ABC analysis for a better commercial strategy
5min • Last updated on Oct 22, 2025

Alexandra Augusti
Chief of Staff
To make your marketing and sales strategies effective, you must first establish a customer segmentation system within your company.
Yet, to prioritise your most valuable customers for your company, you must be able to identify them. It is therefore essential for you to determine those who bring the most value today and those who hold the greatest potential.
You may have heard about the ABC segmentation to rank your customers based on two key axes: their current contribution to revenue and their potential future value.
By providing a clear vision of who your customers are, this matrix helps you identify the most effective commercial actions to take.
👉🏼 This guide will help you understand what the ABC matrix is, how to build it, when to use it, and how to get the most value from it.
What is the ABC analysis?
The ABC (activity-based costing) segmentation plays a key role in customer segmentation and enables a more refined commercial strategy. The very essence of this tool is to identify the customers with the greatest purchasing potential in order to focus your commercial efforts and resources on increasing revenue.
The ABC matrix is inspired by the Pareto principle, stating that 20% of customers are responsible for 80% of the revenue (category A). It also accounts for 30% of customers generating 15% of revenue (category B), and therefore half of the customers (50%) contributing just 5% of the total revenue (category C).
This tool helps determine who to prioritise and which strategy to follow segment by segment
We recommend conducting an ABC analysis at least once a year, when discussing the upcoming commercial strategies and plans.
👇 In the rest of the article, we detail how to carry out and, more importantly, apply the ABC analysis.
How to build your ABC segmentation?
To conduct an ABC segmentation, just follow the few steps below:
