All about Customer Data Infrastructure (CDI)
6min • Last updated on Jul 23, 2025

Olivier Renard
Content & SEO Manager
According to IDC, 80% of the data produced worldwide this year is unstructured. What's more, customers are interacting with brands through a multitude of channels.
Faced with this explosion, companies need to equip themselves with appropriate solutions to integrate and exploit this information effectively.
A Customer Data Infrastructure (CDI) is a set of tools designed to collect, process and organise customer data from multiple sources. It provides a clear, unified view of this data, offering actionable insights for businesses.
Key facts:
A Customer Data Infrastructure facilitates the integration of customer data, ensures its governance and enables identity resolution.
It differs from CDP and DMP: CDI collects and manages data, DMP processes 3rd-party data, and CDP activates data around unified customer profiles.
As a component of a Modern Data Stack, a CDI covers a wide range of use cases. Its implementation involves both data and business teams.
Adopting a CDI involves assessing data compatibility, accessibility and security.
👉 Find out what Customer Data Infrastructure is and how it differs from CDP and DMP. Find out what criteria you need to take into account to implement the right solutions for your needs. 🎯
What is a Customer Data Infrastructure (CDI)?
A Customer Data Infrastructure (CDI) is a set of solutions designed to collect, transform, centralise and administer customer data from different sources.
It serves as the technical foundation for managing data flows within a company, while guaranteeing reliable, usable information for all teams.
Customer data comes from many sources: websites, CRM, marketing platforms, e-commerce tools, etc. This information is often scattered across different systems, sometimes duplicated, siloed or poorly organised.
This makes it difficult to obtain a complete and reliable view of customers, which in turn complicates decision-making and the personalisation of marketing campaigns.
A Customer Data Infrastructure solves this problem by centralising all this data in a single environment. It enables you to :
Bring together data from several tools.
Organise information to avoid inconsistencies (duplication, formats, obsolescence).
Guarantee data quality for more accurate decision-making.
Ensure governance by strengthening compliance, security and control.
In this way, a CDI helps the company to better understand its customers, improve the effectiveness of its campaigns and comply with confidentiality standards.
