Everything you need to know about marketing attribution
8min • Last updated on Apr 7, 2025

Olivier Renard
Content & SEO Manager
Emma is an avid athlete. After work, she spots a stylish pair of trainers on Instagram but doesn’t take any further action. A few days later, she opens a newsletter from another brand and visits their website to compare options.
She then watches a YouTube video reviewing the best running trainers before searching for them on Google Shopping. The following weekend, a Facebook advert reminds her of the pair she originally saw.
She visits a physical store to try different models. Eventually, she purchases her chosen pair via the brand’s mobile app after receiving a special offer.
🤔 Which channel actually triggered the purchase? Was it the first Instagram ad, the Google search, the Facebook retargeting, or the in-store visit? This is where marketing attribution comes into play.
Key takeaways:
Marketing attribution evaluates the impact of different marketing touchpoints on the conversion process.
By improving the understanding of marketing effectiveness, it helps optimise budgets, enhance ROI, and refine strategies.
Various marketing attribution models exist, such as last-click, first-click, linear, and data-driven attribution. Each has its advantages and drawbacks depending on business objectives.
Implementing effective marketing attribution requires a clear methodology and appropriate tools, especially in an omnichannel environment.
🔎 How does marketing attribution work, and which models should you choose? Discover the most commonly used approaches and their benefits for optimising your campaigns. 🚀
What is marketing attribution?
Marketing attribution is a method that analyses and evaluates the impact of each channel in the customer’s purchase journey.
It assigns value to the various interactions a customer has with a brand before converting.
Through this analysis, marketers can determine which touchpoints influence purchasing decisions, whether it’s an advertisement, an email, or an in-store visit.
Consumers interact with multiple touchpoints before making a purchase, making their journey more complex. Marketing attribution helps optimise investment by identifying the most effective channels and adjusting strategies accordingly.
Challenges and importance for businesses
Attribution helps maximise the return on investment (ROI) of marketing campaigns. By analysing conversion data, businesses can:
Allocate their marketing budget more effectively, investing in the most profitable channels.
Adjust campaigns to focus on the most efficient strategies and optimise performance.
Understand the customer journey, identifying how consumers interact with the brand before converting.
Personalise customer experiences, adapting messages and offers based on behaviour to boost loyalty.
Improve forecasting, taking seasonality and trends into account to anticipate performance variations.

Customer Journey Map Diagram
The last-click attribution model is one of the most widely used because it is easy to implement. However, it is often biased, as it assigns all the credit for the conversion to the last channel, without considering previous interactions.
To use a football metaphor, all the credit for the goal would go to the striker, even though it came from a good clearance by a defender and a perfectly timed pass from the playmaker.
For a more accurate analysis, it is therefore essential to adopt an attribution model that aligns with business objectives and reflects the reality of the customer journey.
The main marketing attribution models
There are several attribution models, each with its own advantages and limitations. Some are easy to implement, while others rely on advanced algorithms for more precise analysis.
Traditional models
Traditional attribution models help analyse the impact of marketing channels using predefined rules. While simple and widely used, they have certain drawbacks.
Attribution model | Definition | Benefits | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
Last-click | Assigns 100% credit to the last touchpoint before conversion. | Easy to set up, compatible with most analytical tools. Suitable for companies looking for a quick analysis of simple customer journeys. | Ignores all previous interactions, giving excessive credit to the final touchpoint. |
