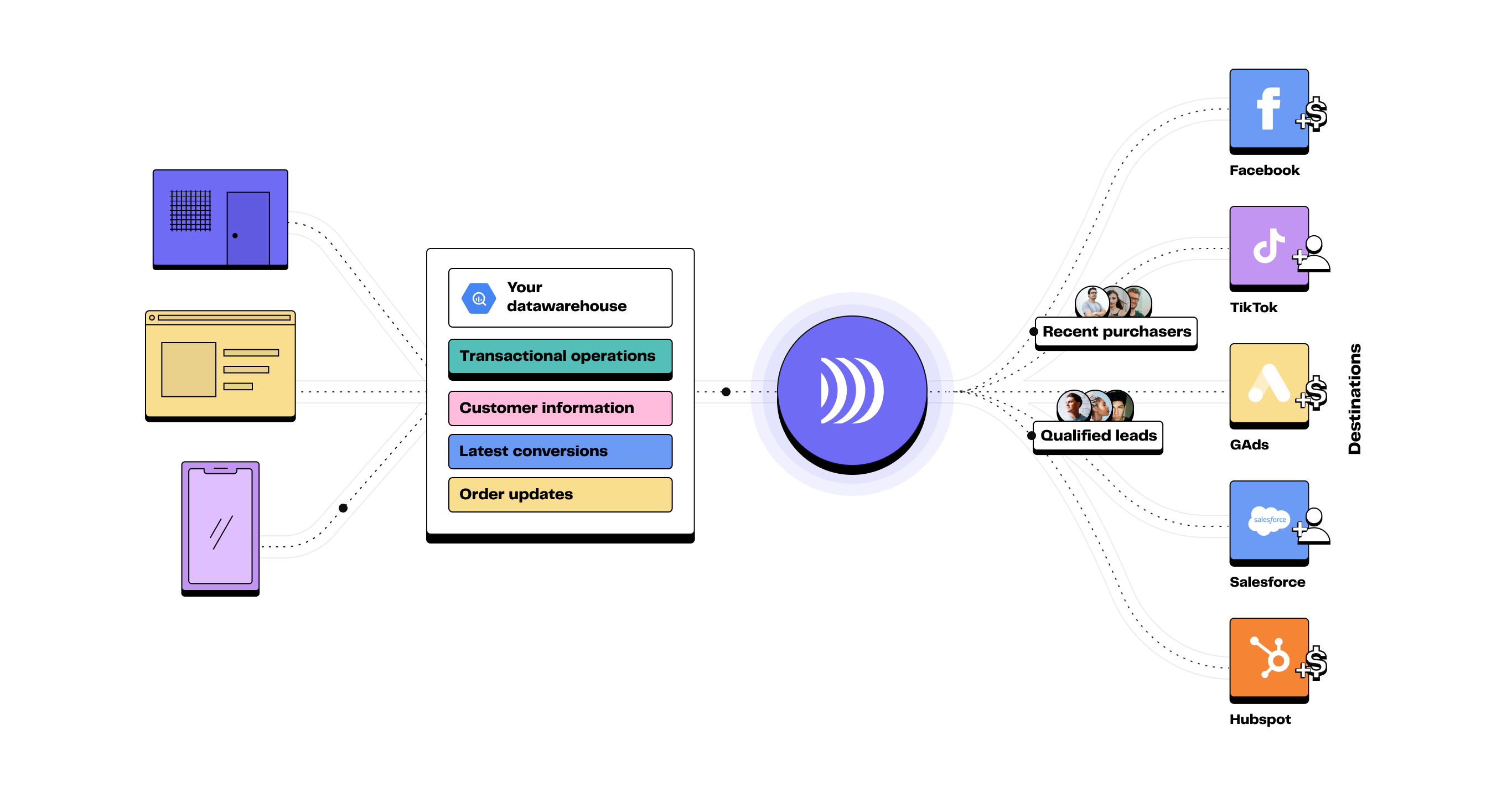
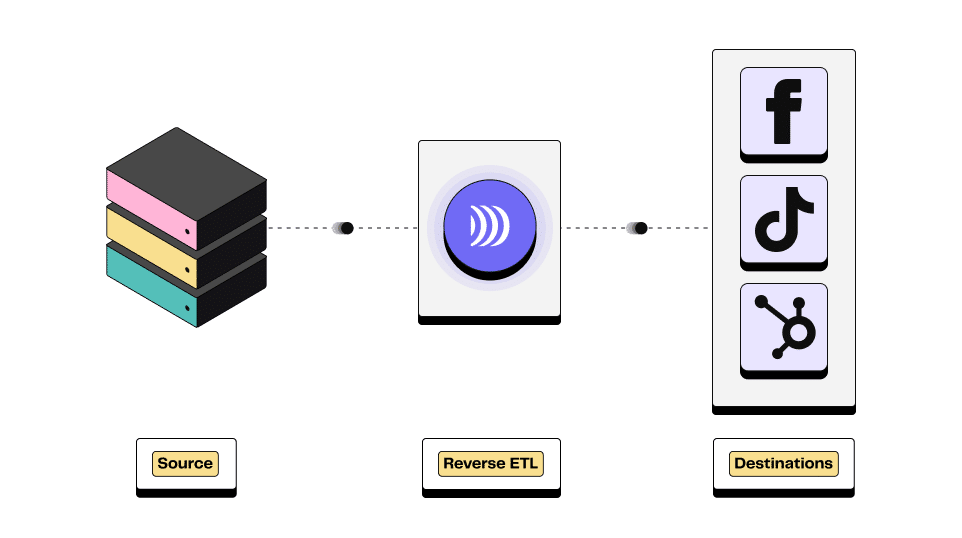
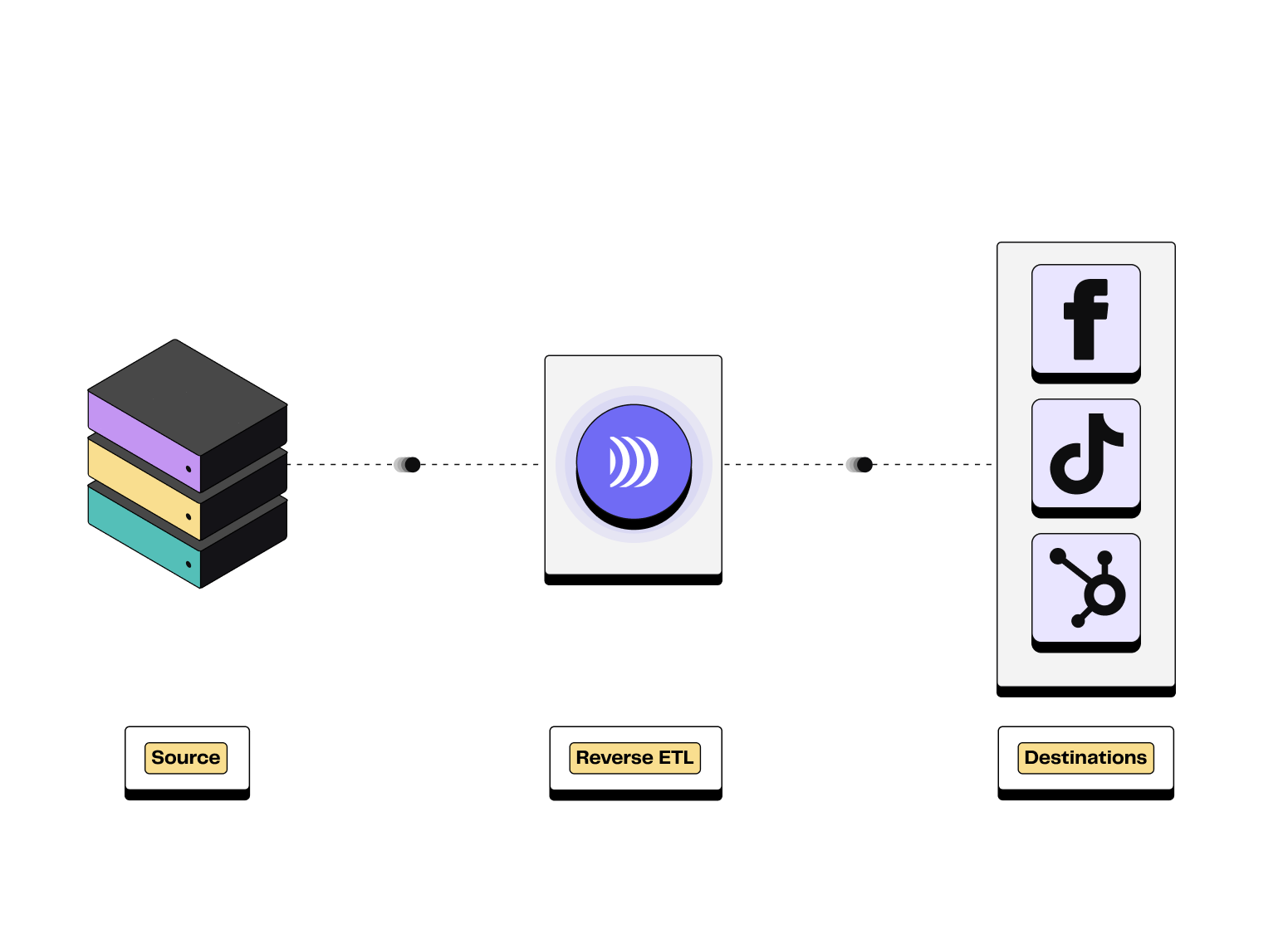
Reverse ETL is a process that enables data stored in a data warehouse to be synchronised with business tools such as CRMs, advertising platforms and automation solutions.
It forms part of a data-driven strategy, transforming centralised data into concrete actions for operational teams.
