The ultimate Guide to Customer Data Platforms (CDPs)
8min • Last updated on Jul 7, 2025

Alexandra Augusti
Chief of Staff
PwC research shows that 32% of customers are likely to leave a brand after just one bad experience. At the same time, 94% of managers consider data on customer preferences and needs to be essential or important.
A Customer Data Platform (CDP) is software designed to create a comprehensive and unified customer database for tracking, analysing, and managing customer (or prospect) interactions.
It helps companies personalise experiences and improve their campaigns.
Key Takeaways:
A Customer Data Platform (CDP) unifies customer data from various sources to provide a clear, usable view.
It collects, aggregates, sorts (especially from a GDPR perspective) and segments data so that it can be activated on different platforms.
A CDP helps improve the customer experience and reduce acquisition costs. It facilitates decision-making based on reliable data.
Choosing a CDP depends on several criteria: compatibility with existing tools, compliance with regulations, ability to evolve with business needs, etc.
📑 This guide summarises everything you need to know about Customer Data Platforms: origin, definition, types of data managed, use cases, benefits, differences and selection criteria. 👍
What is a Customer Data Platform (CDP)?
Over the years, the customer journey has become more complex, with increasing touchpoints. Additionally, Tag Management Systems (TMS) emerged, allowing the collection of online events.
These TMS can then be connected to third-party platforms to collect all this data. To address this challenge, some vendors attempted to reinvent themselves.
In 2013, David Raab, a marketing technology consultant, noticed the emergence of a new type of tool. He coined the term CDP in a blog post:
CDP: Packaged software that collects and organises customer data from multiple sources - such as websites, mobile apps, social media, emails, offline interactions - into a unified database.
David Raab
The chosen name for this platform is intentional and clearly defines its purpose:
"Customer": Covers all functions related to the customer: marketing, sales, technical support, customer success, CRM, etc.
"Data": Emphasises the importance of data, from collection to activation.
"Platform": The CDP not only manages data but also supports other systems.
Since 2013, interest in CDPs has grown significantly, and the topic remains relevant today.
💡 Although the explosion of the "MarTech" landscape from 2013 to 2020 closely associated them with marketing use cases, the scope of CDPs extends to all customer-related functions (sales, support, CRM, etc. - and obviously marketing).
If you want to explore Customer Data Platforms further, you can download our dedicated guide directly.
👇

All you need to know about CDPs
The Origin of CDPs
Platforms for managing customer data have existed for some time, but they have significantly evolved over time. Initially, some CRM providers created connectors with major media activation tools, and some DMPs began including first-party data.
1. CRM
In the early 1990s, businesses used Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems to store customer data. These systems were designed to manage relationships and interactions between companies and their customers and prospects.
They help companies stay connected, streamline and automate their processes. CRMs are still widely used, particularly by the sales and customer success teams.
However, CRMs have a number of limitations and do not cover all the use cases proposed by a CDP. The main differences between CRMs and CDPs are explained in more detail in our dedicated article.
In short, while CRMs are still used today, especially by sales and customer success teams, they have several limitations, including:
Only manages first-party data
Does not centralise data from multiple channels (online and offline)
Focuses solely on sales and customer support, lacking data activation on conventional marketing platforms
2. DMP
In the early 2000s, businesses started using Data Management Platforms (DMPs) to collect customer data for online advertising. These platforms primarily rely on third-party cookies to gather information about unknown audiences (those not yet customers of the brand). Unfortunately, they are not effective in managing known data (from existing customers) or storing data over extended periods.
