Cross selling: definition + how to implement it
5min • Last updated on Dec 19, 2025

Alexandra Augusti
Chief of Staff
Cross selling is a sales strategy that involves offering additional products or services to current or prospective customers. This approach has the potential to not only increase your revenue but also enhance customer loyalty and satisfaction. Online, personalized recommendations can improve user experience.
But how can you effectively activate your data to succeed in your cross selling strategy? What are the benefits and potential pitfalls of such a sales strategy?
💡 We aim to answer all these questions in this dedicated article.
What is cross selling?
A definition of cross selling
Cross selling is a commercial tactic aimed at proposing complementary products or services to those already owned by the customer or about to be purchased. It's one of the most common use cases of data activation.
With the rise of the digital era, cross selling has become much more visible. It is almost inevitable on a website today: categories like "You may also like" or "Frequently bought together" are common when you are on a product page.
However, cross selling has always existed. If you doubt it, just think of popcorn sold in movie theaters or product recommendations in stores by staff.
Companies can boost their sales by recommending:
Complementary products to the initial product (e.g., a charger when buying a phone)
Popular products (in the same category as the initial product)
Impulse-buy products (e.g., insurance for the phone)
Products from another category that are popular with buyers (e.g., a computer)
A McKinsey study highlights that cross selling can represent up to 35% of a company's sales.
On average, cross selling is estimated to increase the average basket by 10 to 20%. The range is broad, but it also depends on the industry and how the cross selling strategy is implemented.
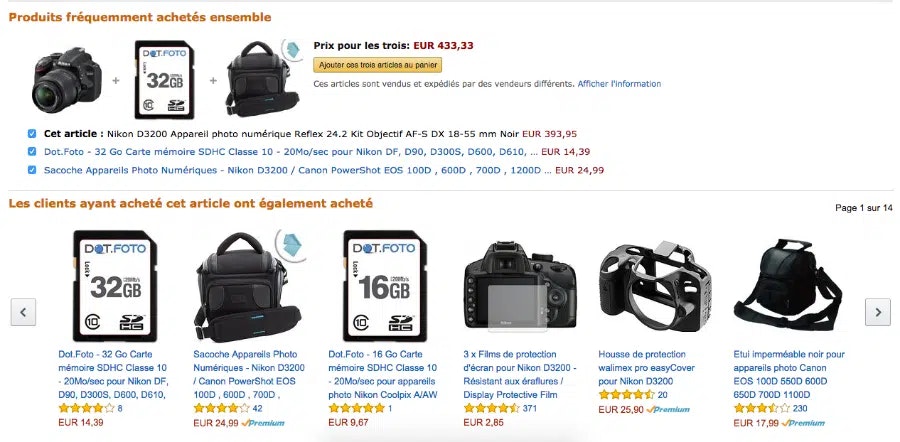
Example: product recommendations on Amazon
Focus on product diversification as a cross selling example
Product diversification represents a long-term cross selling tactic aimed at expanding a company's offerings by introducing new lines of products or services.
When analyzing customer databases, it often becomes clear that "multi-category" customers are among the most spending and loyal. The main goal of product diversification is to suggest alternative or complementary products to loyal customers, encouraging them to purchase in multiple product categories.
A concrete illustration: a company operating in the IT sector and selling computers could expand its catalog to include printers, software, or various accessories. A customer satisfied with a purchase in category A, then in category B, will be more likely to buy a product from category C from this company rather than from a competitor.
Distinguishing between cross selling and upselling
Cross selling and upselling are both commercial enhancement strategies with the common goal of increasing the average basket of a customer. Their difference lies in the nature of the product or service offered additionally.
Upselling focuses on offering a superior variant — more expensive, more efficient, or more comprehensive — of the initial product or service chosen by the consumer. For example, inviting a subscriber to upgrade from a standard plan to a premium option. Conversely, cross selling aims to sell a distinct product or service, which complements the customer's main purchase, such as an insurance offer, extended warranty, or after-sales service.

Cross selling vs. up selling
Why opt for cross selling?
Adopting a cross selling strategy brings several major advantages for a company, both financially and in terms of customer relations.
Stimulate revenue
The main advantage of cross selling lies in its ability to boost sales and, consequently, your company's revenue. By encouraging your customers to add other products or services to their cart during the same transaction, cross selling helps increase the average basket and the conversion rate of your customers.
Enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty
Cross selling also plays a crucial role in improving customer satisfaction and loyalty. If you can offer them complementary products or services that exactly match their expectations, desires, or specific needs, you establish a relationship of trust with your customers.
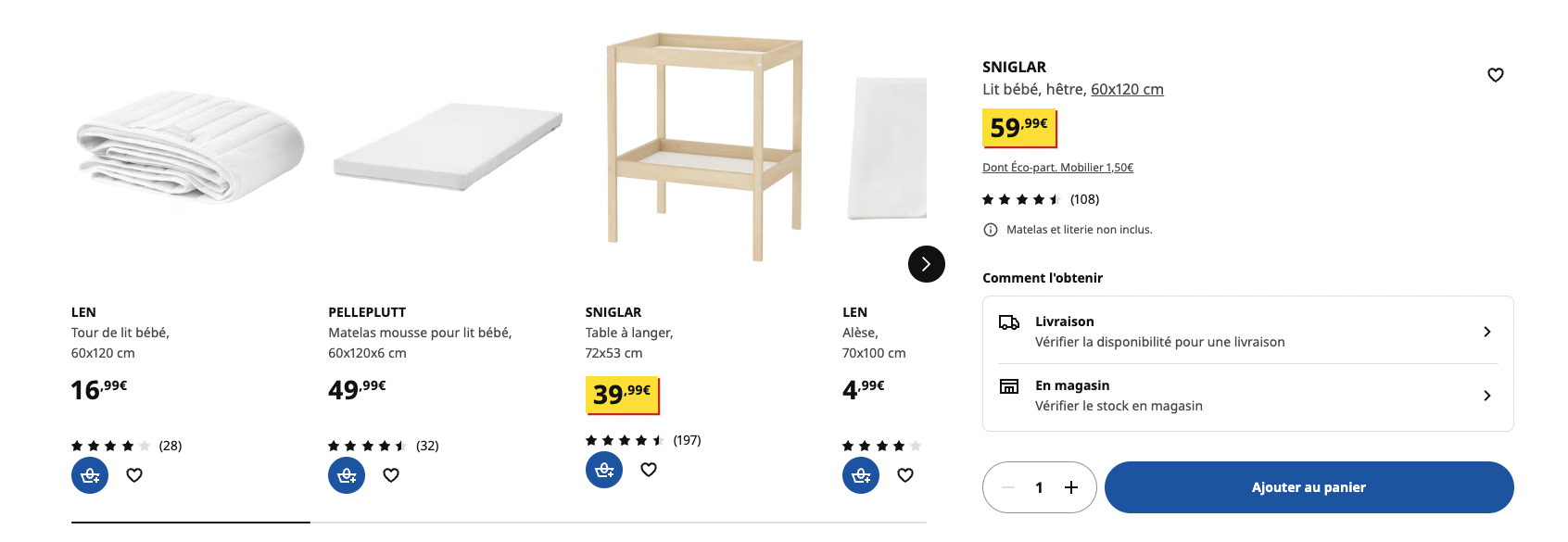
Ikea : cross selling example for a baby bed
Refine marketing and sales strategy
Another significant advantage of cross selling is that it allows you to refine your marketing and sales techniques. By wisely exploiting customer data, segmenting offers, personalizing messages, and adapting communication channels, cross selling maximizes the targeting of customers most likely to acquire complementary products or services. It is an effective method to present relevant and attractive offers, maximizing your return on investment.
Furthermore, cross selling can provide opportunities to better understand customer behavior and further refine strategies.
Is cross selling always a good idea?
While cross selling is often a winning strategy, it is important to be aware of its drawbacks to avoid them effectively.
A study published in the Harvard Business Review in 2012 highlights the potential risks associated with cross selling.
The risk of losing revenue on certain customers
Several reasons could explain revenue losses on customers to whom a company has recommended products for cross selling:
Customers requiring additional support: more items mean more support needed, which can drastically increase your CSM costs (especially for B2B)
Customers waiting for promotions: if your cross sell offers are always accompanied by commercial initiatives, some customers who understood your dynamic may wait for these offers and never buy at full price
Customers systematically returning a product: increasing purchases can also increase the return rate, especially for products that a customer had not initially considered. However, this implies logistical costs for your company, ultimately yielding no revenue
The risk of dissatisfying customers
Cross selling can be perceived as an intrusion, pushing customers towards purchasing unwanted products or services. This perception can lead to a degradation of trust, customer dissatisfaction, or even worse, the end of the customer relationship. To avoid this possibility, it is essential to:
Offer truly complementary and beneficial products or services to the customer, in line with their profile, needs, and preferences.