Data can be transformed and exploited in real-time by sending it directly to operational applications such as CRMs, marketing automation platforms and customer support tools.
Most of the time, when business teams need data in their tools, they have to submit IT tickets and wait a long time to finally have it in their analytics / functional tools. Reverse ETL bridges the gap between data and operational teams. It basically has an inverted function of ETL, allowing the transfer of centralised data from the data warehouse to all operational tools.

Illustration of Reverse ETL process
Reverse ETLs are not only data pipelines. Beyond data transfer, they empower organisations with data transformation processes before sending them to business applications.
Functions like data cleansing, segmentation, and audience creation enhance the usability and relevance of the data across diverse operational systems.
👉🏼 In short, Reverse ETL enables data synchronisation across different systems and apps for accuracy and coherence.
Download our complete guide to Reverse ETL!
👇
Complete guide to Reverse ETL
All you need to understand about Reverse ETL and know to choose the correct one
How does it work?
Reverse ETL operates by executing queries on your data warehouse and transferring the results to your selected downstream tool (whether an advertising destination, a CRM or a campaign automation software).
ETL vs Reverse ETL
The main difference between ETL and Reverse ETL lies in the direction of data flow. Indeed, ETL extracts data from source systems, transforms it according to analysis needs, and loads it into a data warehouse. As explained in the rest of this article, Reverse ETL, on the other hand, transfers data from a data warehouse to business tools.
This distinction is fundamental as it determines the starting point and destination of data within your technological infrastructure.
As its name suggests, Reverse ETL is the opposite of ETL. It enables data centralised in the data warehouse to be transferred to all the company's applications: marketing, sales, customer service, etc.
Components
There are 5 main components to a Reverse ETL:
Source: It refers to the data warehouse (or data lake) where all the data you want to get value from is stored. Snowflake, or Google BigQuery are among the most common data warehouses.
Models: The data model serves as the representation of your data, defining the data you want your business teams to have access to. It is generally created and maintained by a data expert user familiar with the data warehouse. Once it's set up, everyone can use it easily without having to write any code.
Segments: A segment is a subset of the data model. For instance, it is possible to create a segment of 'users living in Europe' or a segment of 'users who spent more than 100€', from the Customers entity (defined in the model).
These segments can be created using SQL queries or a no-code segment builder, as offered by DinMo.
Syncs: It refers to the mechanism of syncing a segment’s data with a downstream tool on a defined schedule. You can configure multiple syncs from the same data model to different destinations, ensuring all parts of your business are working off the same source of truth.
Destinations: A destination refers to any external tool or service to which you can send input data. This is where the data is usually accessed and used by the end users. The most common destinations are ad platforms, CRMs or automated campaign tools.
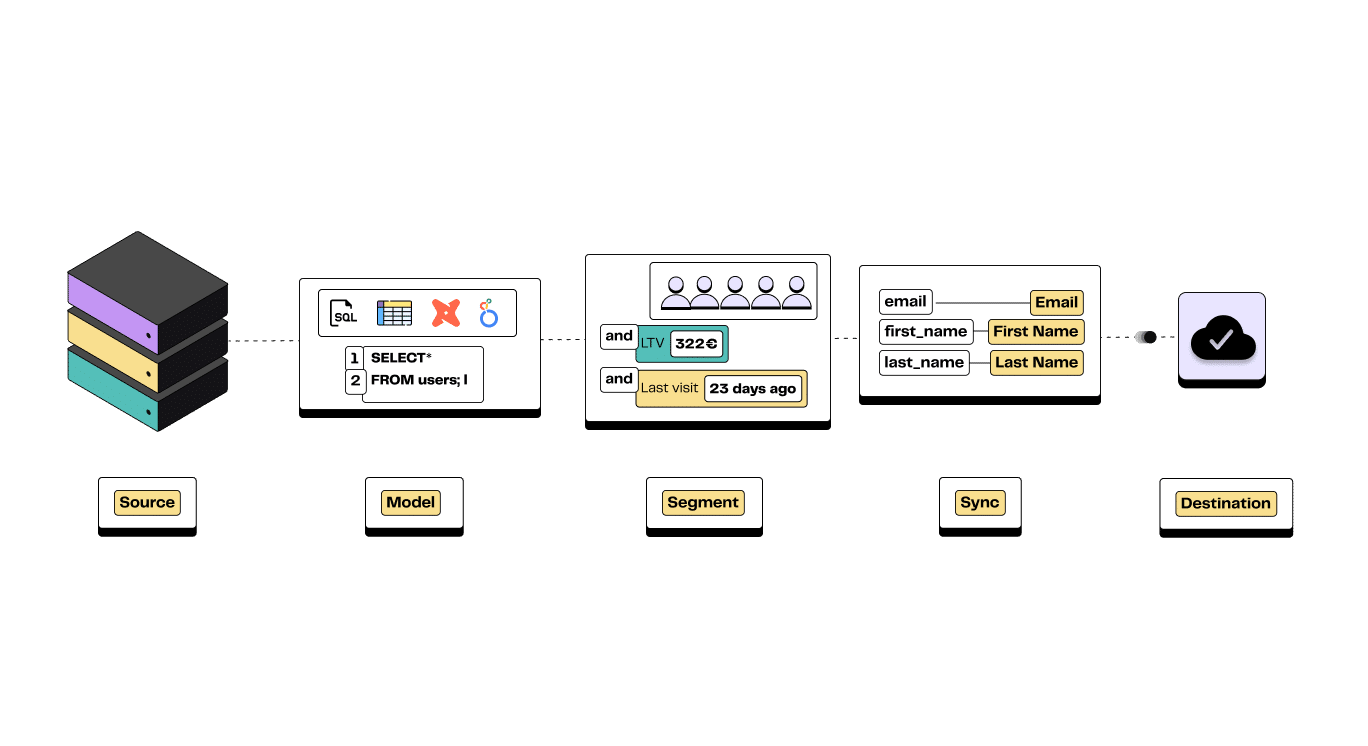
The main components of a Reverse ETL
Benefits of reverse ETL
Reverse ETL helps companies ensure that their data is consistent and always up-to-date across their systems.