In summary, DMPs have limitations compared to CDPs:
Only manages third-party data
No 360° view of the customer
Focuses solely on advertising
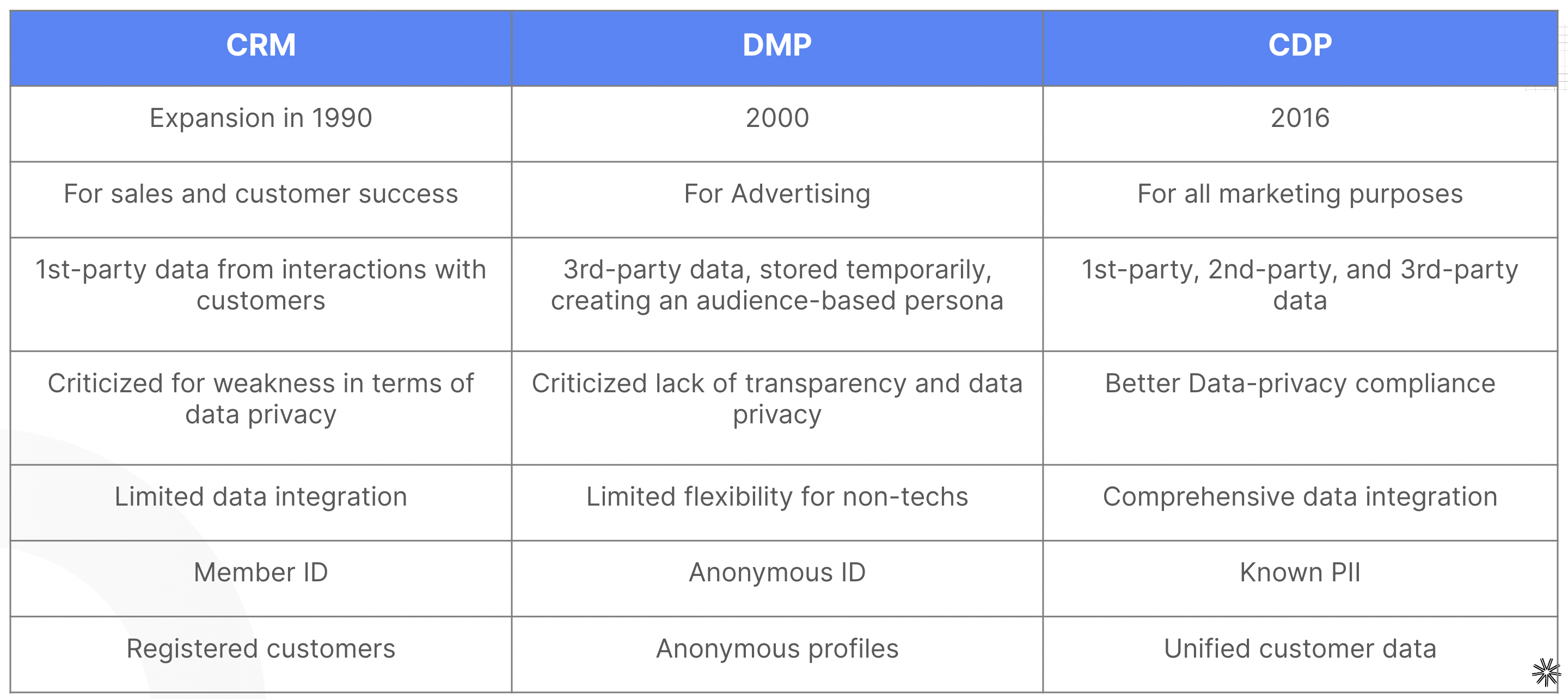
CRM vs CDP vs DMP
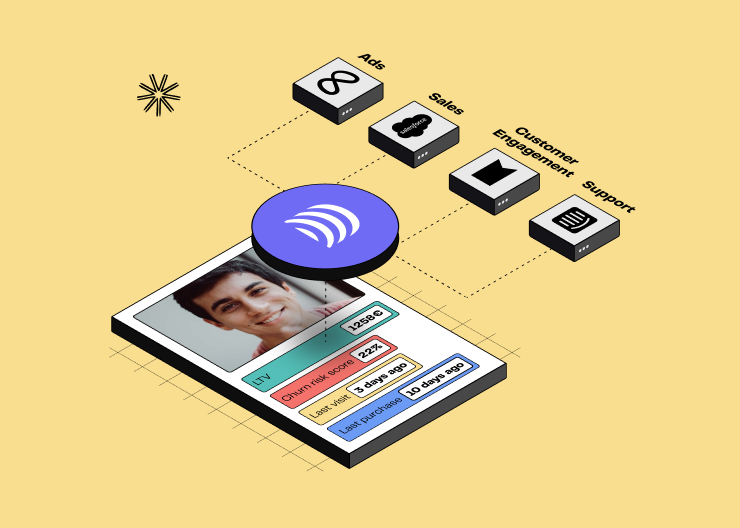
What does a Customer Data Platform do?
