AARRR: The essential growth marketing framework
8min • Last updated on Mar 12, 2025

Olivier Renard
Content & SEO Manager
Have you heard of Dave McClure, Sean Ellis, or Andrew Chen? These experts are among the pioneers of growth marketing*. They laid the foundation for the growth strategies used by modern businesses.
One of their key contributions comes from Dave McClure, who conceptualised the AARRR framework during his famous 2007 conference: Startup Metrics for Pirates. A simple yet effective model designed to help companies optimise their growth.
Key Takeaways:
The AARRR framework is a fundamental pillar of growth marketing. It revolves around five key stages: Acquisition, Activation, Retention, Referral, and Revenue.
Each stage serves a specific goal—attracting, engaging, retaining, promoting, and monetising—without following a strict order. Some versions add a third "A" for Awareness (brand visibility).
Companies like Dropbox, Uber, and Airbnb have successfully applied this model to scale their businesses.
A growth marketer works across the entire customer journey, continuously testing, measuring, and analysing to improve performance. Data drives every decision.
👉🏼 Learn how the AARRR matrix works and why it is essential in growth hacking. Discover how to apply it effectively to optimise user interactions and accelerate business growth. 🚀
What is the AARRR framework?
The AARRR framework is a model used in growth marketing to measure and analyse user behaviour at different stages of their journey. It helps businesses accelerate growth using precise KPIs, known as ‘pirate metrics’.
The model is built around five key levers: Acquisition, Activation, Retention, Referral, and Revenue. It provides a structured approach to optimising the customer journey at each stage—without enforcing a rigid sequence.
Origins and development of the model
This framework was introduced in 2007 by Dave McClure, investor and founder of 500 Startups. During his Startup Metrics for Pirates conference, he presented AARRR as a simple and effective reference model to understand the five key stages of the customer lifecycle.
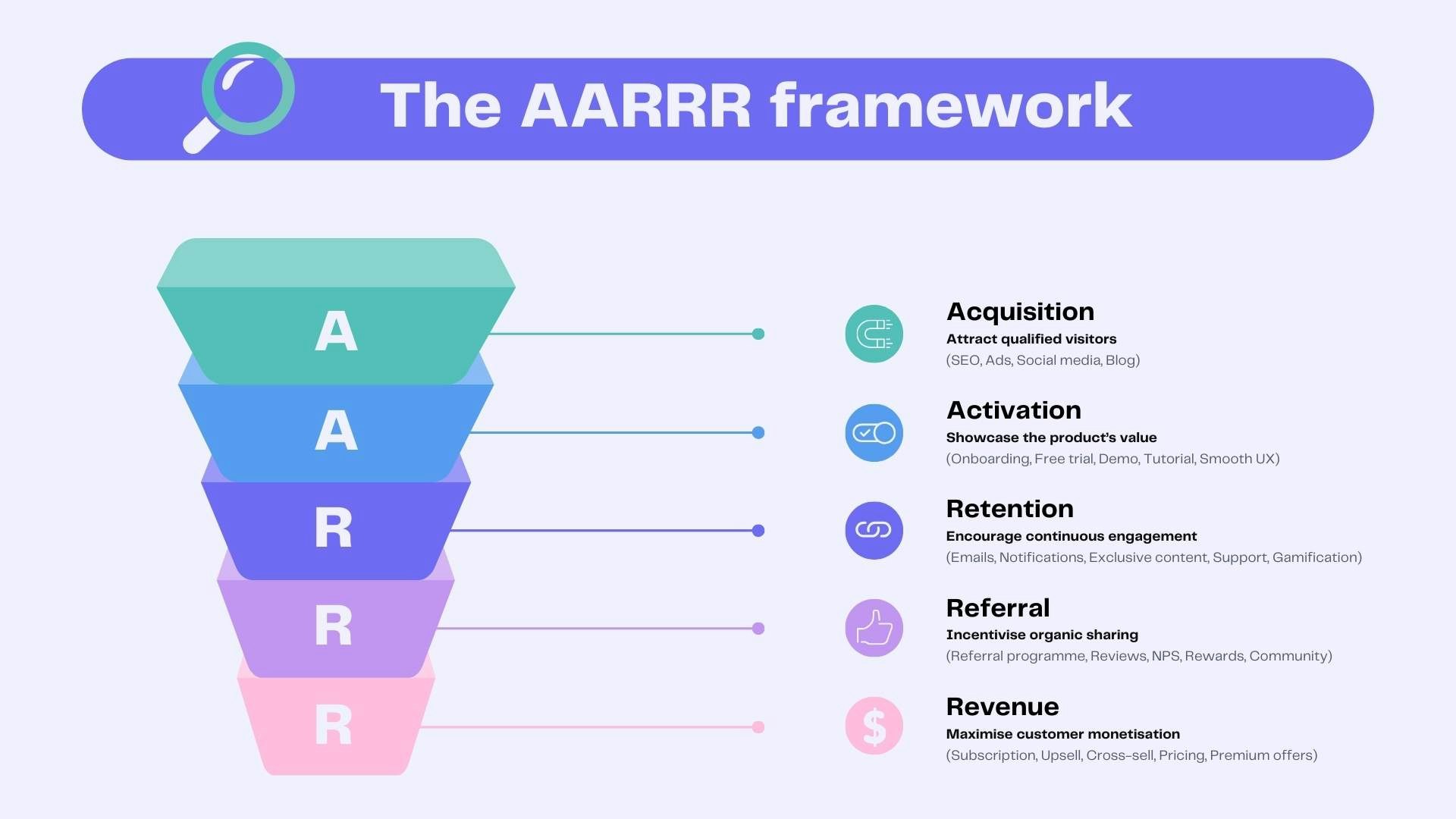
The AARRR framework
With actionable KPIs at every stage, companies can maximise their growth. AARRR focuses on data to measure, test and continuously adjust acquisition and loyalty strategies.
Why is it essential?
The AARRR framework has become a go-to model, especially for startups and SaaS companies. By analysing these five key stages, businesses can make data-driven decisions and optimise their strategies to boost revenue.
Its approach is based on:
Quantitative analysis of the customer journey, using metrics such as activation rate, customer acquisition cost (CAC), and customer lifetime value (CLV).