Your data is then shared across operational systems and teams within your company, ensuring that your data doesn’t become siloed.
With that type of tool, you can achieve a lot of use cases:
A 360° overview of your customer journey
The data team simply needs to make sure that the relevant data is accessible and ready for use in the data warehouse. Therefore, business teams can operate autonomously to perform analytics and get powerful insights in real-time to improve the customer experience.
Quick, data-driven decision-making
Operational teams can use Reverse ETL to gain access to fresh and up-to-date data. This data can be readily loaded into operational systems, ensuring that teams have timely insights. As a result, they can respond promptly to market shifts, customer demands, and emerging opportunities.
More personalised marketing content and campaigns
Advertising is one of the biggest use cases for Reverse ETL. Marketing teams often need to segment data for various purposes, such as creating lookalike audiences, excluding certain customer groups from campaigns, or retargeting top clients. All audiences can be managed centrally and synced in business platforms.
With Reverse ETL, you can send first-party data, such as attributes, traits or custom predictive metrics, to enrich your customer knowledge in your CRM / lifecycle marketing tools (such as Braze). This enables successful personalisation of the customer journey.
Improvement of client operations
Sales tools can be enhanced with information that does not originally exist within them (product usage, channel preferences, etc.).
Support teams can also benefit from Reverse ETL because you can sync real time customer information into their system, so that they can prioritise support actions based on customer usage and contract value.
What are Reverse ETL alternatives?
Moving data can be done in different ways:
manual uploads
with custom pipelines
with other platforms such as iPaaS or CDPs.
Reverse ETL vs. iPaaS
Integration Platform as a Service (iPaaS) is a platform that connects software applications so that a specific trigger in one tool results in a specific response in the other. For instance, a form submission on Typeform can automatically create a new contact in HubSpot.
iPaaS can connect applications via user-friendly APIs, which is particularly useful if you’re talking about a simple point-to-point integration without dependencies. The main difference between Reverse ETL and iPaaS is that Reverse ETL focuses on transferring data from a single origin to the end tools whereas iPaaS allows bidirectional integration (from point A to point B).
Well-known solutions are tools like Workato, Zapier, or Boomi.
An iPaaS simply connects systems in a 1-1 capacity and has several limitations:
It generates a complex network of pipelines and workflows that aren't scalable.
As workflows become complex, users require knowledge of APIs, negating the 'no-code' benefit, as functional teams will depend on assistance from data teams.