1. Classification of customers according to their current financial contribution
The starting point is the creation of an ABC curve to segment the customers based on the revenue they have generated to date. To do this, it’s quite straightforward:
Rank customers in descending order based on the revenue generated
Calculate the cumulative revenue and corresponding cumulative percentage for each customer
Divide the customers into three segments: A (the top 20% of customers), B (the next 30%), and C (the remaining 50%). 💡 Note that you can also use customer scoring to make this initial segmentation.
You can also plot this famous ABC curve to get a visualisation that shows how revenue is distributed across your customer base.
2. Evaluation of customers' growth potential
Next comes the evaluation of each customer's future potential. This step requires:
Establishing criteria defining potential, including but not limited to revenue, customer typology, their engagement with the product, purchase frequency, loyalty, etc.
Assigning each customer a potential score based on predetermined criteria. Note that here it is possible to use predictive attributes to assess the additional lifetime value of a customer and therefore their potential.
Segmenting customers again into three categories: A' (the top 20% with the highest potential), B' (30% with intermediate potential), and C' (the 50% with the lowest potential).
Note that it is also possible to extend the ABC matrix to prospects, by assigning a potential score to each prospect and segmenting these prospects into 3 categories PA’, PB’, and PC’.
3. Obtaining the ABC segmentation
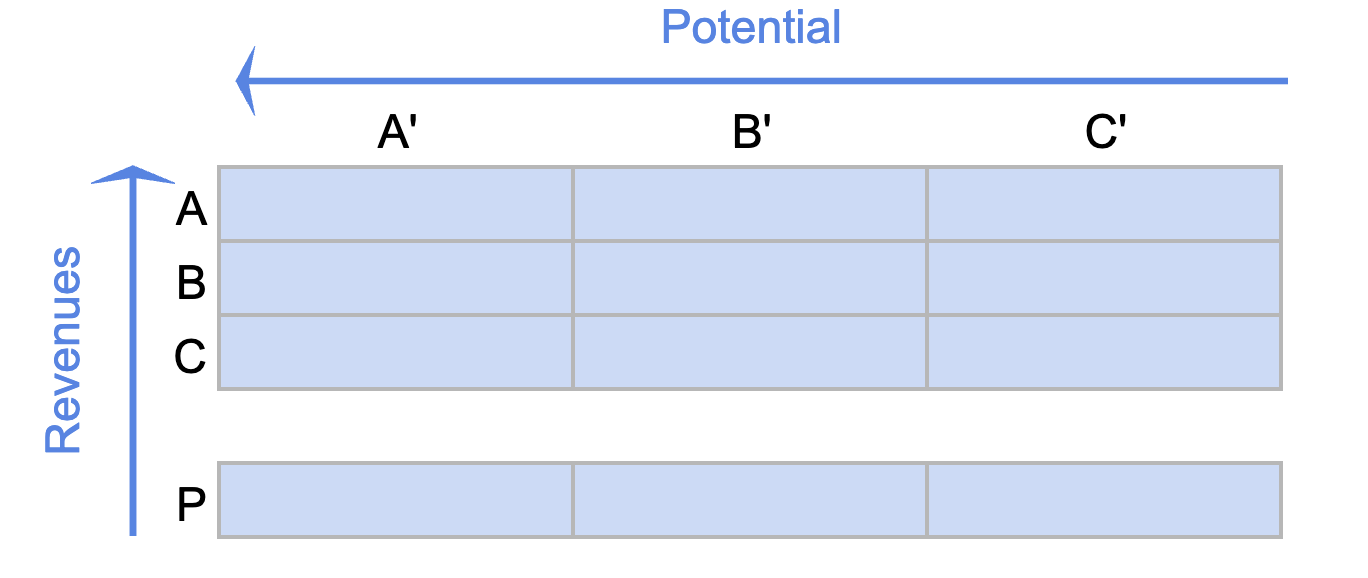
The third phase is the realisation of the ABC segmentation, merging the two previous classifications:
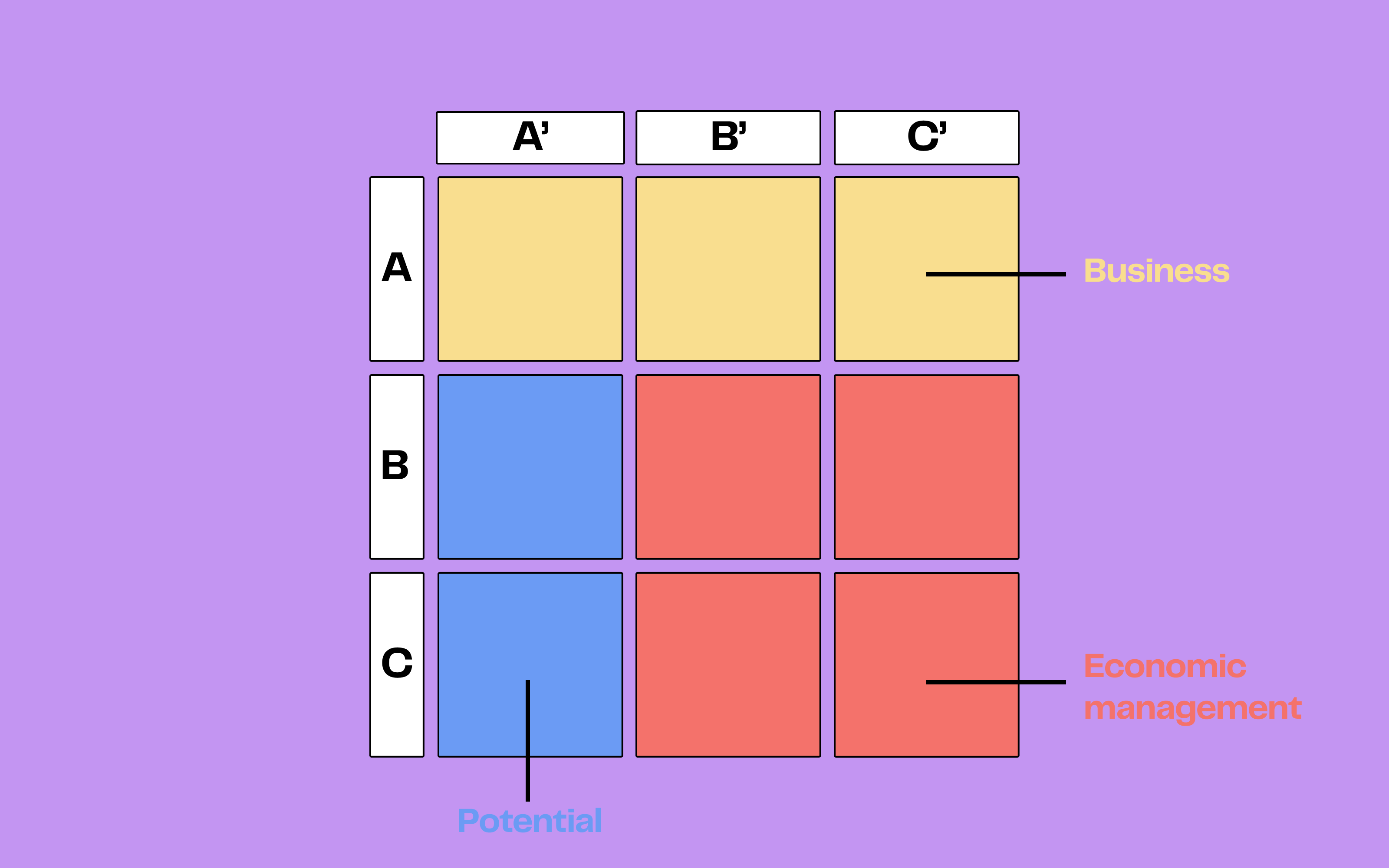
Positioning the customers in a double-entry table, where the horizontal axis displays revenue (categories A, B, C) and the vertical axis potential (categories A', B', C').
