Marketing strategy: definition, methods
10min • Last updated on Nov 28, 2025

Alexandra Augusti
Chief of Staff
Consumers are overwhelmed by advertising messages throughout the day, through various media and marketing campaigns, being exposed to around 1,200 daily advertising stimuli.
In a highly competitive environment, creating a strategic marketing approach and a well-defined plan is essential for any organization wishing to stand out and achieve its objectives.
A well-crafted marketing strategy equips a company with a deep understanding of its market, the ability to effectively target its customers, and the capacity to highlight its products or services persuasively through effective communication and tailored content. As always in marketing, the goal is to reach the right person, at the right time, with the right message, even in a saturated advertising context.
So, what are the essential steps and tools for formulating a marketing strategy?
In this comprehensive guide, we explore what a marketing strategy is, the various applicable strategies and models, and outline the key steps in building one, incorporating an effective communication and content plan.
What is an effective marketing strategy?
A marketing strategy is a detailed action plan defined by a company to achieve its business and marketing goals in the medium and long term, integrating distribution and digital strategies.
This strategic approach aims to optimize the marketing and distribution of the entity's products or services by using various marketing tools to precisely meet the needs of its target customers.
Founded on key principles such as pricing positioning, product/service features, market requirements, communication strategies, and competitive positioning, the marketing strategy seeks to optimize the alignment between the company's offering and the specific demand of its target market.
The objectives of a marketing strategy
The main objectives of a marketing strategy are varied and cover several key aspects of the company's market positioning. In general, an effective marketing strategy aims to effectively reach the target audience:
Increase the company’s visibility and awareness: The marketing and communication strategy strives to place the company in the spotlight, thereby increasing its recognition in the market through various media and campaigns.
Strengthen brand image: Beyond visibility, a clear value proposition combined with targeted marketing strategies will help reinforce the brand's image in the market.
Meet the expectations of targeted consumer segments: Aligning its offering with the desires and expectations of targeted market segments is essential, involving a detailed analysis of consumer behavior and market trends.
Position its offering against the competition: The marketing strategy aims to highlight what makes the offering unique, with the goal of convincing prospects of the superiority of your offering and prompting them to purchase.
Explore new horizons: An innovative marketing strategy can also propel the company into new markets, whether through geographical expansion or reaching new customer segments.
Another often overlooked but essential aspect of a marketing strategy is the ongoing analysis of competitors using appropriate communication and data collection tools. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of your competitors provides a solid foundation for developing your own unique and differential positioning.
With the rapid evolution of technologies, marketing strategies must adapt to incorporate digital approaches. This includes leveraging digital platforms and social media to maximize visibility and engagement across all online marketing channels.
The different types of marketing strategies
There are different types of marketing strategies and models that are important to define before embarking on your own strategy.
A common mistake is the lack of a clear marketing strategy and the multiplication of actions across various channels and social media without any coherence.
A company without a well-defined and adapted marketing strategy may struggle to stand out. Consumers and the public may then have difficulty positioning their offering against the competition.
Well-chosen marketing strategies, often based on Michael Porter's theories and using analytical tools, offer methodical frameworks that enable companies to navigate easily in a highly competitive environment.