Last non-direct click | A variation of last-click, ignoring direct traffic and assigning credit to the last identified marketing channel. | More precise than last-click by filtering direct traffic. Better suited to multi-channel conversion strategies. | Undervalues intermediate engagement channels and does not reflect the entire journey. |
First-click | Allocates full credit to the first point of contact in the customer journey. | Highlights the channels that generate the first interaction and attract new prospects. Easy to implement, useful for optimising acquisition strategies. | Giving credit to the first point of contact can skew the analysis. Does not consider engagement at later stages of the journey. |
Linear attribution | Equally distributes credit across all interactions leading to the conversion. | Provides a balanced view of all interactions. Ideal for customer journeys where all touchpoints have a similar influence. | Does not reflect the real weight of each touchpoint, treating all equally. |
Time-decay attribution | Gives more weight to recent interactions in the customer journey. | This model is ideal for long sales cycles as it values recent interactions. Allows campaigns to be optimised according to prospect maturity. | May underestimate the role of initial interactions in conversion. |
Position-based attribution (U-shape) | Assigns higher credit to the first and last interactions, with remaining credit spread across intermediate touchpoints. | Takes into account both acquisition and final conversion, to offer a good compromise. Better reflects the role of key touchpoints in conversion. | May overlook the impact of intermediate interactions on the purchase decision. |
The main standard attribution models
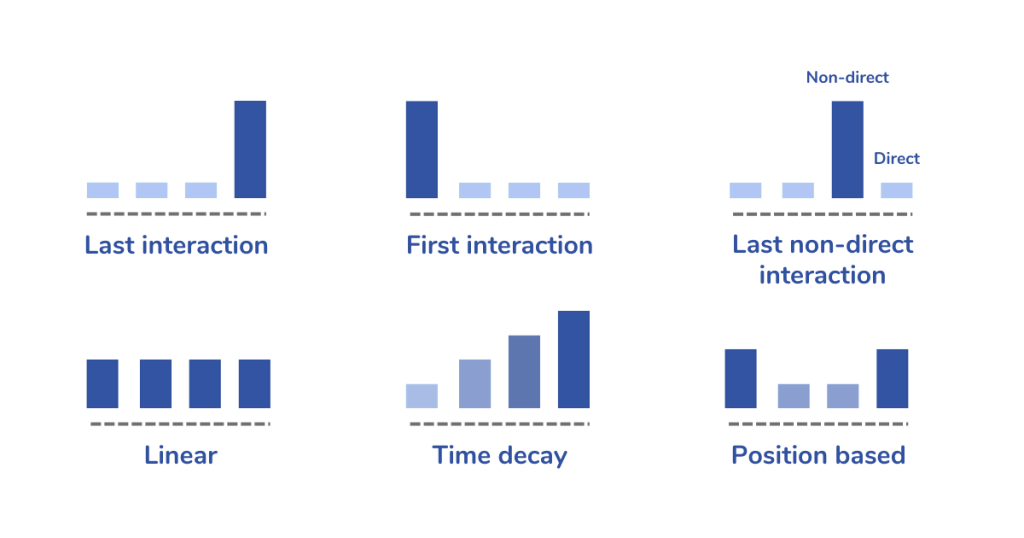
Examples of marketing attribution models
As customer journeys become more complex, traditional attribution models have limitations, especially with the phase-out of third-party cookies.
💡 Since 2023, Google Analytics 4 (GA4) has removed several rule-based attribution models (first-click, linear, position-based, time-decay). Instead, the Mountain View giant now prioritises Data-Driven Attribution (DDA), which uses machine learning to evaluate the actual impact of each touchpoint.
Modern approaches to attribution
New attribution models enable more precise analysis, tailored to an omnichannel and multimodal environment, thanks to data-driven insights.
Data-Driven Attribution (DDA): Uses AI to analyse customer journeys, assigning weight to each touchpoint based on its real impact on conversion.
DDA adapts to user behaviour for greater accuracy. It is used by default in GA4 and Google Ads to refine performance analysis.
Markov Chains: A probabilistic model that calculates the influence of each channel on conversion based on its presence or absence in a customer journey.
By comparing different scenarios, it measures the actual contribution of each contact point using probability calculations. This helps identify the most strategic channels by measuring their impact on conversion.
Shapley Value Attribution: Inspired by game theory, this model assigns a marginal contribution score to each touchpoint based on its incremental effect on conversion.
In other words, it measures how much a specific channel increases the likelihood of conversion when added to the journey. This approach is particularly useful for understanding the exact role of each contact point in a complex customer journey.
These advanced models provide greater accuracy but require large data volumes and sophisticated analytics tools.
Marketing Mix Modeling as an alternative
In a landscape where individual tracking is becoming more challenging, Marketing Mix Modeling (MMM) is making a comeback. This approach evaluates the impact of marketing investments on overall performance using mathematical techniques.
Based on historical data, MMM serves as a particularly valuable alternative for brands operating in an omnichannel environment.
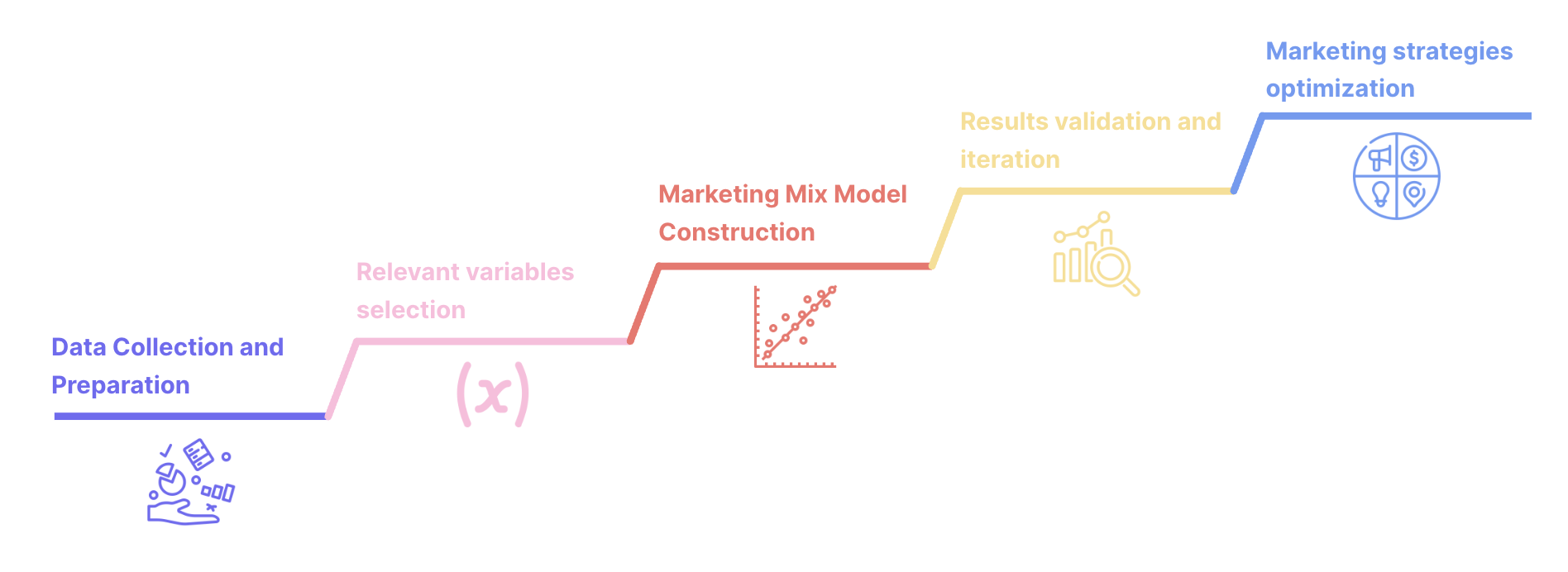
Marketing Mix Modeling: detailed steps
The choice of the right model depends on your objectives, competitive landscape, and your company’s ability to collect and analyse data.
