Retargeting vs Remarketing: Differences and use cases
6min • Last updated on Nov 17, 2025

Alexandra Augusti
Chief of Staff
Retargeting and remarketing are two marketing techniques widely used by most businesses. Although these terms are often used to refer to the same concepts, there are essential differences between the two approaches.
Key Takeaways:
Retargeting relies on browsing data (cookies, pixels, server-side signals) to target anonymous visitors again on Google Ads, Meta, TikTok or other networks.
Remarketing uses first-party, identified data (email, CRM, CDP) to re-engage existing contacts with personalised messages.
A composable CDP unifies these datasets, builds reliable segments and simplifies activation across all channels to maximise performance.
👉🏼 This article aims to clarify these notions to help you better choose between these data activation use cases according to your marketing objectives.
The main differences between retargeting and remarketing
Retargeting and remarketing are two techniques used to convert potential buyers into new customers. Their main objective is to increase the company’s overall revenue.
💡 While retargeting focuses on people (prospects or existing customers) who have recently shown interest in your brand, remarketing focuses on your existing customers based on their level of engagement.
A definition of retargeting
Retargeting focuses on targeting individuals who have already shown interest in your brand but have not yet completed a purchase. It is aimed at those who visited your website, added items to their basket without checking out, or engaged with your content without converting.
In short, retargeting aims to remind these users of their initial attraction to your offers, mainly through online advertisements (social media campaigns, display ads, etc.).
In a multichannel approach, retargeting aims to turn prospects into buyers by encouraging them to return to your website and complete their purchase.
A definition of remarketing
Conversely, remarketing focuses on rekindling the interest of existing customers, especially those who are disengaging or have become inactive. This method relies on direct channels (emails, push notifications or newsletters) to re-engage customers.
The aim is to encourage them to make new purchases or increase their level of interaction with the brand.
The ultimate goal of remarketing is to increase the customer lifetime value (CLV, or LTV) by strengthening relationships with those already within the customer base.
Note that if a prospect has given you their email address, you can still try to include them in remarketing campaigns. However, you must ensure a different message between your existing customers and your qualified leads.
How to implement retargeting or remarketing campaigns?
Retargeting and remarketing strategies require methodical execution to be effective. Their performance depends on the quality of your customer data and how you use it. If your data is incomplete or difficult to leverage, your campaigns will inevitably face limitations.
Let’s look at how to roll out these tactics, step by step.
Data Collection : Before thinking about using your data, you first need to collect it. This step involves gathering valuable data on user interactions with your site and offers.
This collection can range from page visits and product selections to purchases and engagements with your marketing content. We recommend gatherind all the data that could be useful one day in your marketing campaigns.
Data Centralisation : To manage your strategies with precision, this information must be centralised in a single source of truth — typically a data warehouse or a Customer Data Platform (CDP).
The current trend is to turn towards composable Customer Data Platforms based on data warehouses.
Data Activation : Once the data is centralised, it should be made usable in marketing tools (CRM, marketing automation, advertising platforms, etc.). Here again, CDP solutions can be used to automate data flows.
Using Data for Marketing Strategies : Using this data is necessary to set up retargeting campaigns on social networks, using transferred contact lists.
For remarketing, this includes using personalised emails, newsletters, and other forms of direct communication to revive interest in your existing clientele.
💡 By mastering these steps, you ensure that your retargeting and remarketing efforts are both relevant and highly effective, providing you with a better opportunity of driving conversions and securing long-term customer engagement.
Concrete use cases of retargeting
Retargeting after visiting a website
One of the most common uses of retargeting is to recapture prospects who have visited your website without converting. This is particularly important for individuals who have added items to their cart without completing the purchase.
Retargeting then comes into play, targeting these users with specific ads that remind them of the forgotten items, encouraging them to return to the site to complete their order.
Dynamic advertising based on browsing history
Another relevant retargeting strategy relies on dynamic advertising. This method aims to display highly personalised ads to users, aligned with the products they have already viewed on your website.
So, if a user has visited a specific product page, they will be shown ads for that same product while browsing other websites.
Different retargeting tactics can be deployed through various tools on advertising platforms, including Pixels, custom audiences, or Conversion APIs.