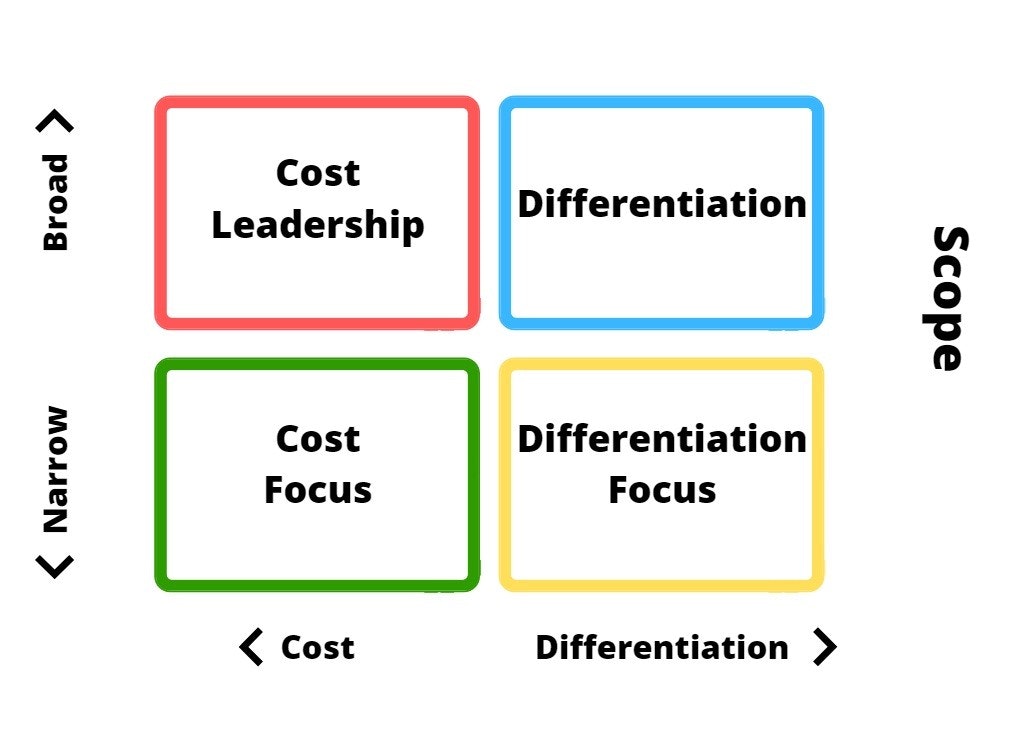
Cost leadership strategy
The cost leadership strategy aims to offer the lowest prices on the market. This approach often requires massive sales volumes to become profitable, optimize distribution, and maintain the attractiveness of the offering. This strategy is most effective when your customer base is broad.
Several factors allow a similar offering at a lower cost: economies of scale due to high sales volumes, exclusive access to certain raw materials, the use of cutting-edge digital technologies, or more efficient production processes than competitors. In this context, it is crucial to monitor cost fluctuations using management tools to avoid selling at a loss.
This strategy is ideal for low-cost offers. However, maintaining a certain level of quality is essential to retain loyal customers.
💡Focus - Penetration strategy:
It is worth noting that a cost leadership strategy can also be effective when entering a market, as competitive pricing is often attractive to a broad audience. The goal is to quickly strengthen the company’s position against the competition through effective marketing campaigns.
Designed to quickly saturate the market through attractive prices, efficient distribution, and targeted promotional campaigns, this strategy often involves significant promotions. It is particularly suited for a company looking to establish itself quickly and gain market share at the expense of established competitors.
However, it is important to remember that if profitability goals are not achieved, this strategy cannot be sustained in the long term.
To ensure successful market penetration, several companies announce their innovations with a differentiation or niche strategy using marketing communication campaigns to stand out, often emphasizing what makes their product innovative or exclusive. This demonstrates the company’s ability to offer a value proposition that attracts and retains consumer attention.
Network marketing (MLM) can also be a powerful lever in market penetration strategies, thanks to its model based on recommendation and proximity. By mobilising a network of ambassadors, companies can quickly reach a wider audience that is difficult to reach via traditional channels when launching an offer.
This model encourages the creation of a relationship of trust, thanks to recommendations from peers. This strategy also allows for rapid and direct customer feedback, while reducing the initial costs associated with massive advertising campaigns.
Differentiation strategy
As previously mentioned, the differentiation strategy applies ideally when the target audience is broad. It is also suitable when the offering is diverse, with a wide range of products or services tailored to different public segments and supported by varied marketing content.
In this marketing strategy, the goal is to focus on the quality of the products and services offered, as well as effective communication, to stand out from the competition. The aim is to differentiate by offering a unique aspect in the sector.
To succeed in your differentiation strategy, first identify the attributes specific to your company. These can be features, functionalities, additional services, or exclusive pricing systems that, thanks to appropriate marketing tools, allow the company to position itself uniquely in the market.