It’s not designed for large-volume batch updates (or is extremely costly when doing so)
It’s not based on a Customer 360 and can result in inconsistent customer experiences
It works like a “black box” and raises governance and quality issues
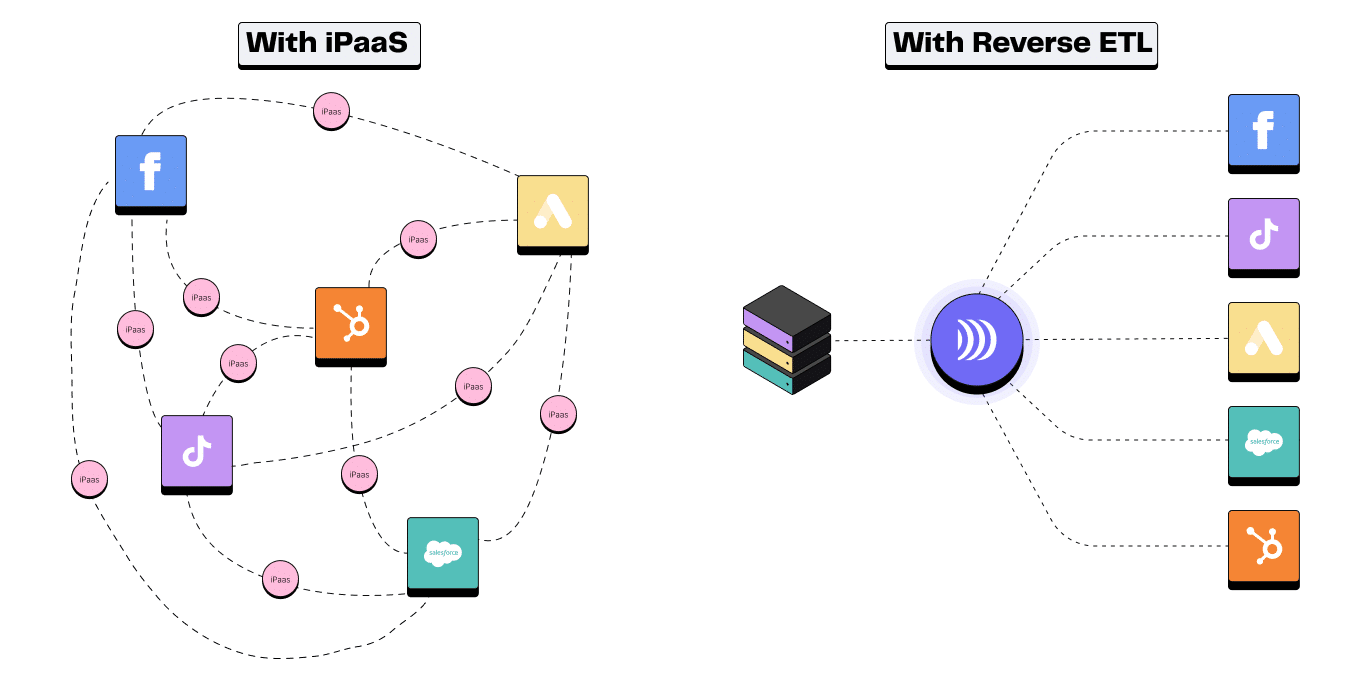
iPaaS vs. Reverse ETL
Reverse ETL vs. CDP
A Customer Data Platform (CDP) is an off-the-shelf solution that stores and organises customer data from multiple sources to create a single source of truth. As such, a traditional CDP is an alternative to the data warehouse. Yet, the CDP offers advanced functionalities besides BI purposes:
Data preparation for business use cases: segmentation, creation of aggregates, customer scores, etc.
Activation to business applications
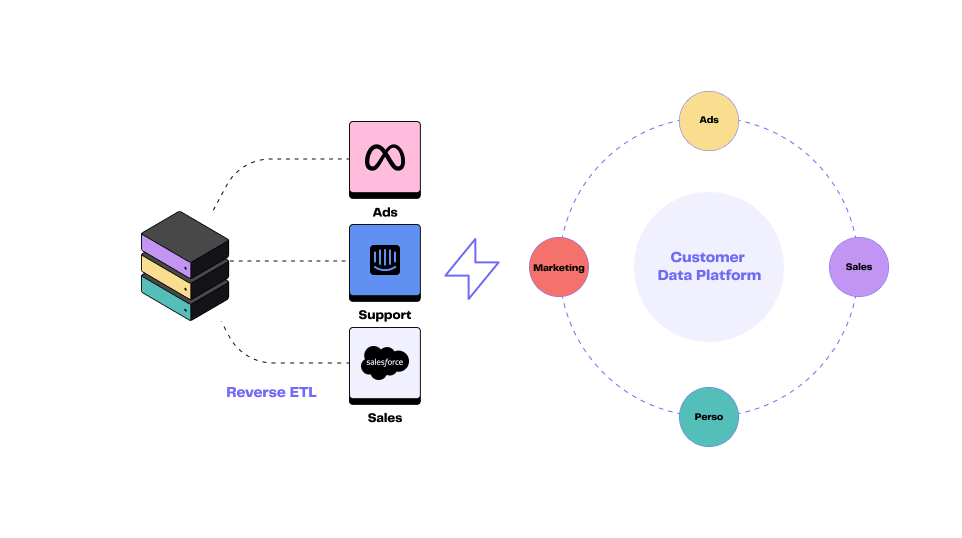
In short, CDP combines the roles of a data warehouse and a reverse ETL. CDP offers more functionalities than Reverse ETL, which remains an essential component of this type of platform.
However, in the fifteen years or so that CDPs have been around, the ecosystem has evolved considerably. Only 1% of companies believe that CDPs meet their current and future needs.
Integrated CDPs have a number of shortcomings:
Rigidity: The CDP imposes its data models and limits the creation of customized models.
Price: A packaged CDP is a costly solution, inaccessible to most small and medium-sized businesses.
Privacy: As it stores data, the traditional CDP is a less secure solution
In their traditional form, CDPs are less attractive. Companies are now turning to composable, or modular, CDPs.
The reverse ETL process is part of the composable CDP, which sits on top of a cloud data warehouse and activates that data to many different destinations.