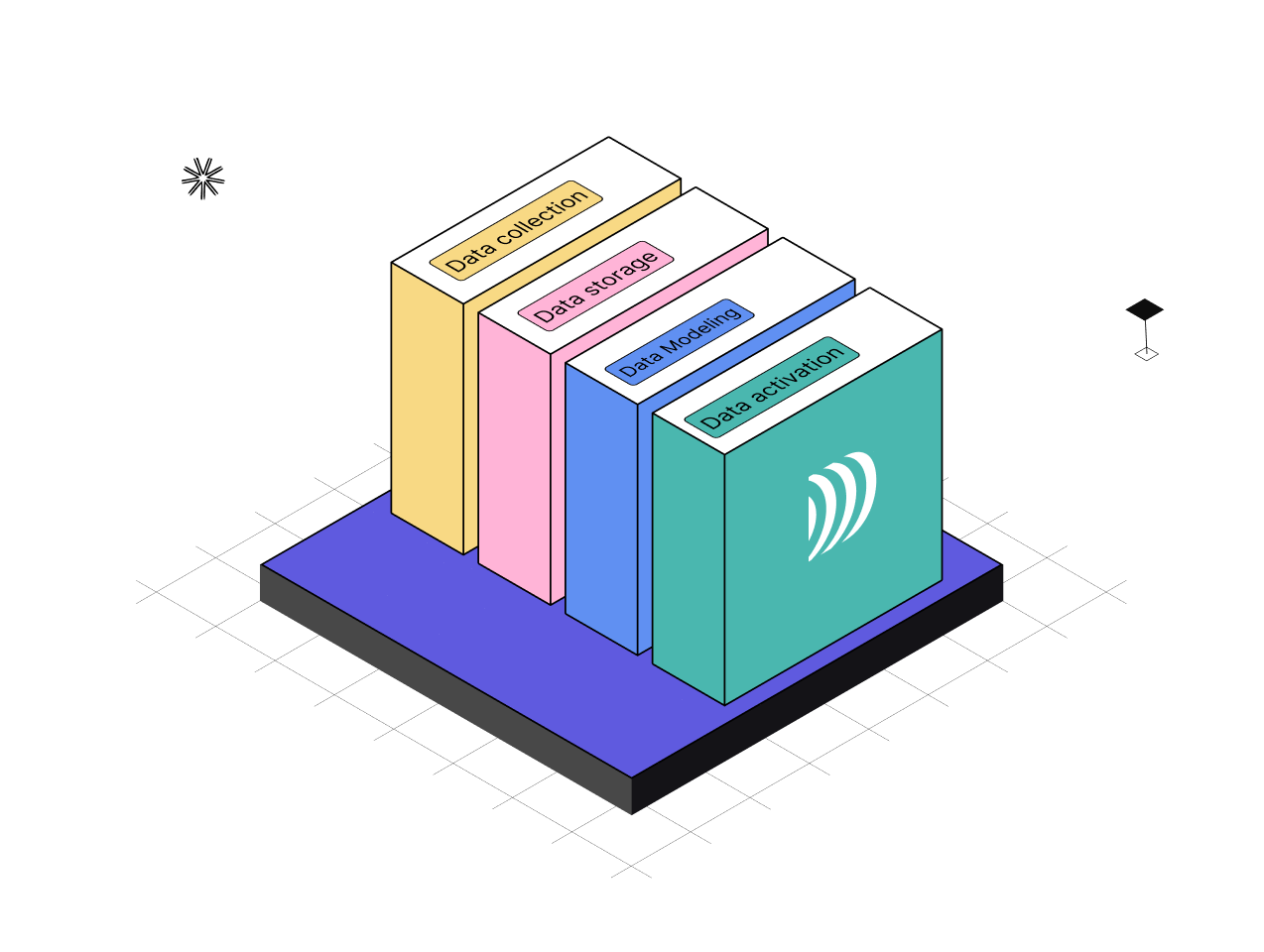
Overall, a Customer Data Platform serves three main objectives.