There are two types of differentiation strategies depending on the model used:
Differentiation through premium: The company then offers a richer offering (additional features, added services, etc.) and of higher quality than its competitors. By uniquely meeting the consumer's needs through refined communication, this strategy often allows for setting a higher price, as customers are willing to pay more for perceived added value.
Differentiation through cost: The company offers a less comprehensive offering, but at a lower price. This can appeal to various consumers, as it allows them to only pay for what they actually consume.
With this strategy, the company’s goal is both to create and maintain its competitive advantage through effective marketing tools, while making it harder for competitors to emerge.
Focus strategy
Unlike the two previous strategies, the focus strategy (also called niche or specialization strategy) is recommended for a narrow target market. It targets a specific, unique market segment and requires a focused offering and a distinct competitive advantage, based either on differentiation or cost, supported by targeted communication campaigns.
This strategy requires a strong competitive advantage, particularly in terms of cost or product specifics, reinforced by effective communication tools, which must be preserved and strengthened to remain competitive.
It offers the advantage of a deep understanding of the product, market, customers, and the expectations and preferences of the targeted segment.
However, this strategy carries the risk of strong dependency on a limited market, which can be risky with changes or shifts in consumer preferences. Moreover, the arrival of new players in the market can significantly impact the company’s performance and its marketing communication campaigns.
How to build your marketing strategy?
The marketing plan must be structured to avoid carrying out actions without coherence. A clear methodological approach, using appropriate tools, clarifies the company’s positioning with its target, thereby ensuring an increased conversion rate.
Here are the main steps for creating an effective marketing strategy:
Step 1: Market analysis
Starting a marketing strategy requires a solid understanding of the market, competitive offerings, and the needs and expectations of your target customers, using appropriate analysis tools.
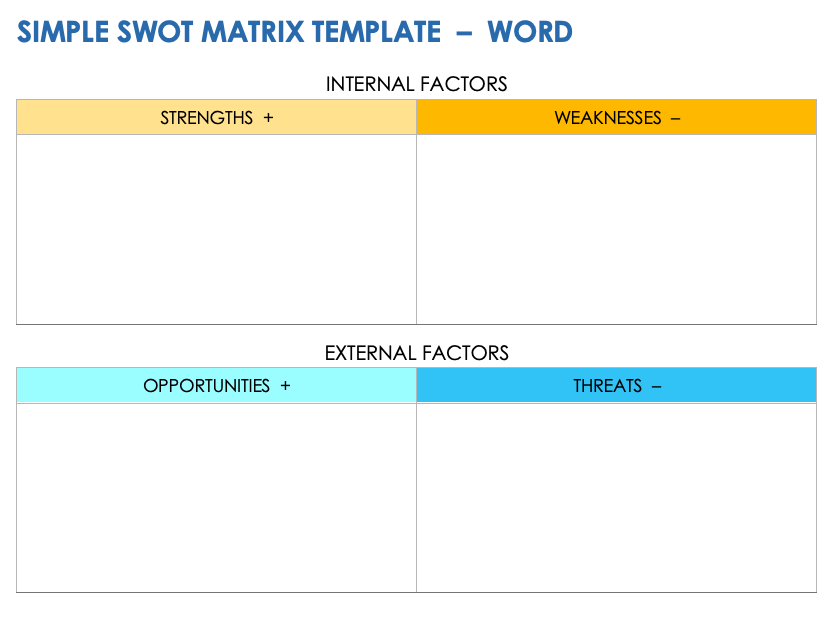
The SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) is an essential marketing tool to conduct a market study, revealing the company’s strengths and weaknesses while highlighting market opportunities.
This tool also highlights the external threats identified in the PESTEL matrix (socio-economic context, legislation, etc.) that the company may face. This type of analysis provides a solid foundation for strengthening your advantages and mitigating your weaknesses.
Step 2: Defining your objectives
With the market analysis done, the next step is to set clear marketing objectives aligned with your overall strategy. These desired results are the core of any successful strategic plan.