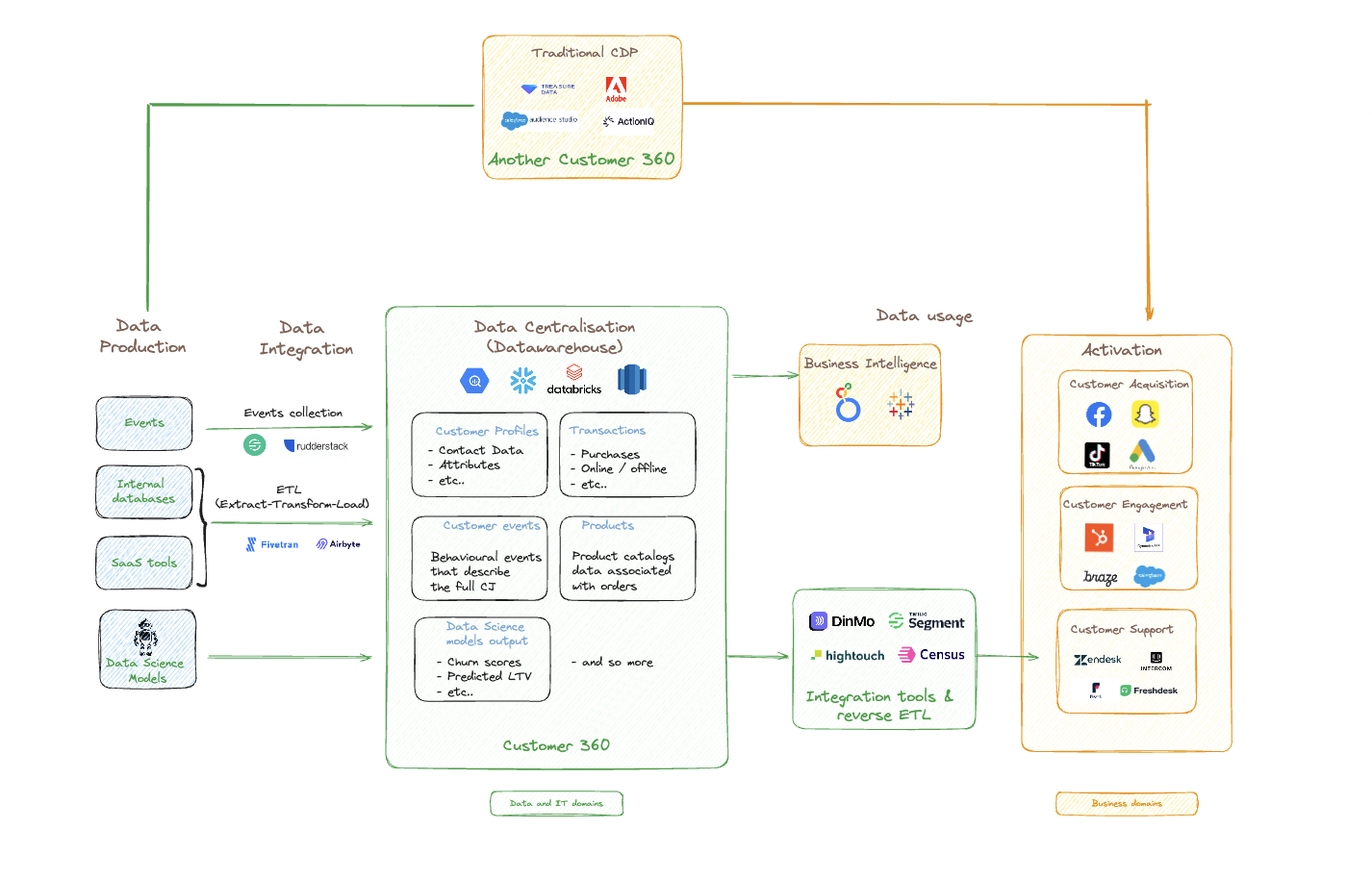
CDP vs. Reverse ETL
Do I need to build or buy a Reverse ETL?
At this point, you're likely already convinced about the value of Reverse ETL. However, you might still be wondering: what if your company created its own API connectors between your data warehouse and operational systems (like Meta, Salesforce, Brevo, etc.)?
On the surface, it seems feasible. Suppose someone on the Customer Success department wants the churn probability from the data warehouse displayed in Intercom. An engineer could look up the Intercom API, understand the relevant endpoints, and create a custom integration. It sounds simple enough.
But what happens when the predictive methods change, the Support team wants more information displayed in Intercom or switch from Intercom to Zendesk?
In such cases, engineers would need to build and maintain another custom integration. This is where challenges arise:
Manually creating API connectors can consume days or weeks. Every third party integration comes with its own specificities and technicalities, which make it even worse.
API endpoints often can't handle real-time data transfer, meaning you could quickly hit a rate limit
Your team would need to constantly maintain these connectors to accommodate changes in underlying tools.