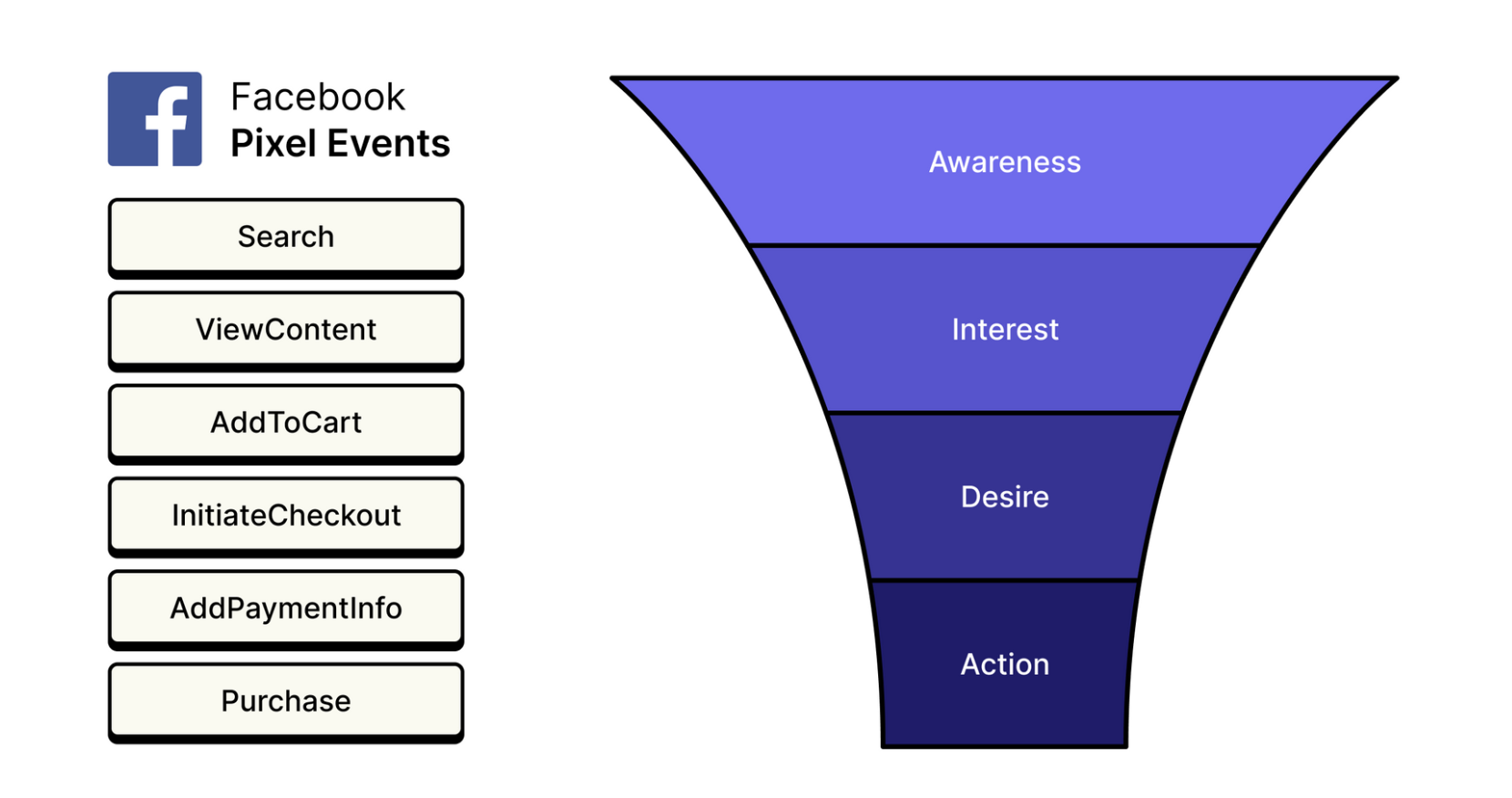
Most valuable conversions are at the bottom of the funnel
By leveraging these technologies, you can design precise and personalised retargeting campaigns that will improve your conversion rate and return on investment (ROI).
Concrete use cases of remarketing
Remarketing plays a key role in re-engaging customers and increasing their value throughout their journey with your brand.
Upsell campaigns
A classic use case for remarketing is upsell campaigns, where customers are encouraged to opt for higher-value offers. This strategy increases the average transaction value by offering complementary products/services or more advanced versions.
You can, for example, offer a free trial of your Premium offer for 7 days, so the customer can compare the two offers for themselves. If they see value, it's highly likely they'll keep this premium version after the trial period!

Cross selling vs. up selling
Loyalty campaigns
Loyalty campaigns aim to strengthen relationships with your current customers and build long-term engagement with your brand. They typically take the form of special promotions, discounts, loyalty points or exclusive benefits for regular customers.
The ultimate goal is to increase customer lifetime value and encourage repeat purchases.
Reactivation campaigns
Targeting inactive customers, reactivation campaigns or "win-back campaigns", are another key use case. Through personalised emails, push notifications, or SMS messages, these campaigns aim to remind customers of the attractiveness of your offer.
Special deals, promotions or reminders of past purchases are among the key techniques used to encourage a return to buying.
These remarketing methods are indispensable for maintaining a lasting relationship with your customers, boosting sales, and increasing customer loyalty - essential pillars for the long-term success of your business.
Conclusion
In today's competitive environment, retargeting and remarketing strategies are essential for increasing conversions and strengthening relationships with your customers. Retargeting focuses on prospects who have expressed interest but have not completed a purchase, while remarketing targets current customers to encourage loyalty and repeat purchases.
To implement these strategies effectively, collecting, centralising and activating customer data through the right tools is essential.
As one of the leading Customer Data Platforms (CDPs) on the market, DinMo greatly simplifies the implementation of such strategies. With DinMo, you can segment your customer base, create precise audiences and seamlessly push them into your marketing tools — all without any technical expertise!
If you want to know more about our offers and product, please don't hesitate to contact us.