Customer Journey Map: a strategic tool for better experiences
10min • Last updated on Dec 19, 2025

Alexandra Augusti
Chief of Staff
63% of customers believe that the best brands exceed their expectations at every stage of the customer journey (Wunderman). Customer loyalty is a major driver of profitability for companies.
Talking about the customer journey means analysing every interaction between your customers and your brand, product or service. This understanding is essential for marketing and customer relationship management.
Key facts:
The customer journey encompasses all the interactions between a company and its customers, from product discovery through to customer loyalty.
A Customer Journey Map (CJM) enables these exchanges to be visualised, so that expectations can be better understood and the customer experience optimised at every stage.
Creating an effective mapping involves identifying key contact points, analysing behaviour and adjusting marketing strategies.
A CDP (Customer Data Platform) centralises and exploits these insights to personalise communication and improve the experience thanks to data.
👉🏼 Discover the customer journey and its main stages. Learn how to harness and activate customer data to optimise the experience at every touchpoint and boost your sales performance. 🚀
What is the customer journey?
Short definition of the customer journey
The customer journey covers all the phases a customer goes through - from initial discovery to recommendation. It also includes the use of the product or service, after-sales service and recommendations.
💡 It is important to note the distinction between the customer journey and the customer experience, even though these two concepts are closely linked.
While the customer journey focuses on the tangible sequence of points of contact with the company, the customer experience looks more at the customer's perception and emotions in relation to these interactions.
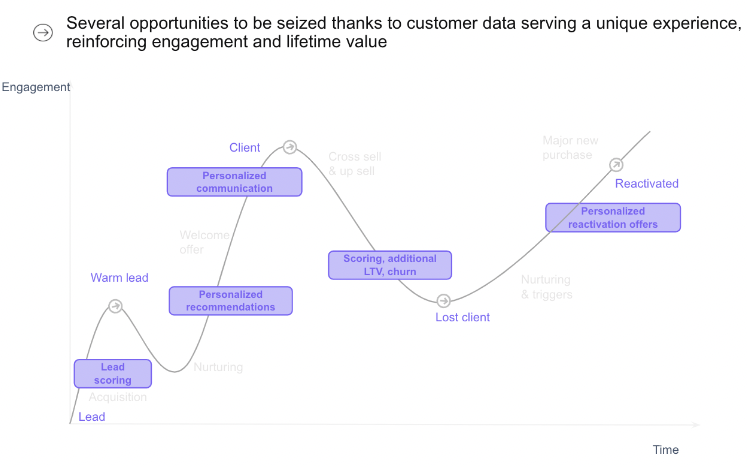
What are the stages of a customer journey?
The customer journey is segmented into several distinct stages, each representing a critical phase in the customer's interaction with a brand. Here’s a detailed look at each of these stages:
1: Awareness
The awareness phase is the initial phase of the customer journey, where potential customers become aware of a brand, product, or service. This can occur passively through advertisements or actively when a customer is searching for a solution to a problem.
At this stage, the goal is to capture the attention of the target audience and build brand recognition. Marketing strategies such as social media campaigns, SEO, and paid media are often employed to increase brand exposure and trust.
2: Consideration
In the consideration phase, the customer has become aware of the brand and is now evaluating various options to meet their needs.
Here, customers conduct research, compare features and prices, and seek out reviews and recommendations from others. The focus at this stage is to provide valuable information that helps customers make informed decisions. This can include engaging content on the company's website, social media interactions, and interactions with the sales team.
3: Conversion / Purchase
The conversion or purchase stage is the point at which the customer has gathered all the necessary information and makes the decision to buy.
This stage is pivotal as it involves the actual transaction. To facilitate this step, businesses use clear and compelling call-to-actions, personalised retargeting ads, and sometimes offer limited-time discounts or promotions to motivate the customer to make the purchase.
4: Retention
After the purchase, the customer enters the retention phase.
Here, the focus shifts from acquiring new customers to retaining existing ones. The goal is to leave a lasting, positive impression and encourage repeat purchases.
This involves offering best-in-class customer support, proactive follow-up communications with tailored offers, and rewards for loyalty. Effective retention strategies help in building long-term relationships with customers.
5: Advocacy
The final step of the customer journey is the advocacy stage. At this point, satisfied customers become loyal advocates who not only continue to purchase from the brand but also recommend it to others.
To foster advocacy, businesses can introduce referral programs, leverage user-generated content, create community spaces for customer engagement, and recognise and celebrate their advocates. This stage is highly valuable as it drives word-of-mouth marketing and can significantly impact brand reputation and growth.