In short, there's little value in your data team building and maintaining pipelines for Reverse ETL, even if it seems cheaper than paying for a solution.
⚠️ When choosing a Reverse ETL solution, be sure to check the criteria important to your business: whether it is SaaS or on-premise, who the users are (technical or business teams), and the integrations offered.
How to choose?
A comparison of existing vendors
🌟 There are several categories of Reverse ETL, and multiple players are positioning themselves on the market:
Integration tools, which focus on simplifying the movement of data for data teams
Generalist tools, which support integration from any source to any destination, but which are dedicated to data teams
Specialised tools, which focus on enabling business teams to use data more effectively, without depending on data teams
We've written a Reverse ETL benchmark to help you choose the right solution for your business.
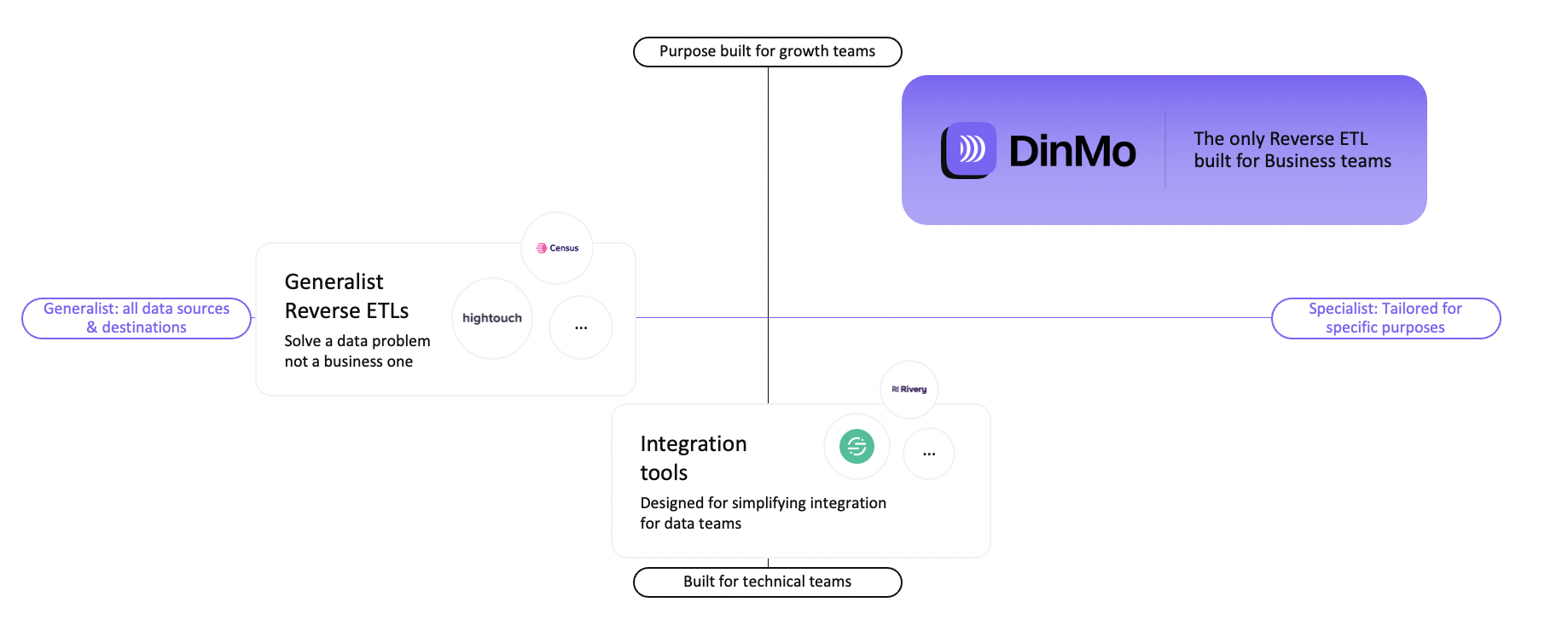
Reverse ETL categories
At DinMo, we not only meet the needs of data teams, but we also offer business teams a tool that they can use perfectly without the need for an engineer.
DinMo is the only Reverse ETL solution that is easy to use for non-technical teams. We combine the code-free user experience of the best traditional CDPs with the simplicity and flexibility of Reverse ETL.
We chose DinMo Reverse ETL because the solution was simple to implement and use. Everything was configured in 1 hour. We were able to build our own segments without going through the data team, and use them directly in our acquisition tools.
Sylvain Seng Bandith, Lead Performance @Ankorstore
If you would like to discuss this with us👇
From Census or Hightouch to DinMo
All in just a few minutes, with personalised support from our team. No-code functionality at no extra cost!
Criteria to be considered
Before purchasing a Reverse ETL or attempting to build one yourself, it's important to know the key features to look for in a potential tool:
Support for your favourite tools: The efficacy and versatility of a reverse ETL tool are largely dependent on the range of destinations it can integrate and interact with. When selecting a tool, it's important to consider not only your immediate needs but also potential future requirements. A specific destination may only be available from a single provider (e.g. Batch).