The objectives should be set following the SMART method (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Realistic, Time-bound), ensuring that each goal is clear, quantifiable, attainable, relevant, and time-limited. Thus, a well-defined objective would be to "increase your sales by 15% over the next six months through targeted marketing campaigns."
Step 3: Customer segmentation
Determining who your target audience is and segmenting your audience is a major prerequisite:
Who are we targeting?
How do we communicate effectively with the target audience?
Which product/service should be highlighted?
The idea of segmenting your market into audiences sharing similar desires and needs facilitates not only the personalization of marketing actions but also ensures a more precise product-customer alignment. To target the audience, it is essential to gather people with similar behaviors. Even if the product sold can be the same (for example, a t-shirt), the sales arguments, based on personalized content, will not be the same for each segment.
Each target can be translated into a persona, which reflects the
specific characteristics of the person, their needs, desires, preferred means of communication, etc., using appropriate segmentation and content creation tools.
Step 4: Positioning the offering
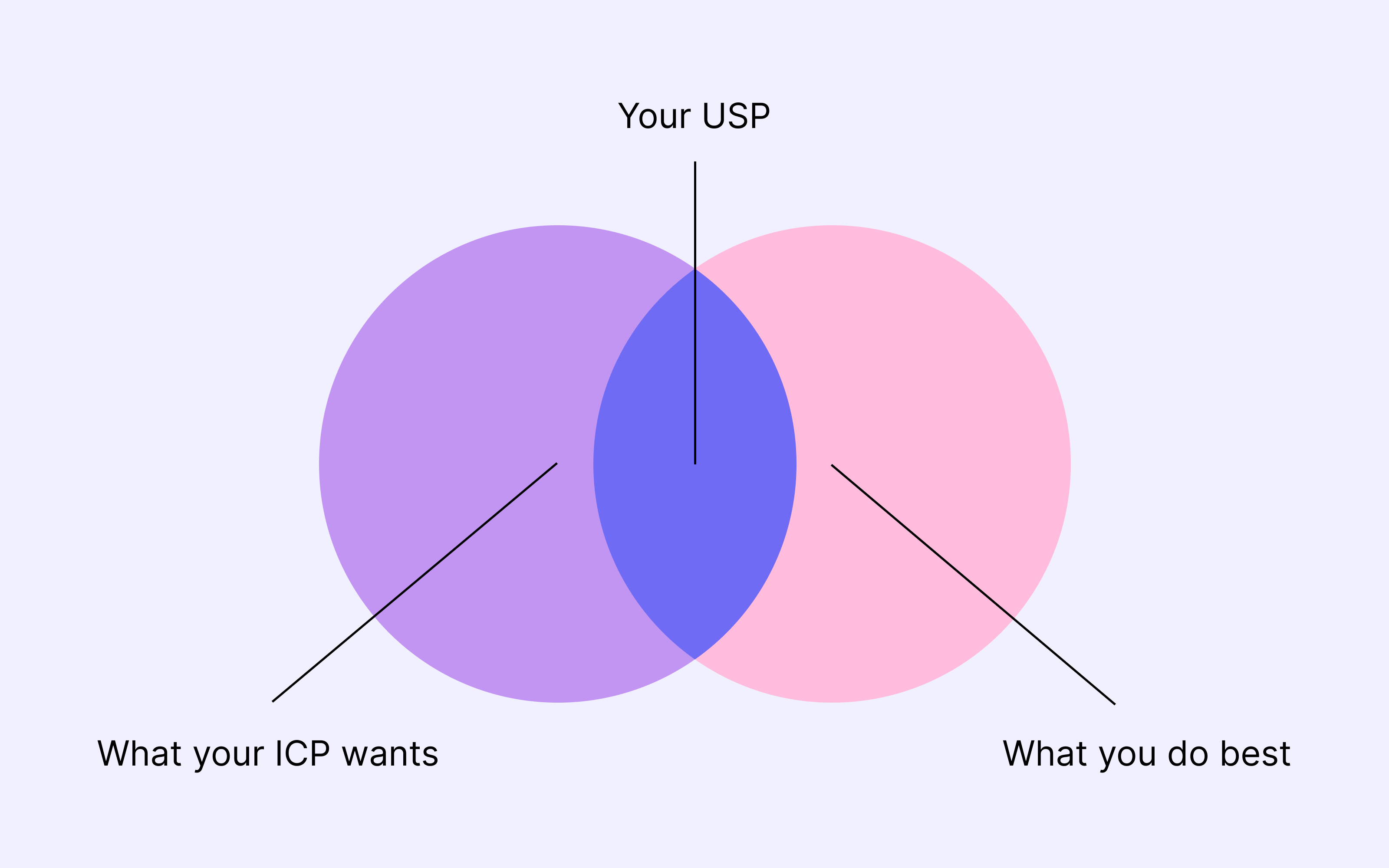
Positioning your offering means defining how it will be perceived by your target customers and how it surpasses the competition. Developing a Unique Selling Proposition (also known as Unique Value Proposition, UVP) is critical in this process, requiring clear communication and relevant marketing content. The UVP should highlight what makes your offer uniquely desirable, whether through its quality, innovation, or customer support, thus leaving your mark on the market.
Good marketing positioning should be explicit, distinct from the competition, and fit within a given context.
Step 5: Action plan and Marketing Mix
The marketing mix is a marketing concept initially represented by the "4Ps":
Product
Price
Place (distribution)
Promotion.
These are the four pillars on which a marketing strategy has historically been based.
The product corresponds to what is offered to consumers, including its features, design, and benefits. The price refers to the pricing policy adopted, which must take into account customers' value perception and competition.
Place, or distribution, concerns the channels used to make the product available to consumers, whether physical or online. Finally, promotion encompasses all communication and advertising actions, including content creation, aimed at making the product known and stimulating demand. Coherent management of these four elements, with the help of appropriate marketing tools, allows companies to optimize their offering and better meet market needs.