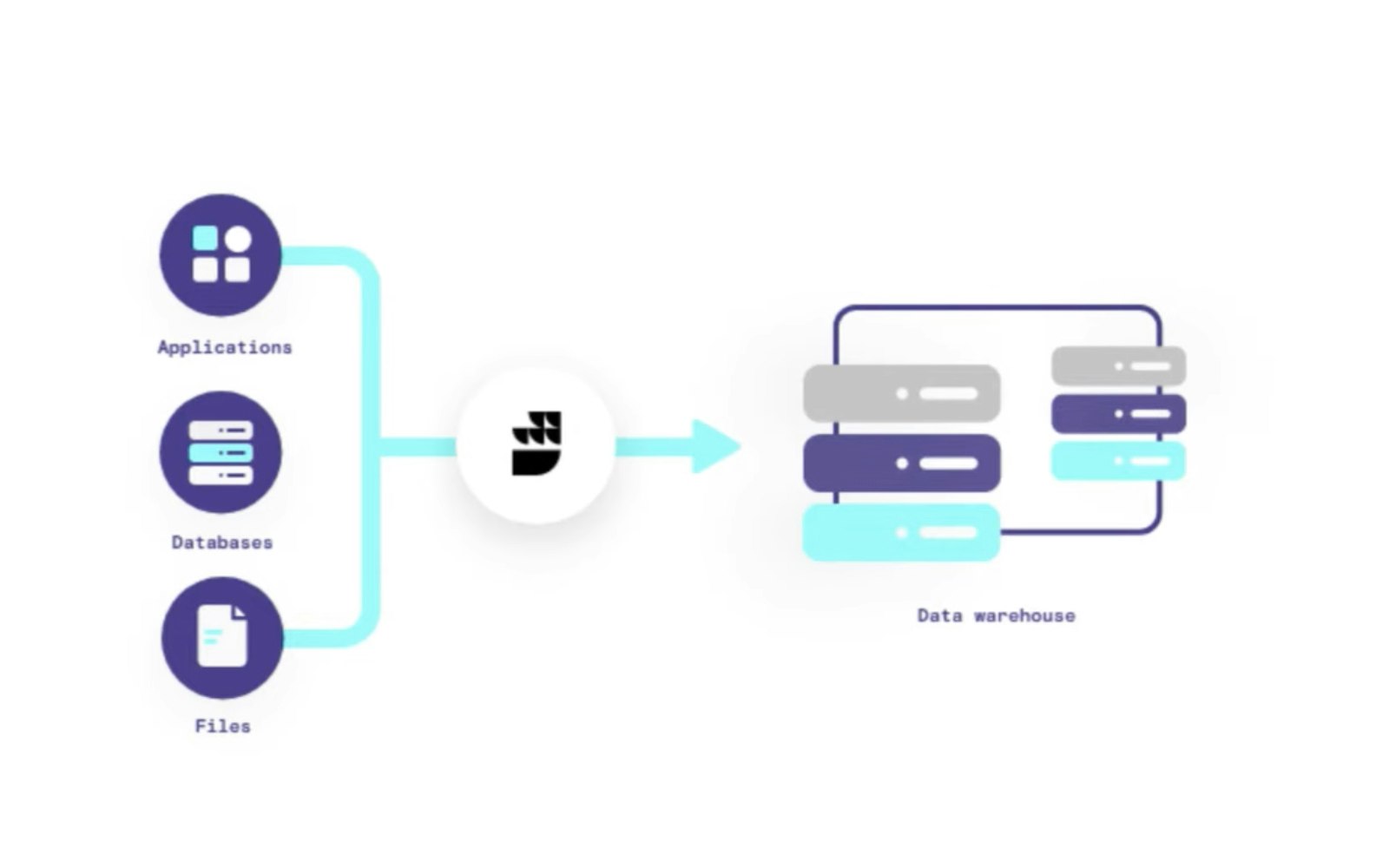
ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) process - Source: RudderStack
What are the advantages of a CDI?
A Customer Data Infrastructure plays a key role in the management of customer data within an organisation. It offers three essential elements:
Breaking down silos: a CDI centralises customer data, previously dispersed across different systems (CRM, e-commerce platforms, marketing tools, etc.).
By bringing this information together in a single environment, it guarantees a clearer and more coherent overview. This is why the CRM cannot serve as a single source of truth.
Governance and compliance: it provides greater control over access to data and ensures compliance with regulations such as the GDPR or the CCPA.
By unifying data in a centralised space, it limits the risks of duplication, loss or mismanagement of sensitive information.
Identity resolution and personalisation: it prepares for data activation by creating detailed user profiles.
These profiles then enable marketers to segment audiences effectively and personalise campaigns using dedicated tools. The Customer Data Infrastructure therefore serves as the technical foundation for delivering personalised experiences across different channels.
CDI vs DMP vs CDP: What are the differences?
The terms Customer Data Infrastructure (CDI), Customer Data Platform (CDP) and Data Management Platform (DMP) are often used when it comes to managing customer data.
Each solution meets specific objectives and has different functionalities. Understanding these differences helps you to choose the tool best suited to your organisation's specific needs.
Customer Data Infrastructure : a CDI is designed for technical teams. It processes and organises raw data flows from several sources (websites, CRM, e-commerce platforms). A CDI guarantees the quality and reliability of the data before it is used in other tools.
Data Management Platform : a DMP mainly manages anonymous, third-party data, such as that generated by cookies. It stores this data for a limited period to target audiences in advertising campaigns.
Customer Data Platform : a CDP aggregates, cleanses and harmonises customer data from various sources (particularly first-party data) within a unified database. It facilitates the segmentation and customisation of marketing campaigns thanks to data intelligence functionalities. With this activation component, it goes further than a CDI.
A distinction is generally made between traditional CDPs and composable CDPs.