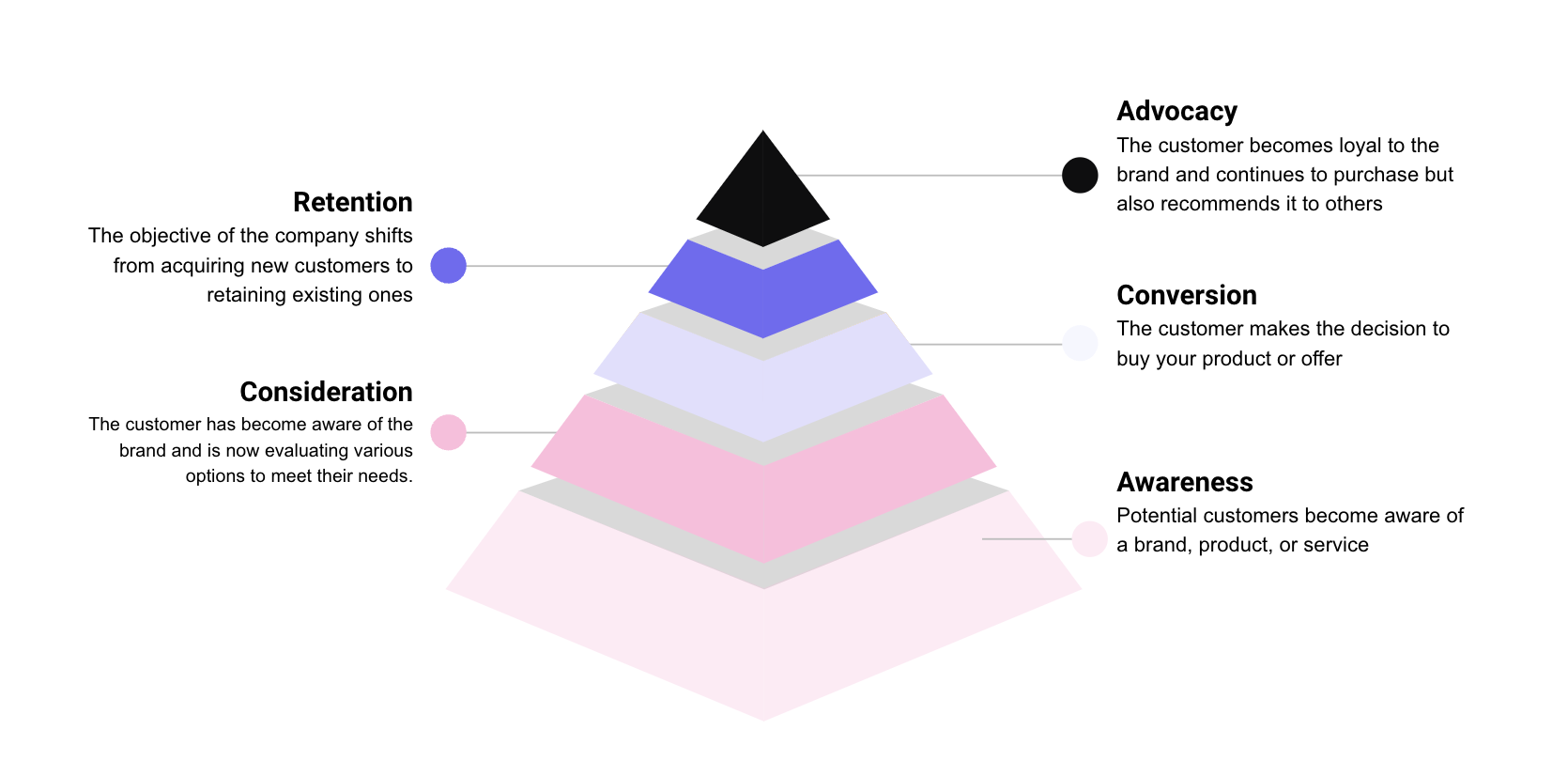
Customer journey: the different stages
A new framework: the 4S
Although still relevant, the traditional funnel model no longer reflects the complexity of today’s buying journeys.
Boston Consulting Group and Google have introduced a new approach known as the 4S: Streaming, Scrolling, Searching, Shopping. This concept helps to better understand consumers’ non-linear movements between content, search, and conversion.
Customer Journey, Buyer Journey, User Journey: what are the differences?
These three concepts are linked and are often confused, but they have distinct roles.
Customer Journey : this encompasses all the interactions a customer has with a brand, before, during and after the purchase.
Buyer Journey : focuses solely on the buying process, from the moment a customer becomes aware of his or her needs through to the final decision.
User Journey : this analyses the user experience (UX) of a product or service, identifying friction points and areas for improvement.
Each approach provides a complementary vision for optimising the customer experience.
What is a Customer Journey Map?
Definition of a Customer Journey Map
A Customer Journey Map (CJM) is a visual representation of the interactions between a customer and a company, from product discovery through to customer loyalty.
It takes into account the buyer persona (typical customer profile), the buyer journey and the points of contact with the company. It is based on real data and includes various elements such as the emotions felt and the actions taken by the persona.
This map makes it possible to analyse each stage of the customer journey, identify friction points and improve the user experience. Thanks to a CJM, companies can better understand their customers and optimise their commercial relationships in the broadest sense.