1. Collect and Centralise Data
Customer data can be scattered across various locations: websites, analytics, emails, CRMs, mobile apps, social media, offline interactions, etc. 'Siloed' business systems operate independently without associating data.
Each system operates using its own data and lacks a 360° view of the customer, which can lead to inconsistent customer experiences.
The goal of Customer 360 (included in the CDP) is to eliminate these limitations by connecting all tools and acting as a single source of truth for proprietary customer data (all while normalising it).
💡 Increasingly, companies are investing in a data warehouse to embody this Customer 360. This new approach has fostered the emergence of composable CDPs, detailed later in the guide.
2. Data Management: Transformation, Modelling, Segmentation
Customer Data Platforms allow the management of data, including:
Transformation and aggregation, often facilitated by Extract, Transform, Load (ETL) processes
Modelling, including enrichment through statistical models, data science, or artificial intelligence (e.g., calculating customer lifetime values, churn probabilities, etc.)
Segmentation into relevant "blocks" (consumer profiles, transactions, product interactions, etc.)
3. Activate Your Data
This crucial step involves synchronising segmented data with business tools so that they can be used, for example, for audience strategies.
Reverse ETL tools have specialised in this specific step, enabling the sending of all data to third-party platforms.
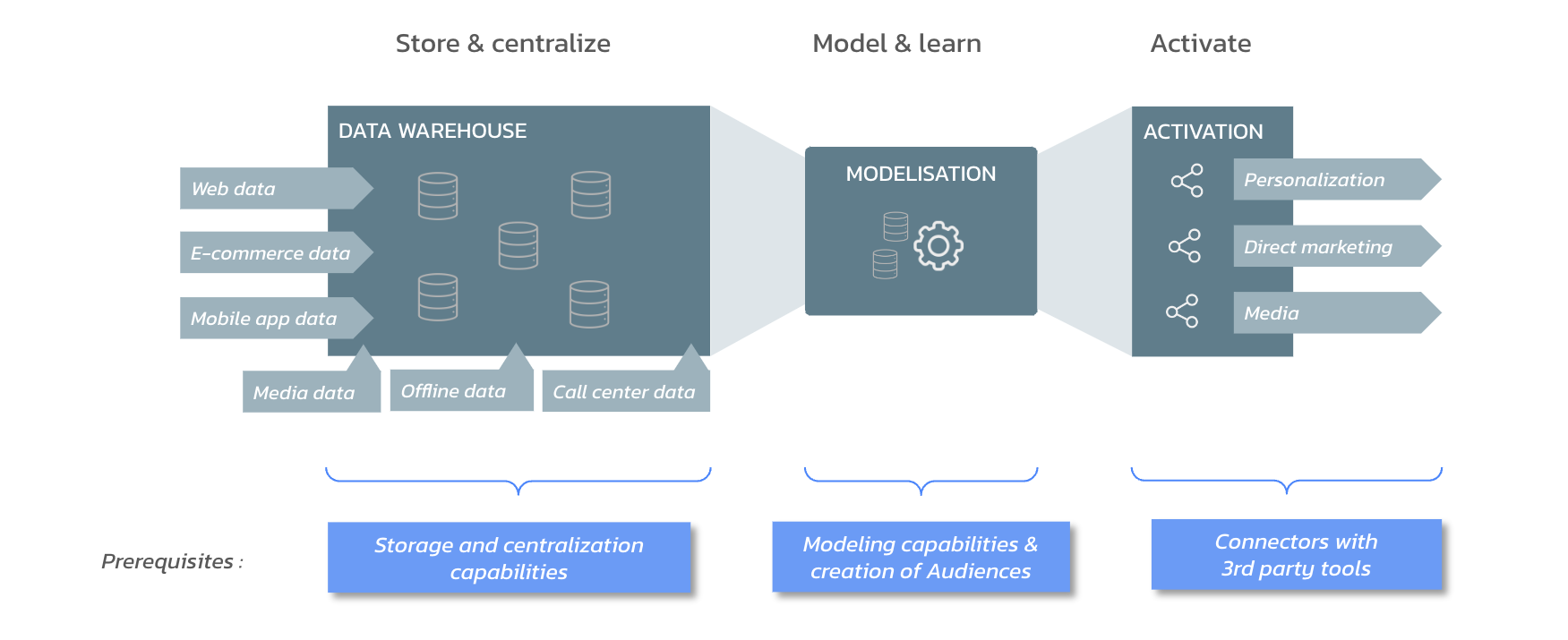
Schematic diagram of a CDP
Other solutions can also assist with activation issues but may not necessarily address centralisation and segmentation challenges.
