Data Taxonomy: Organising data for better utilisation
5min • Last updated on Feb 19, 2025

Olivier Renard
Content & SEO Manager
Businesses generate vast amounts of data daily. However, according to a Seagate study, more than two-thirds of this information remains unused. How can it be structured effectively to unlock its value?
Data taxonomy provides a structured framework to classify data, preventing information fragmentation. It is a fundamental component of a modern data infrastructure.
Key Takeaways:
Data taxonomy enables data categorisation, making it consistent and actionable to maximise its potential.
There are multiple ways to group and structure data, depending on usage: product, customer, or analytics-related. Each model serves a specific business need.
A well-structured data taxonomy improves governance and decision-making. It facilitates data access, analysis, and marketing strategy optimisation.
Implementation follows several key steps, with dedicated tools available to help establish a robust and scalable framework.
🔎 Discover what data taxonomy is, the main types, and its role in information organisation. Learn how to build a logical classification system to enhance data utilisation and improve overall efficiency. 🚀
What Is Data Taxonomy?
Data taxonomy is a method for organising data. It involves classifying information into hierarchical levels (categories, subcategories) based on common characteristics and attributes.
It provides a coherent and structured framework that makes information easily accessible. By logically organising data, taxonomy simplifies data exploitation, analysis, and governance.
This concept is similar to biological taxonomy, where species are grouped into hierarchical classifications called 'taxons' such as kingdom, order, family, and genus. It is also widely used in content marketing.
Data taxonomy differs from other data structuring models, particularly:
Data Classification: In cybersecurity, classification involves labelling and grouping data based on sensitivity levels.
Data Ontology: While taxonomy categorises data, ontology defines relationships between data within a specific context.
Data taxonomy improves governance and decision-making. It is essential for data-driven businesses.
Examples of data organisation
Different types of data taxonomies exist depending on business needs. A company can organise data along several dimensions: products (e-commerce catalogue), customers (CRM segmentation) or orders (tracking and reporting).
👉 Let’s take a simple example. Imagine you manage an e-commerce website specialising in racquet sports 🎾🏸. Below is a step-by-step approach to structuring a product taxonomy.
1️⃣ Define your objectives
You want customers to be able to find what they're looking for quickly and your teams to be able to manage the catalogue efficiently. To achieve this, product data needs to be well organised so that it can be integrated into the CRM and marketing campaigns.
2️⃣ Establish major product categories
To cover all racket sports, you can group products by sport type:
Tennis
Badminton
Squash
Padel
Table tennis
3️⃣ Structure Subcategories / Hierarchies
Each sport has similar product families, allowing you to structure taxonomy as follows:
Sport (Main Category):
Main Equipment (rackets, balls, shuttlecocks…)
Apparel (shoes, t-shirts, shorts…)
Shoes
Accessories (grips, strings, bags…)
For the Tennis category, for example, the breakdown might look like this:
Raquets
Adult
Junior
Balls
Shoes
Apparel (shorts, t-shirts, jackets)
Accessories (grips, dampeners, bags)
4️⃣ Add attributes & filters to refine search
To assist customers, specific data fields must be included:
- Weight, head size, balance, rigidity for the rackets sub-category
- Surface (clay, hard, grass), size for shoes
- Gender, size, material for the textile sub-category.