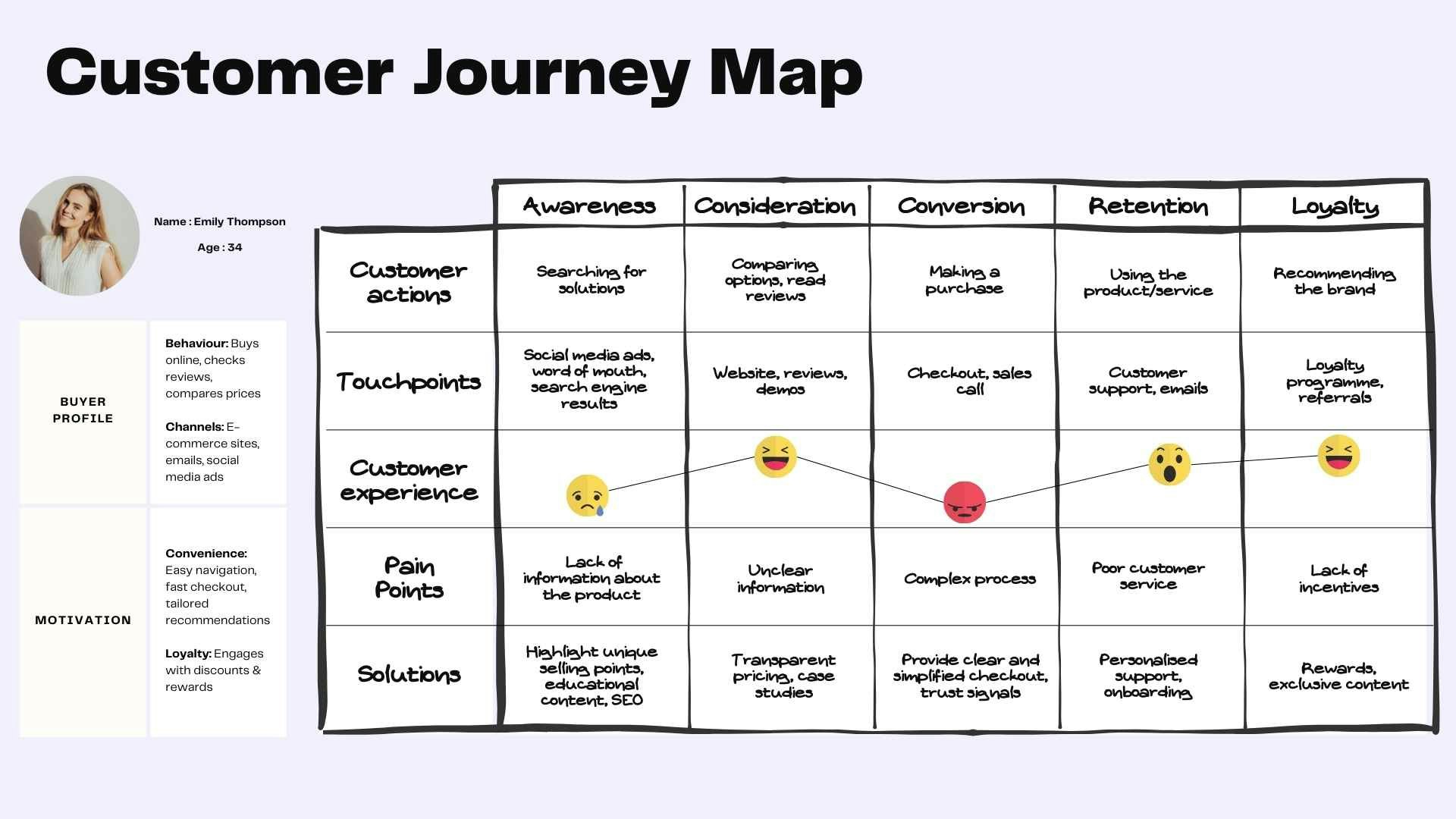
Example of a Customer Journey Map
The benefits and use cases of customer journey analysis
By analysing each phase of the customer journey, companies can identify the strengths and weaknesses of their customer interactions.
Increasing satisfaction, optimising the conversion rate, strengthening loyalty, boosting sales: mapping opens the way to targeted improvements for a smoother, more pleasant experience overall.
A Customer Journey Map helps businesses make decisions based on tangible data. Key benefits include :
Improved customer experience: by identifying bottlenecks and opportunities for optimisation.
Personalised exchanges: by adapting messages and communication channels.
Better allocation of resources: by focusing marketing efforts on key points in the customer journey.
Increased conversions: by streamlining the purchasing process and reducing abandonment.
In addition, customer journey analysis facilitates effective synergy between a company's various teams - whether marketing, sales or customer support - with a view to delivering a consistent omnichannel user experience.
In summary, the customer journey serves as a blueprint for providing outstanding customer experiences and cultivating enduring connections with your clientele.
Examples and use cases:
E-commerce : optimising the conversion tunnel to reduce basket abandonment.
SaaS : improving the user onboarding process.
Retail : better management of the omnichannel journey in shop and online.
Customer Journey Map, Experience Map and Empathy Map: what are the differences?
The CJM is a strategic tool for optimising the experience at every stage, based on concrete data. It complements other types of customer-centric mapping.