Identifying the nine resulting segments from the combinations of classifications. For example, an AA' customer represents both high revenue and high potential.
You thus obtain a crossed ABC matrix of this type:
ABC matrix crosses three specific customer groups determined by their current revenue (x-axis) and three groups characterised by their potential sales (y-axis).
How to use an ABC analysis?
Once the customer database is segmented, it becomes a valuable tool for deciphering the dynamics of your customer portfolio and for creating tailored strategies for each category. Here’s how to proceed:
Focus on the core of your business
Your business assets consist of customers who generate the largest volume of sales. These strategic customers deserve your utmost attention to ensure their loyalty and satisfaction.
This category is commonly called the “core business” and corresponds to categories AA’, AB’, and AC’.
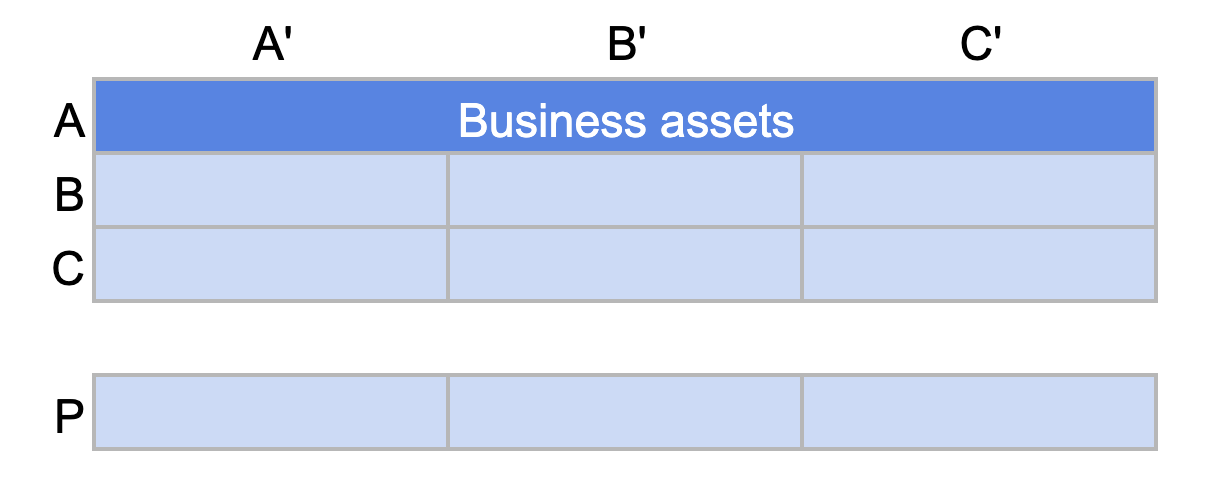
ABC Analysis: Category A corresponds to the "business assets" of a company
To achieve this, you can:
Strengthen customer relations, by offering tailored service, regular follow-ups, and proactive listening.
Offer VIP privileges, such as exclusive promotions, discounts, personalised gifts, etc.
Do everything possible to retain them, by staying vigilant against the competition, anticipating their needs, and quickly resolving any issues.
Your goal should be to maintain or ideally increase the revenue generated by this segment compared to the previous period.
Stimulate growth potential
This category includes customers with average or low revenue but with high development potential. This group corresponds notably to categories AA’, BA’, and CA’.
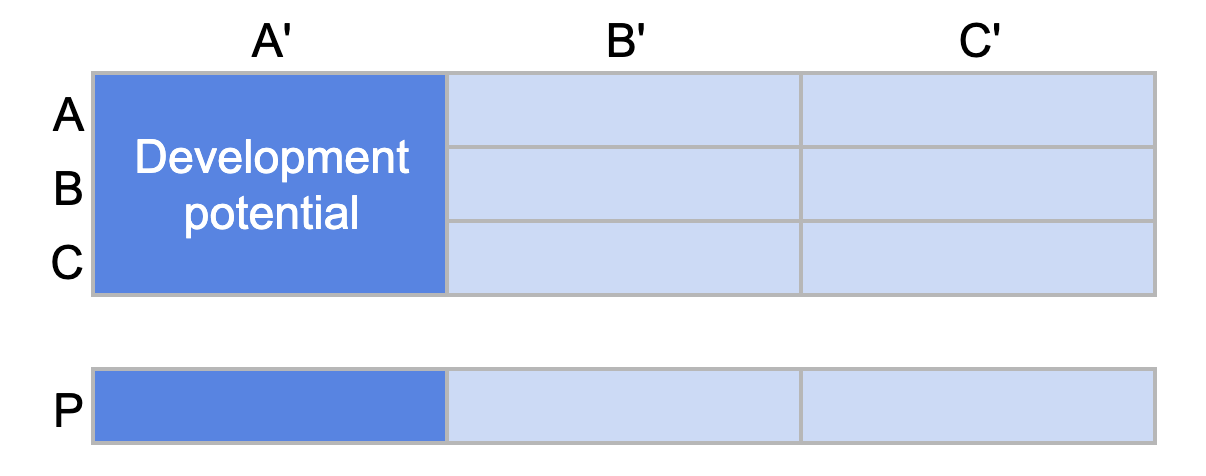
ABC analysis: Category A' corresponds to "development potential"
These are your priority development targets, requiring effort in acquisition and expansion. For this, it is recommended to:
Evaluate the individual potential of each customer, examining their needs, expectations, and future projects to understand where this potential comes from and how to drive conversion.