By activating data in marketing platforms, you can gain a better understanding of your customers, segment your audiences more effectively and deliver more targeted messages.
The main objective is to reduce marketing costs while maximising results. For example, proper activation of first-party data can help to reduce your CAC by 30%.
What data is used in CDPs?
A Customer Data Platform collects various types of data to create a 360° view of customers that can be activated across all platforms. Data includes information that individuals leave when online browsing, in-store interactions, or phone calls, for example.
Each tool can enrich the information already held by another tool. While the CRM generally centralises the most insights about a person's identity, this data is also useful elsewhere.
The CDP can centralise all types of data: first-party, second-party, and third-party data.
The most frequently centralised and activated data in CDPs include:
Profile Data
This includes data related to a customer's identity: first name, last name, email address, age, phone number, etc.
Having as much information as possible about customers has several advantages, including better personalisation of communications and a higher matching rate in third-party tools.
Behavioural Data
Behavioural data is essential for understanding how an individual interacts with your brand. This helps to understand what they are really looking for and how best to communicate with them (via phone, email, etc.).
These data encompasses:
Interactions with customer service
Clicks, page views, events on the website
Email open rates
Transactional Data
Transactional data makes it possible to track purchase history and understand buying behaviour (frequency, seasonality, promotion-related incentives, etc.). This helps identify various buyer groups: big spenders, people who spend little but frequently, people who frequently return their orders, etc.
Product Data
Some CDPs can also centralise product data, although it pertains more to the company than to individual customers. It enables real-time visibility into product stock levels (for each model, size, color, etc.).
Advantages of a CDP
A Customer Data Platform allows the execution of several use cases and saves time for the teams using it.
Consolidation of Customer Data: The number 1 advantage of a CDP is relying on a "single source of truth," providing a holistic and unified view of the customer from multiple sources.
Personalisation of Customer Experiences: From consolidated data, you can further personalise customer experiences based on purchasing behaviours, product preferences, etc.
Advanced Segmentation: The CDP enables the creation of more precise and sophisticated segments, usually without coding, facilitating campaign personalisation. Better segmentation, combined with effective audience strategies, increases the conversion rate.
Optimisation of the Customer Journey: Analysing customer data by the CDP identifies the most effective touchpoints (and the right moments) throughout the customer journey, contributing to optimising overall business performance.
Compliance and Privacy Respect: CDPs help companies comply with data protection regulations (CCPA and GDPR) by managing consents.
Improved Customer Loyalty: By offering more personalised and relevant experiences, companies can strengthen customer loyalty and increase their retention rate.
Informed Decision-Making: CDPs offer advanced analytics and reporting tools based on real-time data, allowing companies to understand their results and adjust their actions accordingly.
Limitations of Traditional CDPs
Like all tools, traditional CDPs (also known as ‘integrated’ or ‘packaged’, as defined in 2013) have several limitations:
Implementation Complexity: A "classic" CDP project can sometimes take more than a year to land. Implementation is often complex and requires significant IT resources to integrate with other systems. Additionally, data models are rigid, forcing companies to rethink their data organisation.