Empathy Map: a tool that focuses on the customer's emotions and perceptions, to better understand their expectations and frustrations.
Experience Map: a broader vision, which is not limited to a single brand but looks at the entire cycle (e.g. one person's journey, including several service providers).
How do you set up a Customer Journey Map?
Customer Journey Mapping is based on a precise analysis of customer behaviour and points of contact with the brand. It requires a methodical approach and the use of relevant data.
Information to be taken into account
Before designing the Customer Journey mapping, it is essential to gather the right information. Here are the main elements to take into account:
Personas: Effective mapping is based on a good understanding of customer profiles. Identifying the expectations, motivations and behaviours of different audiences helps to refine the journey study.
Points of contact: Each interaction between a customer and the company (advertising, website, customer service, social networks) must be catalogued to identify the channels with the greatest impact.
Behavioural data: Observing actual customer journeys via tracking tools (Google Analytics, heatmaps, CRM) helps to understand how customers interact with services and where they encounter obstacles.
Emotions and expectations: Each stage of the customer journey must be analysed from the customer's point of view, identifying frustrations and opportunities for improvement.
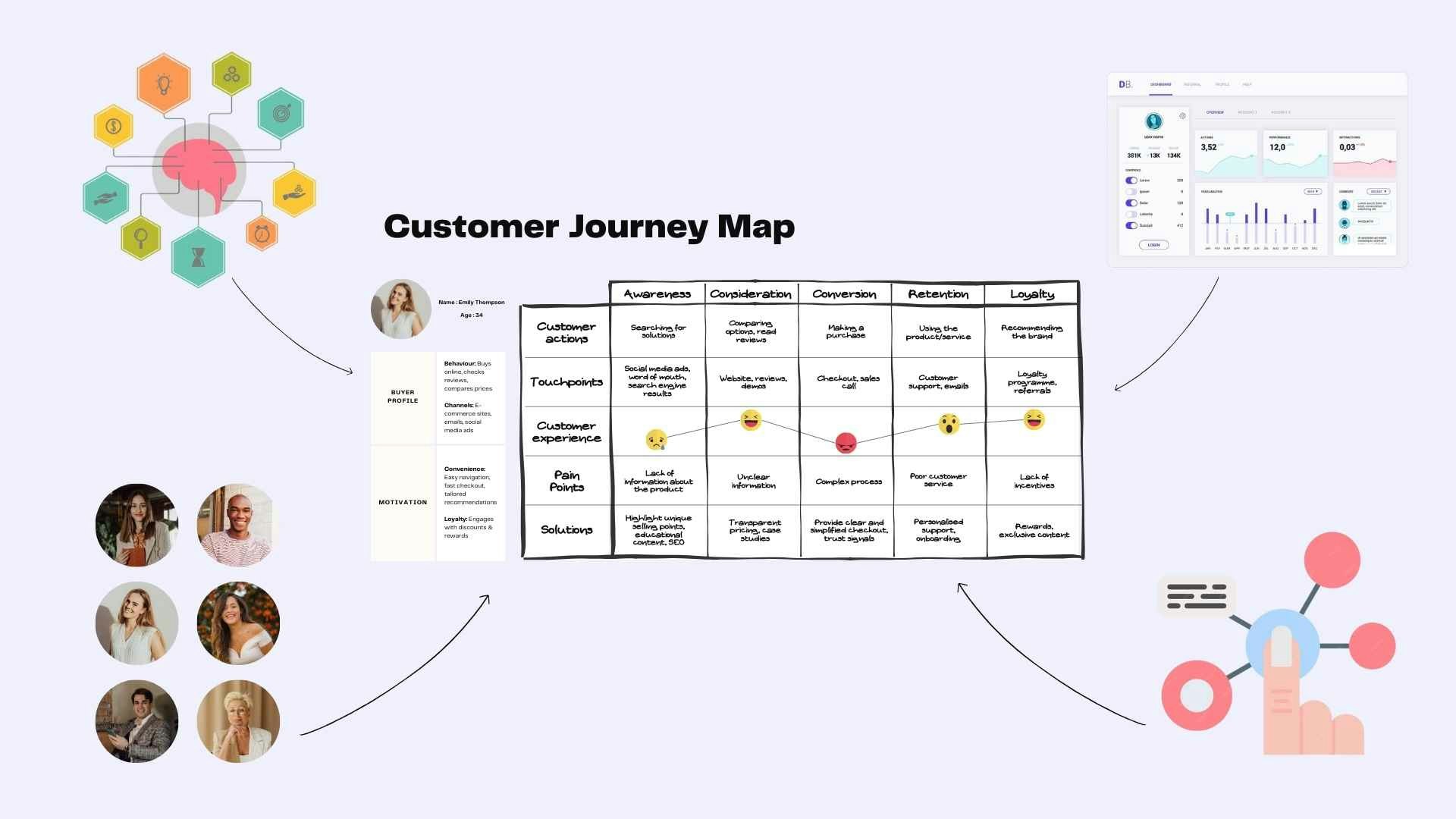
Insights for creating a Customer Journey Map
The stages involved in creating a CJM
There are several stages in designing a CJM:
Collect customer feedback: Questionnaires, opinions, support tickets and surveys provide an authentic view of expectations and difficulties encountered.