Approach cross selling techniques with a consultative spirit rather than an aggressive approach
The risk of complicating data management
Cross selling requires the handling of a wide range of customer data, from acquisition to all interactions with your brand. This demands advanced and secure data management solutions, capable of fine personalization and detailed analysis. Optimizing this process is crucial to ensure sales and avoid unnecessary complications.
To anticipate this challenge, adopting powerful customer data management platforms, like a CDP, is recommended.
How to develop an effective cross-selling approach?
Implementing a successful cross-selling strategy is not easy. It is a process that requires several prerequisites and must be regularly reviewed.
Cross-selling prerequisites
Before diving in, ensure you have two crucial components: a reliable customer database and suitable tools for data activation.
A solid database is essential to gather, store, and analyze information about customers, their purchases, needs, preferences, satisfaction, etc. This information is critical for identifying cross-selling opportunities and personalizing proposals.
As for tools, they must facilitate customer relationship management, segmentation, data activation and transformation, communication with customers, and results evaluation.
Using tools like CRM and emailing software is essential, but not necessarily sufficient.
Choosing the ideal products for cross-selling
The first step towards effective cross-selling is determining which complementary products or services could be offered after the customer's initial purchase.
To do this, rely on customer data, market research, and your knowledge of products or services. To start, we recommend keeping it simple and proposing the product (or category) most frequently bought with a given category.
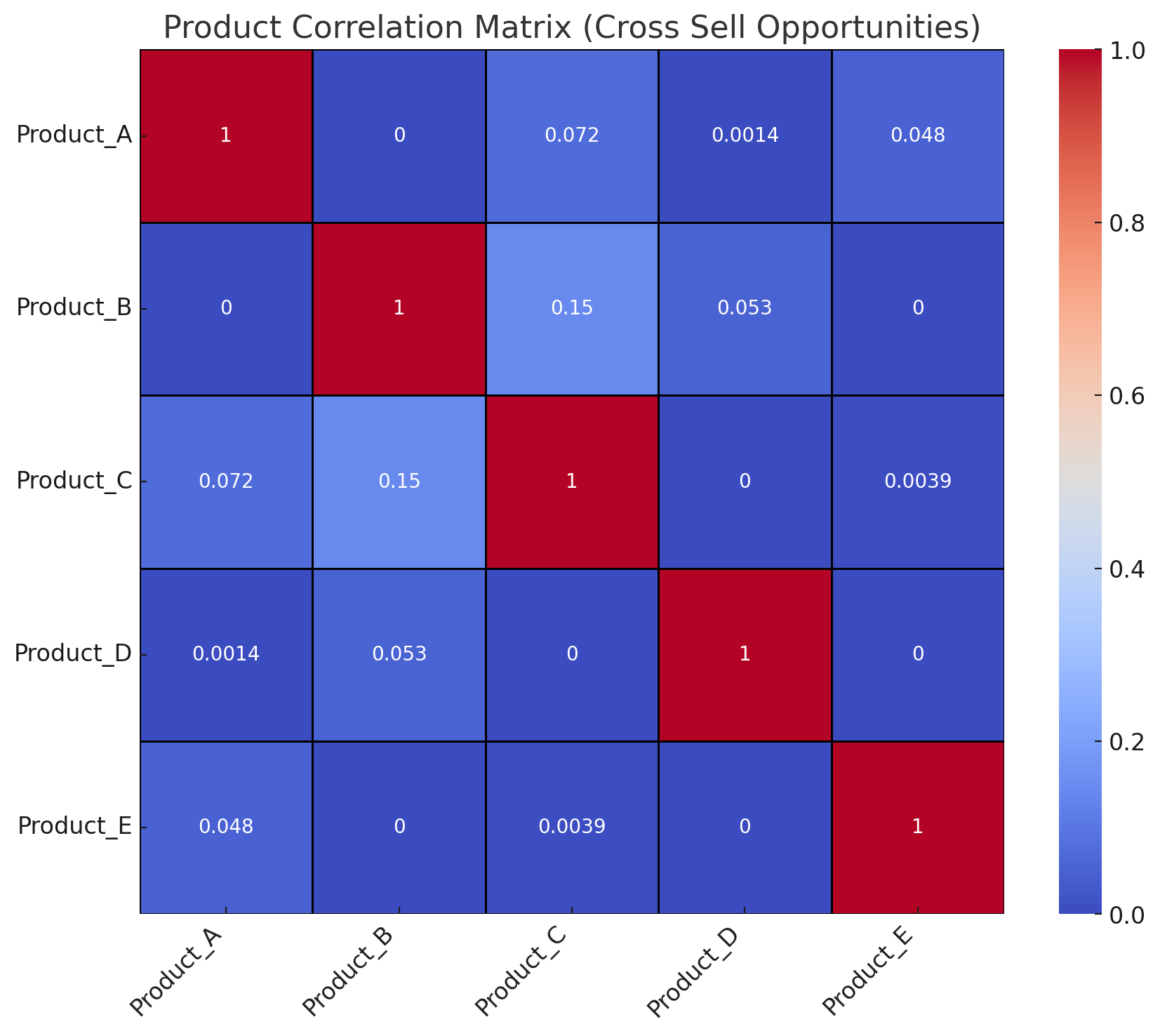
Product Correlation Matrix: Which products sell best when another product has been purchased?
