What is Account-Based Marketing and why should you adopt it?
6min • Last updated on Apr 14, 2025

Olivier Renard
Content & SEO Manager
According to several reports (Gartner, Demand Gen Report), an average of 6 to 8 people are involved in a B2B purchasing decision.
Buyers are both over-solicited and better informed, primarily through digital channels. 90% ignore impersonal messages, and by the time they contact a provider, their purchasing process is often already well underway.
Personalising your approach is therefore no longer optional. It’s essential to capture attention and begin meaningful engagement with a prospect.
Key Takeaways:
Account-Based Marketing, or ABM, focuses on the most strategic accounts rather than targeting a broad audience.
It relies on highly personalised messaging and close collaboration between marketing and sales
There are several types of ABM: from ultra-personalised (one-to-one) to more scalable approaches (one-to-many).
CRM, ABM platforms, activation tools: various solutions support this marketing strategy. A CDP enables efficient segmentation and activation of clients and prospects in a data-driven approach.
👉 Discover what Account-Based Marketing is, its principles, and strategic variations. Learn how to structure your action plan and leverage the right tools to generate real business impact. 🎯
What is Account-Based Marketing?
Account-Based Marketing (ABM) is a B2B marketing approach that involves focusing efforts on a small number of high-potential accounts.
Rather than targeting a wide audience, ABM focuses solely on companies with the strongest commercial potential, improving the return on investment (ROI) of marketing actions.
This approach is built on three pillars:
Perfect synchronisation between marketing and sales teams, also known as Smarketing,
Personalised messaging for strategic clients and prospects,
Coordination of actions across the entire purchase journey.
The outcome: coordinated, targeted, and proactive campaigns that deliver better results.
How does ABM differ from other strategies?
Unlike mass campaigns, ABM does not aim for volume. Instead, it emphasises precision, relevance, and quality of customer relationships.
It is often contrasted with inbound marketing, which draws in leads through content. However, the two approaches are complementary: inbound builds awareness, while ABM focuses on converting key targets.
ABM is primarily designed for B2B, where purchase cycles are longer, involve multiple decision-makers, and warrant a targeted strategy. In contrast, B2C typically involves a single buyer and a shorter decision cycle, making other strategies more appropriate.
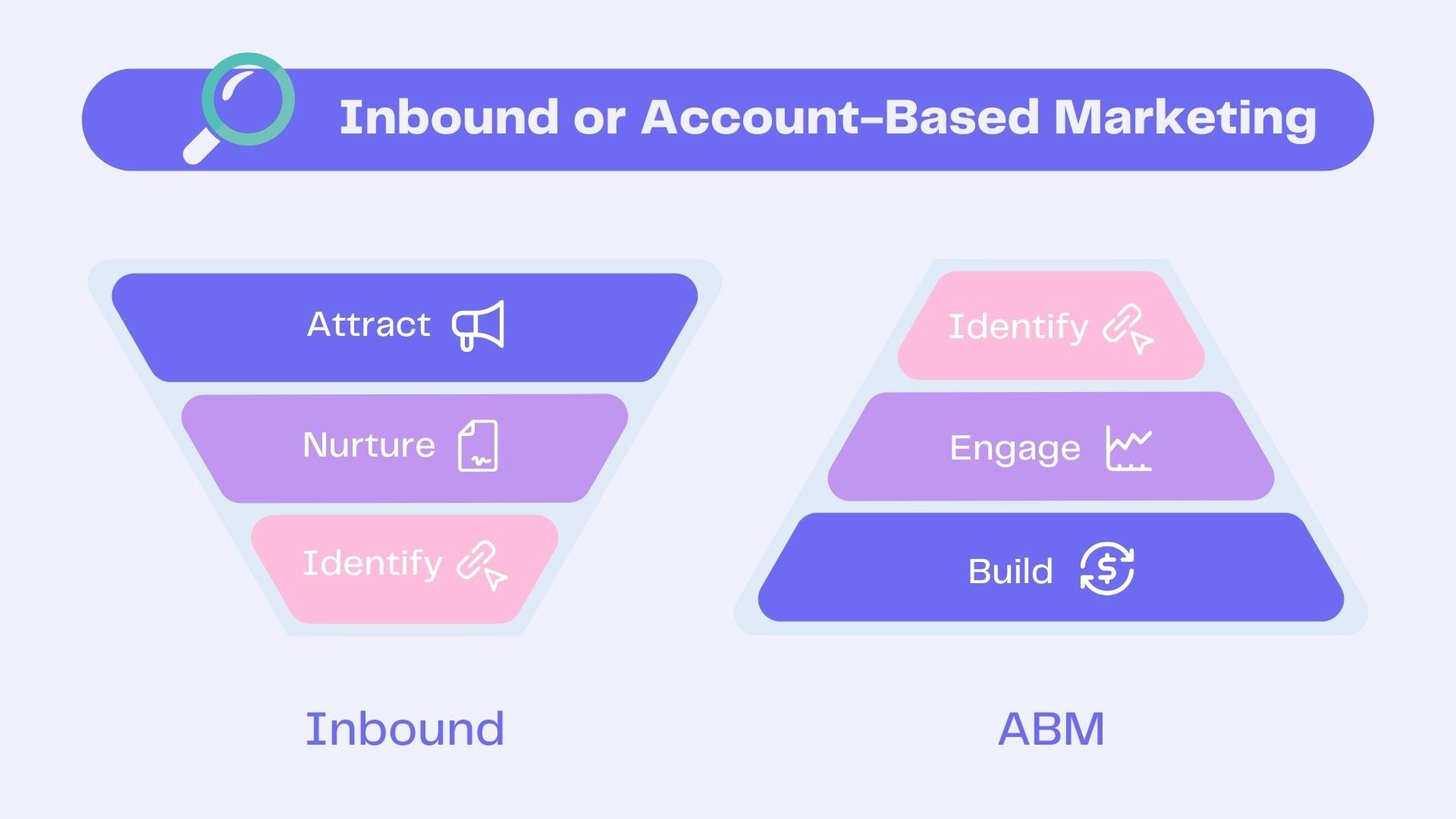
Inbound marketing & ABM
The different types of ABM
Account-Based Marketing generally falls into three levels:
ABM one-to-one, or strategic: the most personalised approach, focused on a very small number of key accounts. Each action is tailor-made, sometimes even at the individual decision-maker level.
One-to-few, or ‘lite’: campaigns target a small group of similar accounts (sector, size, potential). Content is adapted to the segment, striking a good balance between personalisation and efficiency.
One-to-many, or programmatic: a more automated, data-driven approach. It relies on broader segments with lighter personalisation, still based on account-level characteristics.
Why adopt strategic account marketing?