An iterative and experimental mindset, built on test & learn methodologies to continuously enhance performance.
A global and actionable vision, focusing not only on attracting visitors but also on maximising impact throughout the entire customer lifecycle.
The five stages
It is now common to present the AARRR framework in 6 stages, with the addition of the first ‘A’: Awareness. This lever comes into play before acquisition and aims to increase the visibility of a brand, product or service among its target audience.
Let's go back to the basics: Dave McClure's 5 Steps to Success.
Acquisition
Acquisition is about attracting potential customers and turning them into qualified visitors. Strategies vary depending on the chosen channel:
SEO & Content Marketing → To generate sustainable organic traffic.
Paid Advertising (SEA, PPC) → To reach a targeted audience quickly.
Social Media & Influencer Marketing → To engage and build a community.
Partnerships & Affiliates → To leverage credibility from industry leaders.
💡 Example: Facebook Ads campaigns using Lookalike Audiences. By analysing existing customer data, Meta identifies similar profiles and displays optimised ads, increasing the likelihood of attracting high-quality users.
At this stage, the user knows your brand but has not yet interacted with it.
Activation
This is the key stage in the framework. Attracting traffic is not enough—users must take action. Activation occurs when a user realises the product’s value—the famous 'Aha! Moment'.
It’s a phase of interaction between the brand and the user, aiming to bridge the gap between perceived value and actual experience.
Optimising onboarding: Interactive tutorials, welcome emails.
Enhancing UX: Intuitive interfaces, strong CTAs, frictionless experience.
Freemium models: Particularly effective in SaaS businesses.
💡 Examples: HubSpot simplifies CRM onboarding with tooltips to reduce friction. Dropbox offers free storage to encourage initial engagement.
Retention
An activated user does not guarantee long-term adoption. Retention measures the ability of a product to keep users engaged. Unlike loyalty programmes, retention does not always involve direct rewards.
Key levers for retention:
Customer Success & Responsive Support → To guide users.
Personalised Emails & Push Notifications → To sustain interest.
Gamification & Exclusive Content → To encourage ongoing engagement.
Limited Free Features → To drive upgrades and paid subscriptions.
💡 Examples: Netflix, which optimises its recommendations to encourage its subscribers to stay active and consume more content.
Or Google, which offers a $1.99/month subscription for 100GB when your drive is saturated. Barely the price of a coffee to keep your drive and all your files: why leave?