List friction points: Identify the critical moments when customers may hesitate or abandon their journey.
Map interactions: Trace each contact between the customer and the company to better visualise their experience. This can take the form of story mapping.
Know the actions and emotions of the personas: Associate each phase of the customer journey with positive or negative emotions in order to prioritise optimisation.
Define actions according to your objectives: A CJM should lead to concrete solutions, such as improving customer support, personalising recommendations or optimising marketing messages.
Tools, examples and models
There are several tools available to help you structure and visualise your Customer Journey mapping:
Visualisation software: Miro, Lucidchart and Notion can be used to create interactive and collaborative maps.
Analytical platforms: Google Analytics, Clarity, Hotjar and Mixpanel help to identify real user journeys.
Ready-to-use templates: Free templates are available on certain specialist platforms to save time and structure a CJM quickly.
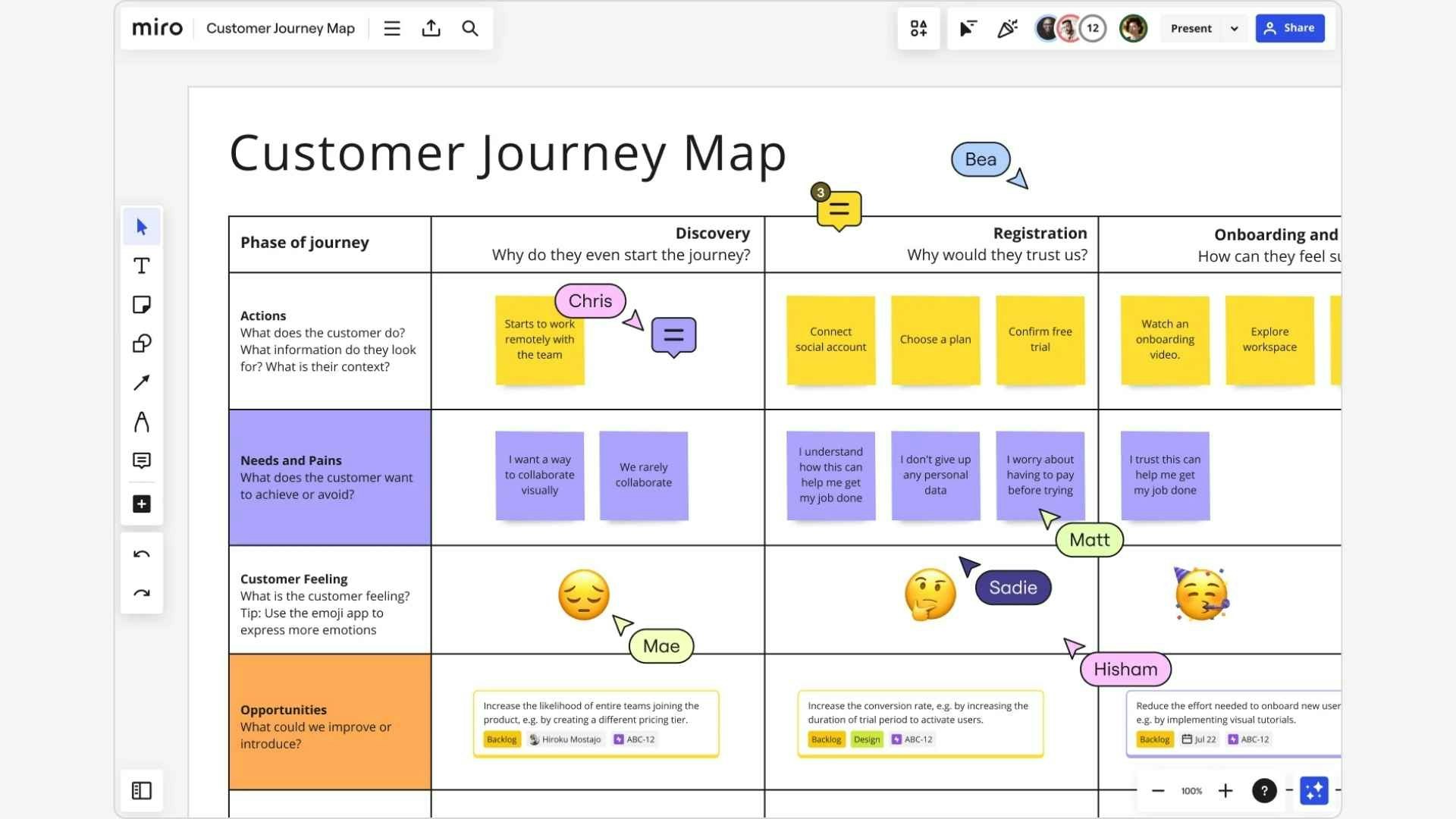
Creating a CJM with Miro (Source: Miro)
Improving the customer journey with CJM
A key use case for data activation is improving the customer journey. To effectively improve each stage, it is essential to perform a thorough mapping.