Account-Based Marketing is based on a simple principle: concentrate your commercial efforts on the right targets and activate them at the right time. It’s an effective way to optimise resources and deliver measurable business impact.
Optimised return on investment.
ABM targets high-potential accounts. By tailoring every action to their challenges, conversion rates increase and budget is better allocated.
Improved customer experience.
Every interaction and piece of content is designed for the specific need of a small group of prospects, resulting in more relevant messages and stronger engagement at every stage of the buying journey.
Stronger sales and marketing alignment.
Both teams work from the outset with shared objectives, enabling better coordination and consistent account management.
Shorter sales cycles.
By addressing the right stakeholders from the beginning, ABM reduces friction and speeds up decision-making, focusing effort where it matters most and saving time on prospecting.
A few examples of successful campaigns
DocuSign: tripling conversions through dynamic content
DocuSign launched a tailored ABM campaign targeting 450 strategic accounts. By using custom landing pages based on industry sector and relevant customer testimonials, they tripled their homepage click-through rate and saw a 22% increase in pipeline within the targeted sectors.
GumGum: a custom comic book to reach a decision-maker
In a more playful yet effective campaign, GumGum created a personalised comic book featuring John Legere, ex-CEO of T-Mobile, as a superhero in a Batman-style story. This ultra-targeted move opened a conversation… which led to a signed contract.

GumGum & T-Mobile (source: GumGum)
How to implement an ABM strategy?
Follow these steps to build an effective Account-Based Marketing strategy.
1️⃣ Define your ICP (Ideal Customer Profile)
Identify the profile of your ideal clients: sector, size, needs, business challenges. This helps focus on high-value accounts. The ICP represents the organisation, while the buyer persona is the individual target.
2️⃣ Select strategic accounts
Identify companies that match your ICP. Use your CRM data, internal insights, or sales intelligence tools to refine your selection.
💡 Techniques like firmographic segmentation or account scoring help prioritise the most promising accounts.
3️⃣ Align marketing and sales
ABM requires tight collaboration between teams. Objectives, messaging, contacts, channels: everything must be coordinated for smooth account management.
4️⃣ Create and distribute personalised content
This is the action phase. Tailor your messaging to the challenges of each account or segment: blog posts, social media, emails, ads, landing pages… Choose the most effective channels depending on the decision-maker's profile: email, social platforms, advertising, events.
5️⃣ Launch, measure, adjust
Track results: engagement, conversions, feedback.
Test different approaches and continuously adjust your campaigns.
KPIs to monitor
ABM uses different indicators from traditional campaigns.
Here are some strategic metrics to monitor:
Engagement rate of targeted accounts (visits, clicks, interactions)
Account coverage: how many contacts reached vs. total identified
CAC (Customer Acquisition Cost) on ABM accounts
CLV (Customer Lifetime Value) generated by targeted accounts
Pipeline variation: number of opportunities or revenue attributable to ABM.
👇

DinMo & Ankorstore | La CDP au service de la performance B2B
Which tools to use?