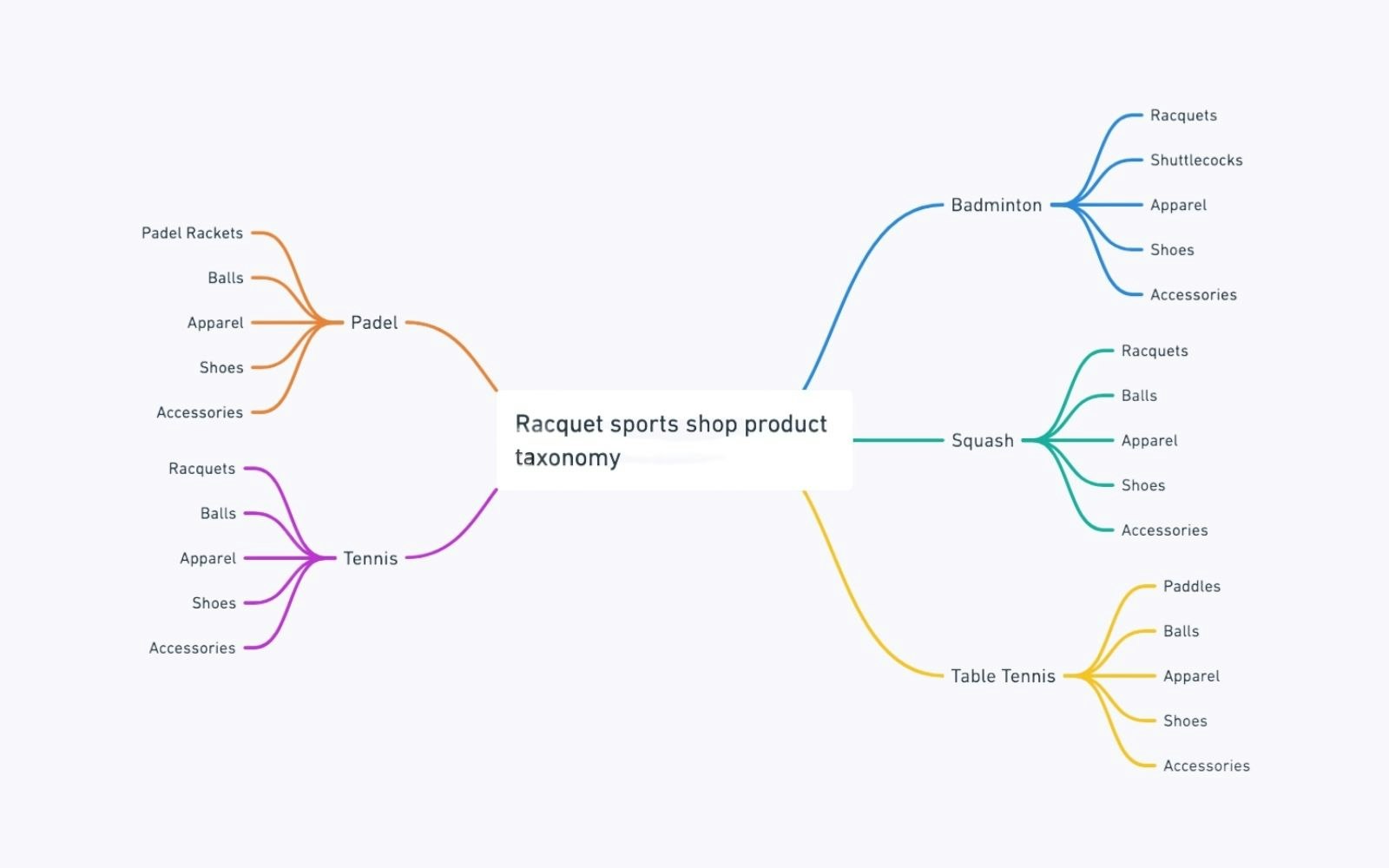
Product taxonomy
The benefits of data taxonomy
A well-organised data structure offers multiple advantages. In this example, product categorisation enables:
An improved user experience: Smooth navigation and intuitive search.
Search engine optimisation (SEO): Better search engine ranking for product categories.
Easier stock management: Clear classification prevents errors.