This process involves identifying the current pain points and areas for improvement at each stage.
Insights
Mapping provides strategic information for understanding customer expectations and behaviour. After analysis, it is possible to identify :
Friction points where customers abandon their journey.
Key moments of engagement that influence conversion.
Unmet expectations that could improve the experience.
By exploiting these insights, companies can adjust their actions, optimise their contact points and strengthen customer loyalty. That’s precisely what lifecycle marketing is all about.
Stages
👇 Here are some best practices recommendations on how to enhance each stage of the customer journey.
How to improve awareness?
In the awareness stage, the primary goal is to educate prospects about your brand and products without necessarily converting them into buyers immediately. Here are three key best practices to improve this stage:
Focus on education: Help consumers understand why they need a product like yours. This can be achieved by creating valuable, informative content such as blog posts, eBooks, white papers, and how-to articles. These content types should address common questions and challenges faced by your target audience, establishing your brand as an authority in the industry.
Choose the right channels: Identify and utilise the channels your prospects use most. For example, if your target audience is active on social media platforms like Facebook and Instagram, focus your advertising and content distribution efforts there.
Be there where your prospect is looking! Ensure that your content is easily discoverable through search engine optimisation (SEO) and other search marketing strategies (Tiktok, Instagram, etc.).
Increase the reach of your advertising campaigns: Don't hesitate to use lookalikes to target people similar to your ideal customers. In all cases, remember to use only the channels that are relevant to your target.
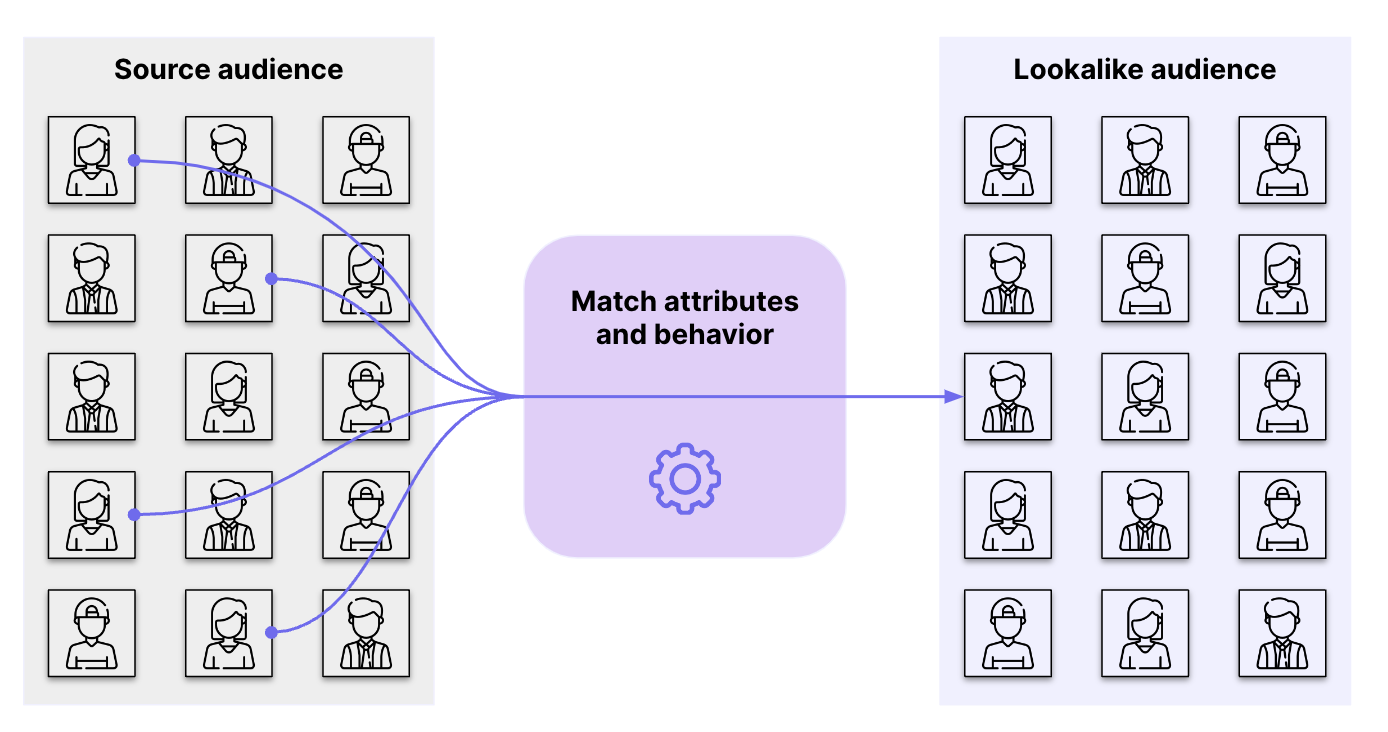
Lookalike: how it works
How to improve consideration?