Various tools support ABM across the entire journey, from identifying accounts to activating campaigns.
Here's a breakdown of the main categories and the most commonly used solutions.
Tool Category | Primary objective | Main providers |
|---|---|---|
Sales intelligence tools | Identify high-potential target accounts, key contacts, and their roles. | LinkedIn Sales Navigator, Cognism, ZoomInfo |
CRM & outreach | Manage relationships and coordinate teams | HubSpot, Salesforce, Lemlist, Apollo |
Personalisation & A/B testing tools | Tailor the user experience and test content variations | Optimizely, AB Tasty, VWO |
Analytics & measurement | Track engagement and measure performance | Google Analytics, Mixpanel, Dreamdata |
Dedicated ABM platforms | Orchestrate and automate ABM campaigns | 6sense, Demandbase, RollWorks |
CDP & activation tools | Unify, segment, and activate data | DinMo, Segment, mParticle |
The main solutions for ABM
Modern selling and social selling
These two concepts are closely linked with Account-Based Marketing.
Modern selling refers to contemporary sales practices based on data, digital tools, and a customer-centric approach.
Key pillars:
Synergy between sales and marketing teams
Use of digital tools (CRM, sales intelligence, engagement platforms…)
Personalisation based on purchasing behaviour
Integration of social selling and content into the sales cycle
👉 It addresses the increasing complexity of B2B purchasing decisions, with better-informed, more autonomous buyers.
As you can see, social selling is a component of modern selling. It involves using social networks (especially LinkedIn) to:
Identify and approach prospects
Build trust
Share relevant content
Guide buyer decision-making early on
👉 Social selling is relational and gradual, built on the seller’s visibility and credibility.
The role of a CDP
One-to-many Account-Based Marketing is based on data and automation.
A Customer Data Platform (CDP) is the ideal tool for collecting, enriching, segmenting, and activating data from multiple sources. It enables the creation of dynamic segments to launch targeted marketing campaigns, even across large volumes of accounts.
It is a key solution for deploying an effective ABM strategy at scale.
Conclusion
Account-Based Marketing is a modern B2B marketing approach designed for today’s more complex, digital, and collaborative purchasing behaviours.
By focusing on high-potential accounts, you improve campaign relevance, align your marketing and sales teams, and maximise return on investment.
With the right combination of data, personalisation, and tools (CRM, ABM platforms, Customer Data Platform), you can move from mass communication to a targeted, coordinated and high-performing approach.
👉 DinMo helps you fully harness the power of your data. Create dynamic segments and activate your campaigns across the right channels, all in complete autonomy.
How does ABM differ from traditional and inbound marketing?
How does ABM differ from traditional and inbound marketing?
Account-Based Marketing (ABM) stands out from more conventional approaches through its highly targeted logic. Traditional marketing aims to reach a broad audience, while inbound marketing seeks to attract leads through valuable content.
In contrast, ABM begins by identifying strategic accounts, then builds tailored campaigns for each specific company or target group. The goal is not to generate volume, but to engage the right decision-makers with the right messages.
This strategy is particularly well suited to B2B contexts, where sales cycles are long and decisions are made by multiple stakeholders. ABM and inbound marketing are not mutually exclusive—they can be combined as part of a comprehensive strategy
When is the right time to implement an ABM strategy?
When is the right time to implement an ABM strategy?
ABM becomes relevant when your business wants to focus efforts on high-value accounts. It’s an ideal strategy for B2B companies dealing with complex buying cycles, multiple decision-makers, and high average order values.
It is especially useful when traditional prospecting fails to generate new opportunities or when sales teams want to concentrate on specific, high-potential accounts.
Before launching, make sure you have a clearly defined ICP (Ideal Customer Profile), sufficient resources to produce tailored content, and strong coordination between sales and marketing.
How do you choose the right target accounts?
How do you choose the right target accounts?
Building a list of target accounts is a critical step in any ABM strategy. Start by defining your ICP: the type of company that best matches your product or service.
Use objective criteria such as sector, company size, revenue, digital maturity, and technologies in use. Leverage your CRM data, sales intelligence tools, or intent data to identify the most promising accounts.
You can also implement a scoring model to prioritise accounts based on potential and engagement level. The more rigorous your selection process, the more effective your actions will be.
What role does data play in an effective ABM strategy?
What role does data play in an effective ABM strategy?
Data is the foundation of any successful ABM strategy. It helps you identify the most relevant accounts, understand customer needs, and personalise messaging with precision.
Firmographic and behavioural data, along with insights from your CRM, allow you to build targeted segments and tailor your approach to each company. A Customer Data Platform (CDP) enables marketers to centralise this information, track engagement signals, and activate campaigns across the right channels.
Without a reliable data foundation, ABM loses its relevance and impact. Smart use of data is what separates a generic campaign from one that drives real success.