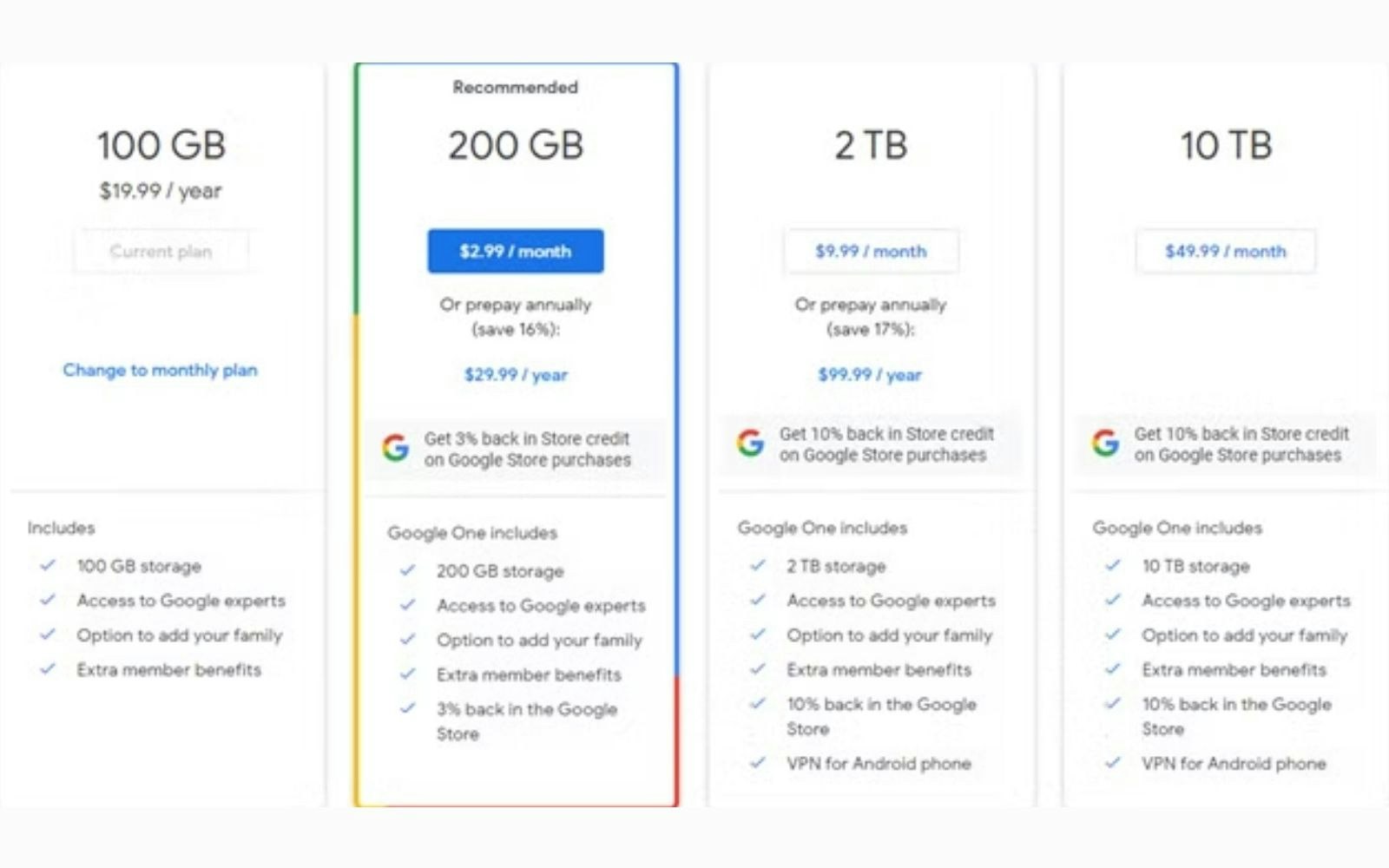
Google One Subscription (Source: Google)
Referral
A satisfied customer can become a powerful growth driver. Referral marketing leverages word-of-mouth and incentivised sharing to turn customers into brand advocates.
Referral Programmes → Rewards and bonuses for referrals.
Customer Reviews & Ratings → To strengthen credibility.
Encouraging Social Sharing → Leveraging user-generated content.
💡 Example: Dropbox exploded in growth thanks to a referral programme offering 0.5 GB of extra storage to users who invited their contacts. Or Netflix, which has made it easier for people from different households to share an account until 2023.
Revenue
A successful AARRR strategy must lead to a profitable business model. Monetisation can be achieved through:
Subscriptions and freemium models (SaaS, digital platforms)
Upsell and cross-sell to increase the average basket and customer value
Optimised pricing and paid retention strategies.