For greater efficiency, we recommend centralising all data in a cloud data warehouse. By leveraging a single source of truth, businesses can refine their decision-making and maximise their return on investment. The Composable Customer Data Platform (CDP) DinMo facilitates this approach.
How to implement an effective strategy?
Well thought-out attribution helps to optimise the performance of marketing campaigns by avoiding common mistakes. Here are the main steps and recommended tools for a reliable analysis.
Key steps
1️⃣ Define your objectives
Before anything else, it is crucial to determine what you want to measure. A brand focused on acquisition will analyse data differently from one prioritising customer retention.
2️⃣ Map the customer journey and identify key touchpoints
Analysing customer interactions helps to better understand which channels genuinely influence conversions. This step is essential for data collection and selecting a relevant attribution model.
3️⃣ Choose the most suitable model
Last-click, first-click, linear, data-driven… The chosen model should reflect the reality of the business and purchasing cycles.
4️⃣ Leverage first-party data for more reliable analysis
With the phase-out of third-party cookies, businesses must capitalise on their own data to ensure more accurate and compliant attribution.
5️⃣ Continuously test, adjust, and optimise
Marketing attribution is not static. It is essential to analyse performance, experiment with A/B testing, and refine the model based on results.
❌ Mistakes to avoid
Relying solely on the last-click model. While it simplifies analysis, it does not reflect the full customer journey.
Neglecting the impact of cross-device interactions and offline touchpoints. A customer may engage in-store and across multiple devices before making a purchase.
Underestimating the importance of first-party data. With third-party cookies disappearing, first-party data is now essential for effective attribution.
Tools and solutions to optimise marketing attribution
Several solutions can automate attribution and improve tracking accuracy. They help businesses better understand performance and adjust campaigns accordingly.
Google Analytics
GA4 offers advanced reporting and a data-driven attribution model. The tool relies on artificial intelligence to redistribute conversion value based on observed interactions. Implementing a precise tagging plan is essential to capture all relevant data.
Multi-Touch Attribution (MTA) tools
Solutions such as Ruler Analytics, Segment, and HubSpot enable businesses to analyse the combined impact of multiple channels, providing a more detailed view than traditional attribution models.
Conversions API
With the phase-out of third-party cookies, advertising platforms like Google and Meta recommend using conversion APIs to transmit conversion events directly from the server.
CRM: A useful but limited solution
CRMs are widely used to manage interactions with customers, prospects, and partners. They can also help attribute conversions, but they often remain limited to lead management and do not cover the entire omnichannel journey.
This is why a CRM cannot serve as the single source of truth.
The value of a data warehouse and a composable CDP
A composable CDP leverages data stored in a cloud data warehouse.
Data centralisation: The data warehouse consolidates information from multiple channels (web, CRM, ads, emails, etc.) for more reliable analysis.
Comprehensive customer journey view: The CDP unifies customer data from both online and offline touchpoints, effectively handling cross-channel and cross-device interactions.
Campaign optimisation: More accurate attribution enables real-time strategy adjustments.
DinMo synchronises audience segments with marketing tools to maximise ROI.
Conclusion
Marketing attribution is essential for measuring the impact of each channel and optimising campaigns. A data-driven approach and first-party tracking have become indispensable in response to the phase-out of third-party cookies.
The right tools help improve attribution accuracy and activate audiences effectively. The composable CDP DinMo streamlines this process by unifying data and automating segment synchronisation for optimal campaign management. 🚀