DinMo integrations
Robust syncs: Data synchronisation is arguably the most crucial aspect of a reverse ETL tool. It should be not only fast but also reliable. It's essential to choose a provider that uses an efficient approach to data synchronisation, such as only syncing data that has been changed or updated. This approach results in substantial time and cost savings.
Powerful observability: A reverse ETL tool should provide robust monitoring capabilities that allow for quick error detection and resolution. Alerting features and clear, easy-to-understand monitoring features can significantly speed up the troubleshooting cycle, ensuring minimal disruption to your data teams.
Security: Data security is paramount when using a reverse ETL tool. Your chosen provider should have demonstrable compliance with all relevant regulatory requirements to ensure the protection of your sensitive data.
For instance, this includes compliance with regulations like CCPA/GDPR, certifications such as SOC 2, secure data storage practices, robust data encryption methods.
Ease of use: Reverse ETL tools are designed to streamline and simplify data management tasks, especially for business teams. Therefore, they should be user-friendly and accessible. Look for features like no-code functionalities, intuitive user interfaces, and straightforward data mapping processes that don't require advanced technical knowledge (of APIs for instance).
Ease of implementation: A good reverse ETL tool should be easy to set up and start using. The data model should be flexible enough to accommodate your specific needs, and anyone who has access to the data warehouse should be able to configure the tool without much difficulty.
Support: Data experts and resources (good documentation, tutorials, etc.) must be available to help your team overcome any obstacles.
Transparent and scalable Pricing: Of course, pricing is another important factor to consider when choosing a tool. Make sure you fully understand the provider's pricing structure, which might be based on the number of destinations or active syncs, for example. Also, consider how the cost might change based on your usage. While entry prices may initially seem reasonable, they can quickly escalate as your needs grow, so it's important to choose a solution that can scale with you.
Conclusion
As businesses strive to navigate the data landscape, Reverse ETL emerges as a key enabler for unlocking the true potential of centralised data. Its role in bridging the gap between data warehouses and business applications positions it as a transformative force in the modern data strategy toolkit. By understanding its functions and advantages, organisations can embark on a journey towards data-driven excellence.
👉🏼 Ready to elevate your data stack? Schedule a demo with us and see how our Reverse ETL platform can get your ETL solution up and running in minutes!
💡If you'd like to find out more about how Reverse ETL can benefit your company or need help with data activation, please don't hesitate to contact me (alexandra@dinmo.com)
*Source: IDC Worldwide Software and Public Cloud Services Spending Guide
FAQ
What are the most common use cases for Reverse ETL?
What are the most common use cases for Reverse ETL?
Reverse ETL is used to synchronise data from a data warehouse with operational tools. Here are the main use cases:
- Targeted marketing: creating precise audiences for personalised campaigns on advertising systems.
- Customer personalisation: Send enriched data to marketing automation tools for tailored interactions.
- Optimised sales: Prioritise leads using data updated directly in the CRM.
- Improved customer support: offer faster responses thanks to consolidated information.
To find out more, discover how Reverse ETLs are used in business.
How long does it take to implement a Reverse ETL?
How long does it take to implement a Reverse ETL?
With DinMo, implementing a Reverse ETL is quick and intuitive. In less than an hour, you can :
- Configure your connections with the data warehouse and your business tools (CRM, advertising services, etc.).
- Create ready-to-use data segments, with no technical skills required.
- Synchronise your data in real time with your applications, for immediate implementation.
Thanks to its simplicity and no-code interface, DinMo is one of the fastest solutions on the market to adopt, even for non-technical teams.
Can a Reverse ETL replace a CDP?
Can a Reverse ETL replace a CDP?
A Reverse ETL does not replace a traditional CDP, which stores, analyses and manages customer data in a dedicated platform. However, the Reverse ETL process, as a data pipeline, is used in all Customer Data Platforms.
Reverse ETL is also an essential building block of composable CDPs, an approach that combines the advantages of a data warehouse and customised data activation. Indeed, it is possible to build your own Composable CDP by exploiting the customer repository of your data warehouse and a Reverse ETL tool to enable segmented data to be sent to marketing tools. Rather than operating as a separate entity, the Composable CDP integrates seamlessly into any technical environment.
The advantages of Composable CDPs :
- Flexibility: Unlike the rigid models of packaged CDPs, Composable CDPs are based on the data warehouse models already in place in companies. The Reverse ETL can then transform this data to meet the technical requirements (API) of the various marketing solutions.
- Optimised cost: You are not limited by the pre-packaged and expensive functionalities of a CDP. You choose the tools (data warehouse, Reverse ETL, BI tool, etc.) according to your needs.
- Enhanced security: Data remains in your data warehouse, avoiding duplication and offering greater control in terms of confidentiality and compliance (GDPR, CCPA).