Today, we speak of the 7Ps of Porter. The 7Ps of the marketing mix extend the traditional model by adding three elements: People, Process, and Physical evidence.
People refers to all those who interact with customers through various communication channels, influencing their experience.
Process refers to internal procedures and workflows that ensure effective service delivery, while Physical evidence includes any tangible element that reassures the customer about quality, such as store layout, customer testimonials, or online proof elements.
Step 6: Measuring results and adjustments
Your marketing strategy, far from being static, must evolve in response to market feedback. This means evaluating the overall performance of the deployed strategy using analytical tools, analyzing customer and competitive data, and making necessary adjustments. It is essential to track top KPIs to understand the evolution of the impacts of the marketing actions, including communication and digital initiatives, put in place.
This constant adaptation ensures the continued relevance and strategic strength of your marketing approach.
Marketing strategy trends
Today, customers most often discover a business by surfing the web and social media. Hence the importance of digital marketing!
Digital marketing encompasses all the techniques and tools used on digital platforms and channels such as the web, social media, and content creation.
Digital marketing strategies cover various dimensions, including social media publishing, banner creation, display advertising campaigns, search engine optimization (SEO), inbound marketing strategies, content strategy, etc.
Companies today are required to consider offering online sales opportunities or customer journeys that begin online and continue in-store, thereby optimizing their distribution and services.
In a fully digital approach, social media is now a preferred tool to build a strong relationship with consumers, thanks to simplified exchanges, discussions, and dedicated content campaigns.
Conclusion
In short, developing a comprehensive marketing strategy is a key pillar for the success of any business. This strategy makes it easier to implement actions.
It must include an in-depth market analysis using appropriate tools, SMART goal setting, precise identification of the target audience, strategic positioning of the offering, the design of the marketing mix, and ongoing adjustments based on market feedback, including digital communication and content aspects.
To optimize the implementation of each component, DinMo offers several resources and tools. Whether it’s for customer segmentation, data activation, content creation, or detailed result analysis, DinMo is your ally in continually building and adapting a robust and effective marketing strategy.