In the consideration stage, potential customers are researching whether your company or product is the best fit for their needs. Here are some strategies to enhance this stage:
Highlight differentiators: Clearly outline what sets your product or service apart from the competition. This can be done through comparison guides, case studies, and detailed product descriptions.
Collect and showcase customers reviews: Gather as many reviews as possible and prominently display them on your website and other marketing materials. Reviews act as strong social proof and can significantly influence a customer’s decision.
Show reassuring elements: Use third-party endorsements such as customer partners testimonials, podcasts, and webinars to build trust.
Retargeting ads for prospects who have visited your website can also help keep your brand top of mind during their research phase.
How to improve conversion?
To improve the conversion stage, you need to analyze the customer journey mapping to identify and eliminate any purchase barriers. Here are some strategies to consider:
Analyze and address barriers: Use customer journey mapping to understand the pain points that might be preventing conversions (delivery fee, payment failures, etc.). Address these issues by simplifying the purchase process or providing clear, concise information about this process.
Provide incentives: Offer incentives such as free delivery, discounts, or limited-time promotions to motivate customers to complete the purchase. Running ads with time-sensitive offers can also drive conversions (e.g. “Only 1h left to take advantage of this special discount!”).
Collaborate with sales teams: Regularly communicate with your sales teams to gather insights and find new ways to improve the conversion process. This collaboration can help in identifying and resolving any bottlenecks in the sales funnel.
Leverage remarketing: Target users who have interrupted their purchasing process with targeted remarketing campaigns to re-engage them. Don't hesitate to use the various channels at your disposal: CRM, advertising platforms, etc.
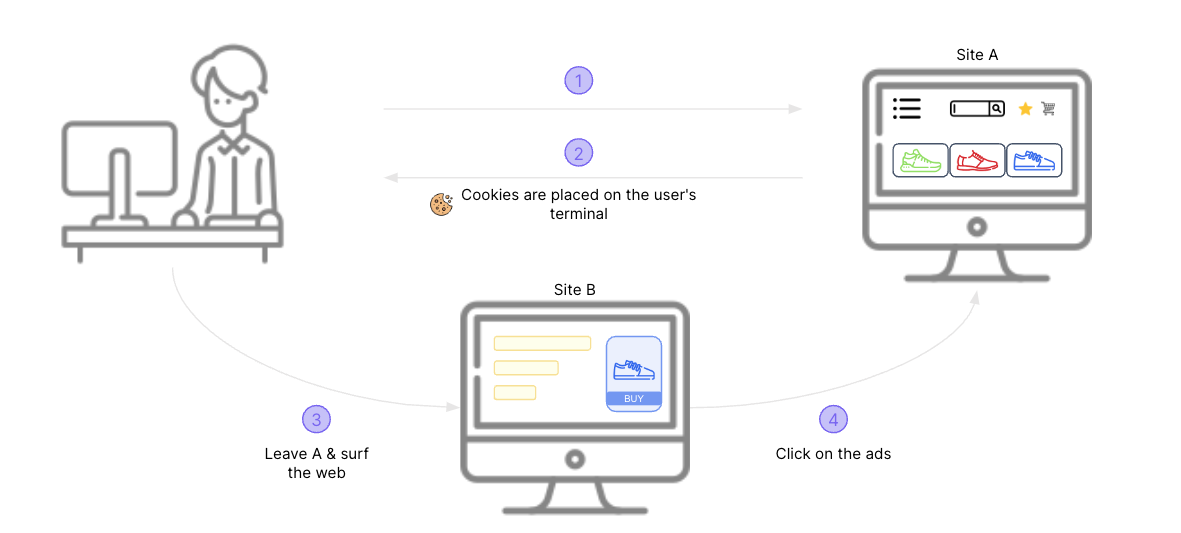
Third-party cookies are used to track online behaviour and retarget customers
How to improve retention?
Improving the retention stage is critical, as the chances of selling to an existing happy customer are significantly higher than to a new customer. Here are some best practices to enhance retention:
Maintain regular communications: Keep in touch with your customers through regular emails, newsletters, or other communication channels. This helps in maintaining a strong relationship and keeps your brand in their minds.
Create personalised content: Use first-party data to create personalised content that resonates with your customers. This can include tailored product recommendations and exclusive offers based on their preferences and behaviors. You can use artificial intelligence recommendations to promote cross-selling and upselling opportunities.
Establish a seamless relationship: Ensure that the customer experience is seamless across all touchpoints, online and offline.
Leverage predictive analytics to identify at-risk customers and proactively engage with them to prevent churn. Offering product recommendations can also enhance their overall experience and encourage repeat purchases.
How to improve advocacy?
In the vital stage of advocacy, our aim morphs into transforming satisfied consumers into steadfast brand advocates who eagerly recommend our offerings to others.
Embarking on this mission, we employ several tactics to fortify our bond with these customers:
Acknowledge customer feedback: Expressing gratitude for customer feedback and incorporating it into enhancing our products and services signifies our high regard for their input. This action reflects our commitment to their satisfaction and enriches their overall experience with our brand.