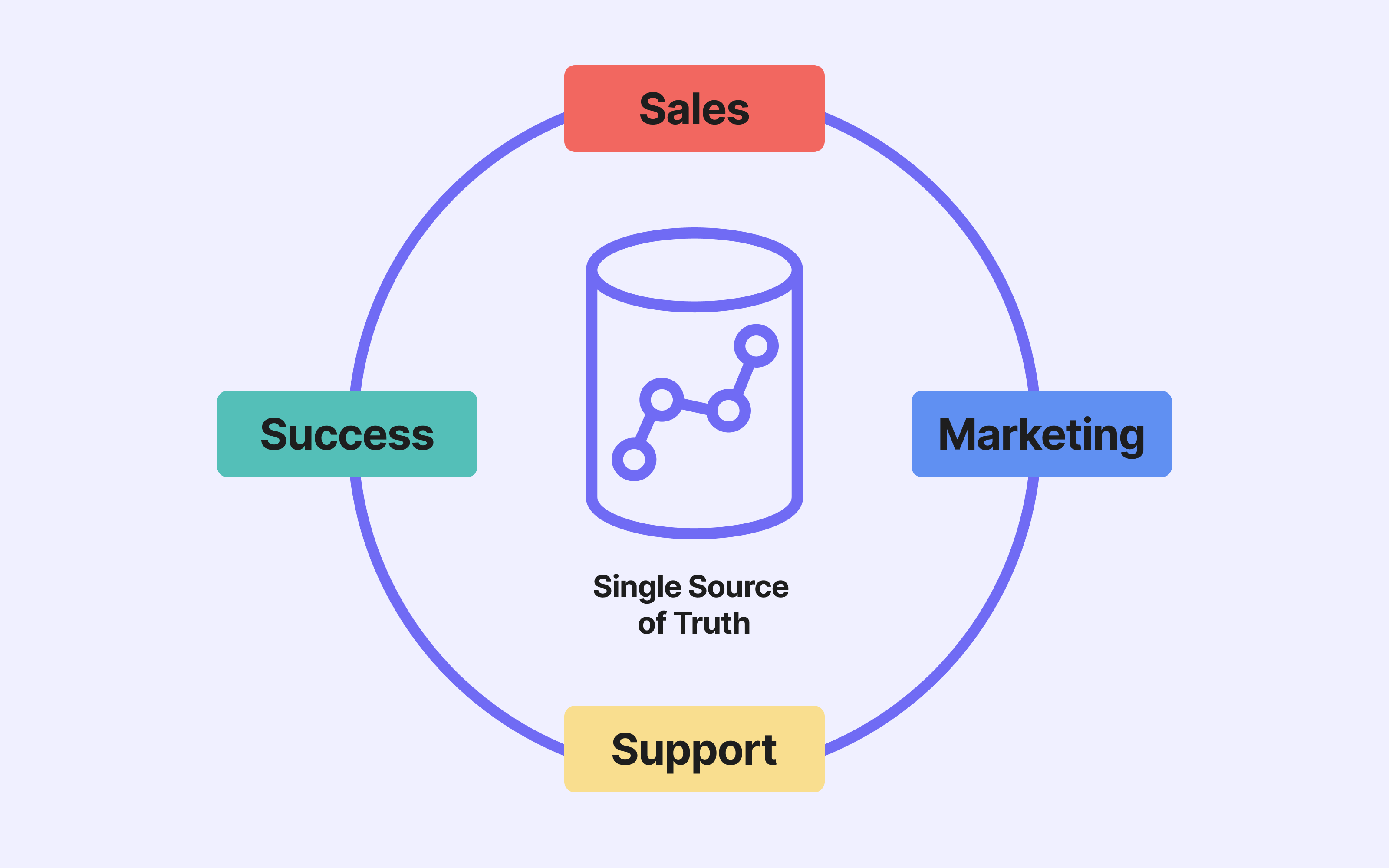
However, data taxonomy extends beyond product categorisation. It applies to all data used within a business. Here's what it might look like for an e-commerce site in general.
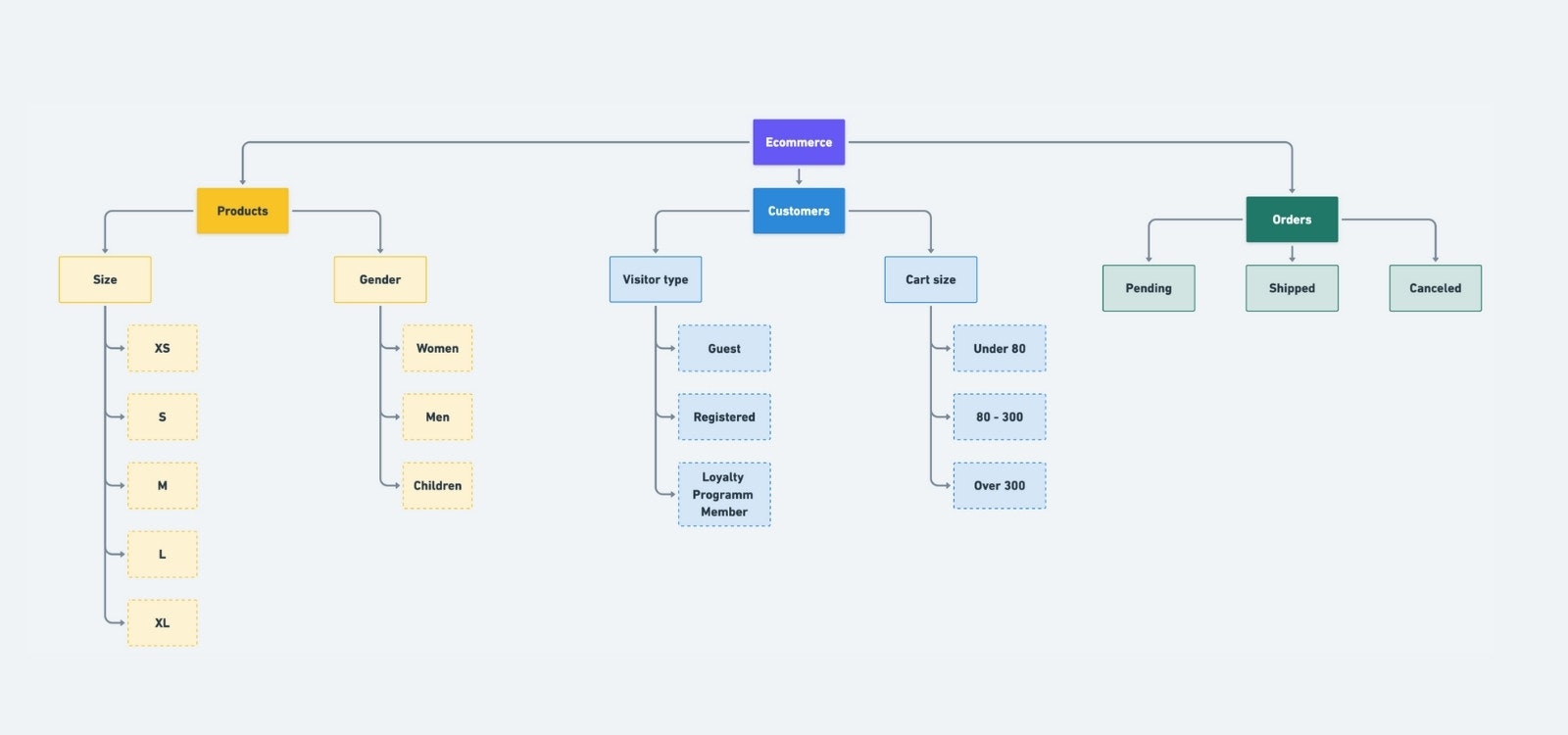
Ecommerce data taxonomy
This global approach ensures:
Consistency across company-wide data. A clear structure that makes it easier to manage and use.
More effective analysis. A well thought-out taxonomy improves insights and decision-making.