Paradoxically, no-commitment offers are very effective at retaining users, who feel free to opt out at any time.
💡 Example: Amazon optimises its Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) by offering Prime subscriptions and personalised product recommendations.
👉🏼 Enjoy McClure's presentation in Seattle in 2007 (5min).
As explained, unlike a classic funnel, these steps do not have to be taken in a precise order. The recommendation phase, for example, is highly beneficial for activating new customers.
How to measure AARRR’s effectiveness?
The AARRR framework is based on a data-driven approach: each lever must be measured precisely in order to identify what works and optimise it on an ongoing basis. To achieve this, it is essential to track relevant KPIs and use appropriate analysis tools.
Monitoring the right KPIs at every stage
Each lever in the AARRR framework relies on specific indicators to assess performance and guide action.
Acquisition: Where do users come from?
KPI → Traffic, Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC), CTR, conversion rates.
Activation: Do users experience the product’s value?
KPI → Activation rate, time-to-conversion, early engagement.
Retention: Do users return regularly?
KPI → Retention rate, churn rate, session frequency.
Referral: Do customers recommend the product?
KPI → Net Promoter Score (NPS), referral volume, social shares.
Revenue: What is user profitability?
KPI → Lifetime Value (CLV, or LTV), ARPU (Average Revenue per User), conversion rates.
Tools to analyse and optimise each lever
Measuring the performance of the AARRR framework requires solutions tailored to each need:
Analysis of traffic and user behaviour
Google Analytics: tracking traffic sources and conversions.
Matomo: open-source alternative for web tracking without compromising on confidentiality.
Microsoft Clarity: heatmaps and session recordings to analyse UX.
Product interaction and engagement tracking
Mixpanel: measurement of key user actions and activation.
Amplitude: advanced analysis of user journeys and retention.
Measuring satisfaction and recommendation
SurveyMonkey / Typeform: feedback collection and NPS calculation.
Hotjar: behavioural analysis via heatmaps and in-app surveys.
Continuous optimisation through data analysis
Tracking KPIs is not enough: the growth hacker must constantly test, analyse and adjust. A/B testing, cohort analysis and conversion funnel monitoring help to identify levers for improvement.
💡 Case in point: A SaaS company is seeing a low activation rate despite good traffic. By analysing sessions with Microsoft Clarity, it identifies friction in onboarding. By simplifying this process, the activation rate increased by 15%.
A successful AARRR strategy relies on well-defined metrics and appropriate tools. The challenge is to transform this data into actionable decisions to optimise each lever.
Thanks to its predictive attributes, DinMo's Customer Data Platform promotes growth by activating your customer data on the most effective channels.
FAQ
What is the difference between AARRR and classic funnel marketing?
The classic marketing funnel, or conversion funnel, breaks down the buying journey sequence by sequence: discovery, consideration, conversion, loyalty. More linear, it focuses on acquisition and conversion, without always incorporating recommendation.
AARRR is a more global and iterative model, structured around five key levers: Acquisition, Activation, Retention, Recommendation and Revenue. Unlike the traditional funnel, it is not a method with a strict order. It is based on data analysis and continuous optimisation.
Its aim is to optimise each user interaction to maximise the growth and monetisation of a product or service.
Can AARRR be applied outside SaaS?
Yes, the AARRR framework can be applied to many sectors beyond SaaS (Software as a Service).
In e-commerce, it optimises acquisition via SEO, activation with welcome offers and retention with targeted emails.
In media and content, it structures engagement: acquisition through social networks, activation through newsletters, retention through exclusive content and monetisation through subscriptions.
In marketplaces, it improves conversion and loyalty through personalised recommendations and referral programmes.
Although it was introduced in 2007, AARRR is a modern model that can be adapted to any business looking to attract, engage and monetise its audience.
Why is Dropbox cited as a case study in growth marketing?
Dropbox is an emblematic example of the application of the AARRR framework, thanks in particular to its viral recommendation programme. It owes part of its success to its head of marketing at the time, Sean Ellis, who is regarded as the inventor of growth hacking.
Rather than investing heavily in advertising, the company set up a simple referral system: each new user invited offered additional storage to both the referrer and the sponsored user.
This considerably reduced the customer acquisition cost (CAC) while boosting activation and retention. Dropbox quickly reached several million users, proving the effectiveness of referral marketing and organic growth based on encouraging sharing.
*Or growth hacking, although this term is less commonly used today.