Cost: The entry cost for traditional CDP licenses is over £100,000. Some licenses, for larger companies, can even reach a million! Ongoing operating costs are also high.
Data Security: A packaged CDP stores your data. This raises governance questions, exacerbated by their operation as a 'black box'.
For these reasons (and others!), new Composable CDP solutions are emerging in the market, driven by the rise of Reverse ETL tools and modern data warehouses.
👉🏼 For more info, check our comparison guide between CDP and Composable CDP

Data Activation
How to choose a CDP?
To succeed in your CDP project, here are 5 steps we recommend you follow:
Define Your Needs, Use Cases, and Objectives: Your CDP should be able to integrate with all your tools and enable the use cases that are important to you. Pay particular attention to both your current and future needs, especially regarding destinations.
Define Your Data Hosting Criteria: With a traditional solution, your data will be held by the CDP vendor. Composable CDPs, hosted in the cloud or on-premises, allow you to maintain control over your data. Discuss this with your legal teams to determine the most suitable solution for your company.
Ensure the Solution is Easy to Use and Meets Your Needs: Otherwise, it will never be used by end-users. According to a Forrester report, only 11% of companies are fully satisfied with their current CDP, due to its complexity.
Ensure the Tool is Easy to Deploy: Particularly, it should not require a complete upheaval of the current IT organisation. If a CDP meets your needs, it is worth setting it up quickly to implement the first use cases. However, traditional CDPs often take several months (or even years) to implement.
Identify and Measure Any Additional Criteria Specific to Your Company
If you want to find out more about the process of choosing a CDP and want an overview of the different players on the market, don't hesitate to consult our 2025 guide for CDP buyers.
Conclusion
At DinMo, we remain convinced that activating your data is key to performing in a challenging economic context. If you want to discuss CDPs in general or our modular approach, let's have a coffee ☕️ to go deeper.
FAQ
How does a CDP ensure compliance with regulations such as GDPR?
How does a CDP ensure compliance with regulations such as GDPR?
A Customer Data Platform (CDP) helps businesses comply with regulations like GDPR and CCPA by centralising and securing customer data within a compliant infrastructure. It complements your Consent and Preference Management Platform (CMP), which manages cookie banners and opt-in forms.
A CDP ensures full traceability and auditability, supporting compliance with user rights (access, rectification, deletion). It minimises misuse risks by activating only hashed and authorised data.
A composable CDP enhances security by leveraging the company’s existing infrastructure, reducing risks linked to data duplication.
What are the key differences between a composable CDP and a traditional CDP?
What are the key differences between a composable CDP and a traditional CDP?
A traditional CDP is an all-in-one system that centralises, transforms, and activates customer data within its own platform. As a packaged solution, it typically lacks flexibility and raises governance concerns, as data is duplicated in a proprietary environment. Leading providers include Salesforce, Adobe, and Segment.
In contrast, a composable CDP relies on an existing data warehouse to centralise and activate data. This modular, highly customisable solution integrates seamlessly with the company’s existing tools, offering greater control and scalability. Key providers include DinMo, Hightouch, and Census.
Composable CDPs are particularly suited to agile businesses adopting a Modern Data Stack. They enable quick implementation of initial use cases (marketing, sales, technical support).
What does the term modular CDP mean, and how is it different?
What does the term modular CDP mean, and how is it different?
At DinMo, we often use the term modular CDP to refer to a composable CDP. It highlights the flexibility of our solution, which is built on independent tools connected to an existing data infrastructure, such as a data warehouse.
Unlike packaged CDPs, a modular CDP does not impose rigid functionalities. Each module (collection, segmentation, activation) can be selected based on the company’s specific needs, following a Best-of-Breed approach.
This ensures optimal integration with existing systems and complete control over data. This tailored offering reduces costs, improves scalability, and aligns with modern data-driven strategies and regulatory requirements.