Seamless interoperability between tools, thanks to a unified reference system.
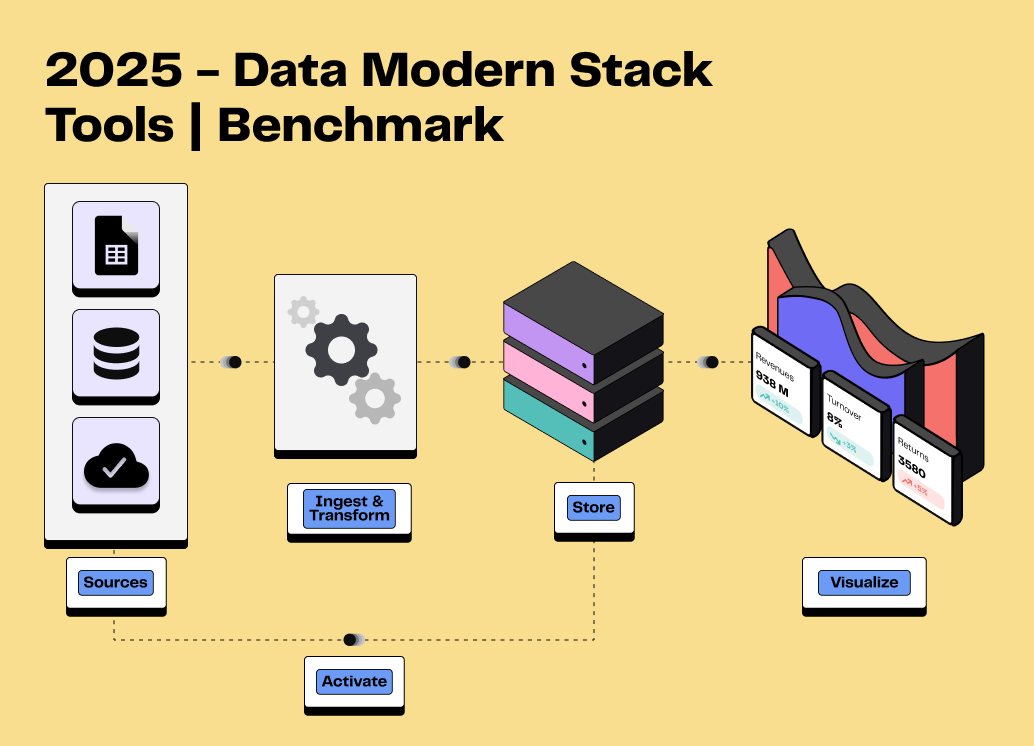
An essential component of a Modern Data Stack
A well-managed data taxonomy helps organise and classify data, ensuring it is usable and actionable. To achieve this, it is crucial to define clear categories that align with business needs. Maintaining a consistent structure across all tools and updating it regularly ensures continued effectiveness.