A traditional CDP stores and processes data in its own system. In contrast, a composable CDP uses data stored in the company's cloud data warehouse, without creating a copy.
Criteria | CDI | DMP | CDP |
|---|---|---|---|
Main objective | Organise and manage data flows. Helping businesses make better data-driven decisions in real-time. | Collect and segment anonymous data for advertising. | Create unified customer profiles and audience segments to trigger activations. |
Target audience / Use cases | Technical teams. Data collection, management and governance. | Acquisition teams. Targeted advertising campaigns. | Marketers. Personalising campaigns, reducing churn, increasing LTV. |
Type of data | Raw data: behavioural, transactional, first-party. | Third-party data (anonymous, cookies, advertising identifiers). | Identified customer data (PII): first-party, behavioural, transactional. |
Storage duration and data management | Long-term storage in a data warehouse. Total control of data. | Short-term storage (30 - 90 days), based on cookies and IP addresses. | Medium/long-term storage. Continuous updating of customer information. |
Types of company | Data-driven companies with a dedicated technical team. | Companies with a strategy of mass acquisition through advertising. | Companies looking to personalise the customer experience. |
Main suppliers | RudderStack, Metarouter, Oracle GoldenGate, Matillion. | Lotame, Nielsen, Oracle Bluekai. | DinMo, Hightouch, Census, Segment, Imagino |
The differences between CDI, DMP and CDP
How do you set up a Customer Data Infrastructure?
Setting up a Customer Data Infrastructure involves following a precise process to ensure effective management of customer data. Here are the key criteria and the steps to follow.
Criteria for choosing your solution
There are a number of aspects to consider when choosing your CDI:
Compatibility with existing systems: the platform must integrate easily with your existing tools (CRM, cloud data warehouse, analytics tools etc.). Native connectors with the main data warehouses (Snowflake, BigQuery or Redshift) make it easy to automate data flows.
Scalability: the solution must be able to manage a growing volume of data without any loss of performance. It must be flexible enough to adapt to changes in your infrastructure.
Data security: Prioritise a CDI offering solid guarantees of protection for sensitive data (encryption, GDPR / SOC2 compliance).
Ease of use: an intuitive tool enables rapid adoption by technical teams. By offering flexible configuration options, the platform can be adapted to your company's specific needs.
Support and assistance: responsive support makes it easy to resolve any technical bottlenecks quickly. Take a look at the training resources available to help your teams master the tool.
The main stages in setting up a Customer Data Infrastructure
Needs analysis: define your objectives (better governance, centralisation, preparation of marketing actions).
Solution selection: compare the tools available, taking into account the criteria outlined above.
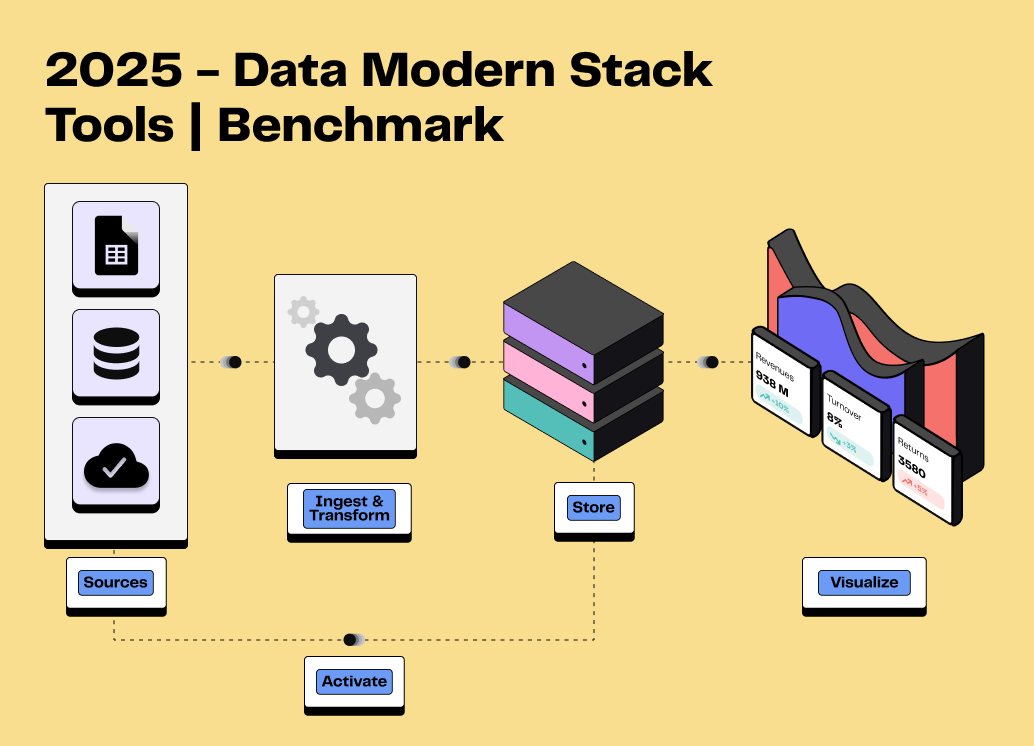
Data source integration: connect all your sources (websites, CRM, marketing tools) and deploy an ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) process to collect, standardise and load data.