Develop specific strategies for this group, by creating tailored offers, persuasive sales arguments, and purchase incentives.
⚠️ Focus your efforts on a limited number of key customers instead of spreading your resources across the entire segment. Favour quality over quantity in interactions. It is better to concentrate your efforts on a single sub-segment of this clientele rather than trying to target everyone (and thus no one).
The challenge is to achieve a significant increase in revenue with this group to reach your growth objectives. Your "development potential" customers of today are your "core business" of tomorrow.
For your new prospects, focus mainly on those who have the most potential (category PA’). Once everyone in category PA’ has been converted, you can focus on category PB’.
Optimise economic management
The “economic management” segment concerns customers who contribute little to your revenue and have low development potential. These customers are represented by categories BB’, BC’, CB’, and CC’.
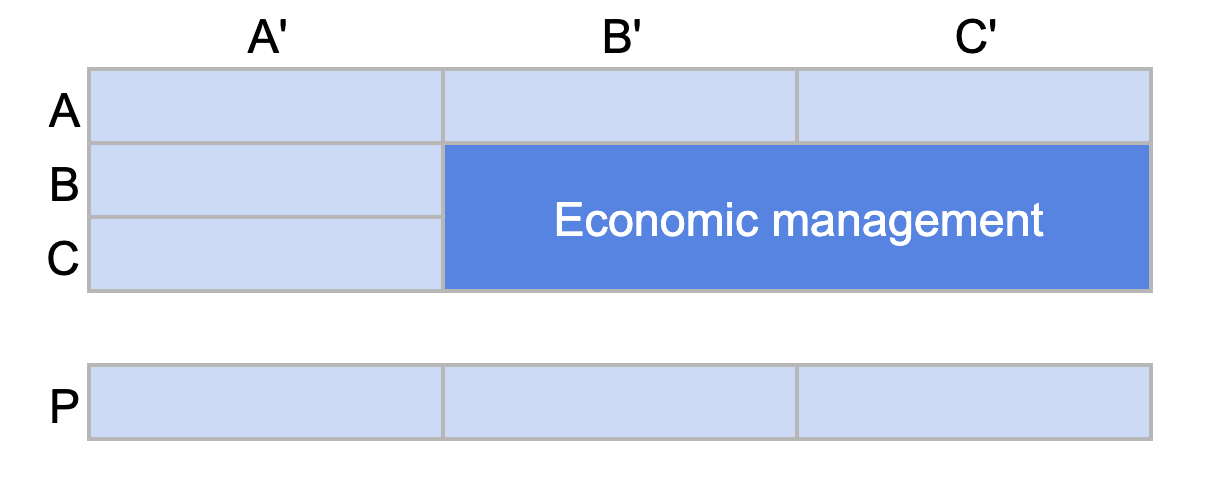
ABC analysis: Categories BB', BC', CB' and CC' correspond to "economic management'.
They represent a low stake for your company and should be managed efficiently, without wasting time or resources. In this context, you can:
Apply a ratio of time and/or resources proportional to the revenue, limiting interactions with these customers and offering them standard formulas.
Automate customer interactions, through the integration of digital technologies such as automatic newsletters, chatbots, or online forms.
The objective is to maintain, or even slightly increase, the revenue generated by this segment while minimising costs and associated risks.
Additional considerations
💡 To monitor the success of your strategies based on your ABC segmentation, do not hesitate to conduct cohort analysis (for example, tracking the evolution of the cohort "all customers who were in group AB’ in January 2024").
By leveraging the ABC segmentation, you have the opportunity to significantly improve your commercial performance, focusing on the people who bring the most value to your company. This translates into the retention of your key customers, the development of your high-potential customers, and optimised management of your lower-priority customers.
However, thinking about your customer segmentation should not be an annual task that you then forget. It should truly define all your sales and marketing actions and should be regularly reviewed to remain up-to-date and relevant.
🌟 DinMo is an activation platform that enables you to build any customer segment without writing code and keep it constantly up to date in any marketing or sales platform. To learn more about the importance of customer segmentation and which strategies could benefit your business, feel free to contact us.