Algorithms like Next Best Offer allow for much finer recommendations to your customers but are sometimes more challenging to implement.
Identifying opportune moments for cross-selling
The second step involves identifying the strategic moments to engage in cross-selling with the customer. These moments should be chosen considering the customer's purchase journey, engagement, satisfaction, etc. The most opportune moments are generally at the time of purchase (especially on the payment page) or a few months after.
Also, choose the most appropriate communication channel for each moment: website, email, phone, chat, social networks, etc.
Selecting receptive customers for cross-selling
The third step is to identify customers most likely to be interested in cross-selling. These customers must correspond to a qualified profile (need/budget/timing).
To do this, base your criteria on customer segmentation, such as profile, behavior, loyalty, etc. It is also crucial to adapt the marketing discourse and argument according to each customer.
Deploying a cross-selling campaign
The fourth crucial step in the cross-selling process involves the active development of the campaign. This means strategically designing, disseminating, and evaluating your cross-selling initiatives using a selection of specialized tools, including CRM software, emailing services, and social networks.
To successfully execute this strategy, it is essential to follow several steps:
Enrich the customer database with product recommendations for each customer
Segment the customer base
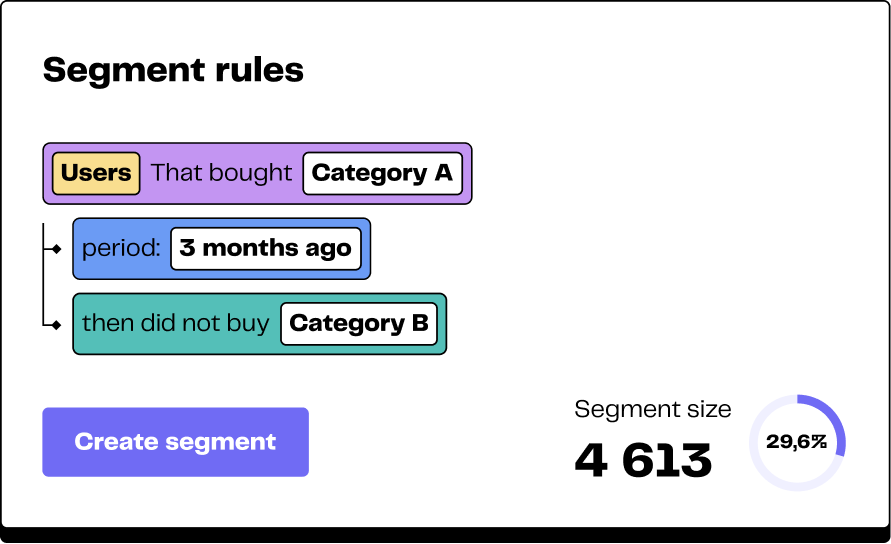
Send audiences to tools (CRM, emailing, social networks) automatically via a Reverse ETL tool
Configure the campaign in the tools
Final thoughts
Cross selling is a method that allows you to offer your customers complementary products or services to those they have already selected or are about to buy. Adopting this technique can boost revenue, improve customer satisfaction, and revitalize your marketing strategy.
To turn cross selling into a resounding success within your organization, it is essential to develop a tailor-made strategy that perfectly aligns with your customers' desires, needs, and expectations while providing them with undeniable added value.
If you have any questions regarding the concrete implementation of your cross-selling strategy, do not hesitate to contact us.