Implement governance processes: define quality and compliance rules to manage data securely.
Team training: support your technical and business teams to ensure optimum use of CDI.
Measure the effectiveness of CDI: regularly assess data quality (accuracy, completeness, absence of duplicates). Analyse the impact of centralisation on decision-making and business process improvements.
Conclusion
A Customer Data Infrastructure eliminates silos and gives you back control over your customer data. It collects, unifies and secures all your information, making it reliable and usable.
A CDI facilitates identity resolution and offers a better understanding of the customer journey for more precise and personalised activations. By strengthening governance and compliance, it contributes to more responsible and efficient management.
👉 Find out how DinMo can help you segment and activate your customer data effectively. 🚀
👇
Keep in touch
FAQ
What types of data should be included in a Customer Data Infrastructure ?
What types of data should be included in a Customer Data Infrastructure ?
A Customer Data Infrastructure should centralise various data types to create a unified customer view. This includes:
- Behavioural data: Website visits, app interactions, and engagement metrics.
- Transactional data: Purchase history, subscriptions, and order details.
- First-party data: Data collected directly from customers through forms, surveys, or account registrations.
- Demographic data: Age, location, and preferences.
By combining these data sources in a data warehouse, a CDI ensures data governance and provides a single source of truth for better decision-making and personalisation.
Which teams are involved in using a Customer Data Infrastructure?
Which teams are involved in using a Customer Data Infrastructure?
A CDI benefits multiple departments across a business by ensuring data management and quality.
Key roles include:
- Data teams: Data engineers and architects manage the data warehouse, ensuring data flows correctly through ETL pipelines and remains reliable.
- Marketing teams: Use the Reverse ETL and CDP linked to the CDI for segmentation and targeted campaigns based on unified customer profiles.
- Legal and compliance teams: Oversee data governance practices to ensure compliance with regulations like GDPR and CCPA.
By facilitating collaboration between technical and operational teams, a CDI helps businesses activate their data more effectively.
What are the main use cases of a Customer Data Infrastructure?
What are the main use cases of a Customer Data Infrastructure?
A CDI addresses several critical use cases for data-driven marketing and business operations:
- Marketing personalisation: By consolidating customer insights, businesses can create more relevant and targeted marketing campaigns.
E-commerce: A CDI powers product recommendation engines by centralising data from multiple sources, improving personalisation and conversion rates.
SaaS companies: Use CDIs to optimise acquisition campaigns by analysing user activity and trial engagement patterns.
- Data automation: A CDI automates data flows between systems like CRM platforms, CDPs, and analytics tools, ensuring real-time access to updated information.
- Advanced segmentation and analytics: Businesses can build customer profiles and segment audiences based on behavioural data and purchase patterns.
A well-implemented CDI enhances data activation while ensuring data quality and regulatory compliance across all platforms.