Offer special incentives: As a gesture of your appreciation for their enduring loyalty and the recommendations they make, you can bestow upon your loyal customers exclusive benefits. These perks can range from VIP status and discounts to complimentary products, serving as tangible tokens of our gratitude.
Simplify Referrals: You can streamline the referral process, enabling your devoted clientele to effortlessly introduce your brand to their acquaintances, colleagues, and kin. By fostering an environment conducive to social media sharing and rewarding successful referrals, you further improve this advocacy.
KPIs
A number of key performance indicators (KPIs) are used to measure the impact of optimising the customer journey:
Conversion rate: Evaluates the effectiveness of interactions at each stage.
Churn rate: Indicates customer loyalty and satisfaction.
Customer Lifetime Value (CLV): Measures the value generated by a customer over time.
Net Promoter Score (NPS): Reflects the propensity of customers to recommend the brand.
Average time spent per stage: Identifies the phases requiring adjustment.
By monitoring these KPIs, you can adjust your strategy in real time to improve overall performance.
CDP for an optimised customer journey
To technically implement and enhance each stage of the customer journey, you need to follow a structured approach that involves data centralisation, segmentation, integration with marketing tools, and continuous iteration.
Step 1: Collect and centralise all customer data
The first step is to collect and centralise all customer data into a single, unified database, such as a data warehouse (or a Customer Data Platform, CDP). This centralisation is essential for reducing data silos, improving data quality, and providing a single source of truth for your organisation.
Data warehouses, like those provided by Snowflake, BigQuery, or Redshift, serve as the central location to collect and store all incoming data from various sources. This includes data from sales, marketing, customer support, and other first-party and third-party sources.
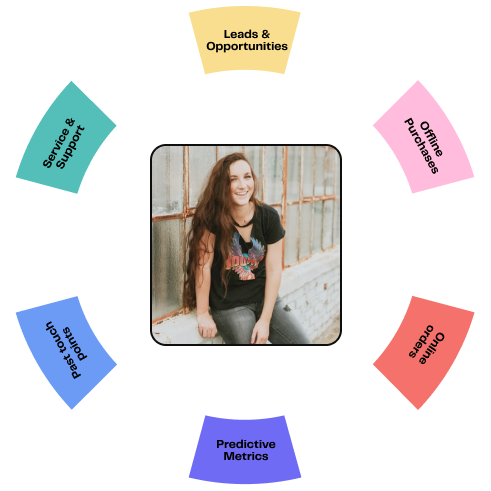

Customer 360, centralising all customer data
Step 2: Segment your database by customer journey stages
Once the data is centralised, segment your database based on the different stages of the customer journey (awareness, consideration, conversion, retention, and advocacy). This segmentation helps in understanding the specific needs and behaviors of customers at each stage.
For example, you can segment prospects from the “consideration” stage based on their interaction history and engagement levels to tailor your marketing strategies accordingly.
Step 3: Make data available in marketing tools
Ensure that the segmented data is accessible and integrated with your various marketing tools. Here’s how you can make this data available for different stages:
Awareness Stage: Integrate data with social media platforms, content management systems, and other channels where you engage with potential customers.
Conversion Stage: Use Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems to access customer data and personalise the sales process. Send data to advertising platforms for retargeting purposes.
Retention and Advocacy Stages: Utilise CRM and customer support tools to maintain regular communications and offer tailored content and offers to existing customers.

Data Activation
Step 4: Run marketing campaigns and iterate
With the data integrated into your marketing tools, you can now run targeted marketing campaigns tailored to each stage of the customer journey.
Execute campaigns based on the segmented data. For instance, run social media ads for awareness, send personalised emails for consideration, offer incentives for conversion, and provide loyalty programs for retention.
Iterate and optimise: Continuously monitor the performance of these campaigns and iterate based on the feedback and data insights. Use analytics to identify what works and what doesn’t, and make necessary adjustments to improve the customer experience and campaign effectiveness.
By following these steps, you can technically achieve a cohesive and data-driven approach to enhancing each stage of the customer journey, leading to improved customer experiences and increased business success.
Conclusion
In a nutshell, mastering the nuances of the customer journey is imperative for fostering an environment that not only captivates but also retains prospect and customer interest, ultimately propelling business success and growth.
Every phase within the customer journey spectrum, from the initial awareness to the pivotal advocacy stage, demands meticulous planning and execution. By effectively gathering and centralising critical customer data, categorising this information based on the respective stages of the customer journey, and synchronising it with your marketing mechanisms, crafting campaigns that resonate on a personal level with your audience becomes feasible.
DinMo, a pioneering customer data platform, stands as a beacon for businesses striving to refine their marketing strategies. Its unparalleled capability to natively connect to your data warehouse, unveil a comprehensive 360-degree perspective of your consumer base, and facilitate seamless audience synchronisation across diverse platforms through one-click activation, streamlines the complex process of harnessing customer data for business purposes.
🌟 To explore the transformative potential of DinMo, a free trial can be secured by contacting us!