Key steps to implement a data taxonomy:
Define the objectives: Identify the business needs and uses of the data and the tools used;
Organise the data: Structure clear categories and adopt a coherent nomenclature. Define metadata.
Simple spreadsheet tools (Excel, Google Sheets, Airtable, Notion) or diagramming tools (Miro, Mindmeister, Whimsical, drawSQL) may be enough to design the first diagrams with different levels of depth;
Involve the teams: Work with the data, marketing and IT teams to ensure adoption.
Use appropriate tools: Facilitate management with dedicated solutions.
Data catalogue platforms such as Atlan, Alation and Castordoc enable companies to organise, explore and govern their data efficiently.
Update regularly: adapt the taxonomy to changes in the company and in regulations.
Driving business performance through taxonomy & data activation
Consumer-focused taxonomies, combined with an analysis of interactions across all marketing touchpoints, enable precise segmentation. Reverse ETL solutions can then be used to activate the customer data in the datawarehouse, targeting the right audiences and the right channels.
A well thought-out taxonomy directly improves business performance. It optimises reporting, refines marketing targeting and reduces data silos. By ensuring rigorous classification, companies gain in efficiency and maximise the impact of their marketing campaigns.
DinMo makes it easier to send the right message, at the right time, to the right place and to the right person.
FAQ
What are the key components of an effective data taxonomy?
A well-structured data taxonomy helps businesses organise and categorise information efficiently. The key components include:
Groups and categories: Data should be classified into logical taxonomies based on its use and relevance.
Metadata and attributes: Each dataset needs structured metadata to improve understanding and accessibility.
User experience focus: A good taxonomy is designed for easy search, retrieval, and analytics.
Scalability: The system should adapt to new technologies and growing customer data.
Governance and consistency: Businesses need clear rules and terms to maintain data quality.
An effective taxonomy helps businesses improve decision-making, optimise content classification, and enhance overall market insights.
How does data taxonomy improve business intelligence and decision-making?
A data taxonomy enhances business intelligence by structuring information into clear categories and groups. This makes it easier for teams to understand relationships between datasets, track market trends, and gain insights.
With a strong taxonomy, companies can:
Improve analytics: Organised data helps businesses generate accurate reports and forecasts.
Enhance customer experience: Better data structure leads to personalised user journeys and recommendations.
Optimise research and decision-making: Well-classified data supports faster, more data-driven strategies.
By using taxonomies, businesses reduce time spent searching for relevant information, ensuring that decision-makers work with the best available data.
What are the common challenges when implementing a data taxonomy?
Implementing a data taxonomy comes with challenges that impact business efficiency and customer experience. Some common issues include:
Inconsistent data structures: Different teams may use different terms and categories, causing confusion.
Lack of governance: Without proper rules and metadata management, taxonomies become outdated and inefficient.
Technology limitations: Businesses may need new platforms to integrate taxonomies across financial, customer, and product data.
Time and resources: Developing a scalable system requires investment in research, analytics, and user training.
Despite these challenges, using best practices and adopting the right technology helps businesses build a structured and reliable data system.